Liver mass physical examination: Difference between revisions
(→Skin) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
'''Inspection''' | '''Inspection''' | ||
* | *Caput Medusae | ||
'''Auscultation''' | '''Auscultation''' | ||
*''Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur'' | *''Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur'' | ||
| Line 45: | Line 44: | ||
'''Palpation''' | '''Palpation''' | ||
*Abdominal distention | *Abdominal distention | ||
*[[Hepatomegaly]] | |||
*[[Splenomegaly]] | |||
===Musculoskeletal=== | ===Musculoskeletal=== | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 25 March 2016
|
Liver Mass Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Liver mass physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Liver mass physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Liver mass physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [2]
Overview
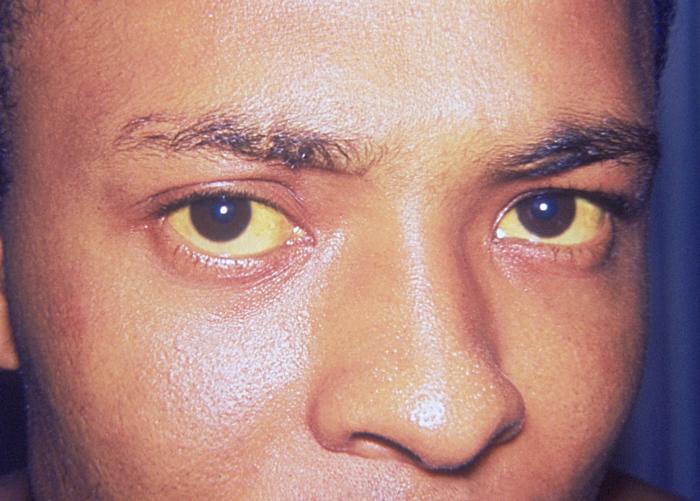
Physical examination findings of liver mass will depend on location and size of the tumor. Usually large liver tumors may cause pain and tenderness in palpation of the abdomen due to stretching of the liver capsule. On the other hand, liver masses with smaller size can present with no remarkable findings. Common physical examination of patients with liver mass, may include: janudice, hepatomegaly, abdominal tenderness, splenomegaly, abdominal wall vascular collaterals, and weight loss.
Physical Examination
- The following physical examination findings may be present among patients with liver mass:
General appearance
Vital Signs
- Decreased SPO2
- Tachypnea
- Tachycardia
- High-grade fever
- Low-grade fever
Chest
Inspection
- Chest alopecia
- Rapid rate of breathing
Auscultation
- Decreased/absent breath sounds
Percussion
- Dull percussion
- Reduced chest expansion
Abdomen
Inspection
- Caput Medusae
Auscultation
- Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur
- Described as a venous hum in patients with portal hypertension
- Present in patients with cirrhosis
Percussion
- Dull percussion
Palpation
- Abdominal distention
- Hepatomegaly
- Splenomegaly
Musculoskeletal
- Peripheral edema
- Muscle rigidity
- Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Skin
Inspection
- Pallor
- Jaundice
- Plantar and palmar erythema
- Dermatographic urticaria, or "scratching marks"
- Nail changes
- Muehrcke nails
- Terry nails, or "luekonychia"