Hepatitis E causes: Difference between revisions
Joao Silva (talk | contribs) |
Joao Silva (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*HepG2/C3A cell line of hepatoma<ref name="pmid21262830">{{cite journal| author=Shukla P, Nguyen HT, Torian U, Engle RE, Faulk K, Dalton HR et al.| title=Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. | journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | year= 2011 | volume= 108 | issue= 6 | pages= 2438-43 | pmid=21262830 | doi=10.1073/pnas.1018878108 | pmc=PMC3038723 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21262830 }} </ref> | *HepG2/C3A cell line of hepatoma<ref name="pmid21262830">{{cite journal| author=Shukla P, Nguyen HT, Torian U, Engle RE, Faulk K, Dalton HR et al.| title=Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. | journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | year= 2011 | volume= 108 | issue= 6 | pages= 2438-43 | pmid=21262830 | doi=10.1073/pnas.1018878108 | pmc=PMC3038723 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21262830 }} </ref> | ||
===Genotypes=== | ===Genotypes=== | ||
Molecular studies of [[HEV]] lead to the classification of the [[HEV|virus]] into 4 [[genotype]]s: | Molecular studies of [[HEV]] lead to the classification of the [[HEV|virus]] into 4 [[genotype]]s:<ref name="pmid22549046">{{cite journal| author=Kamar N, Bendall R, Legrand-Abravanel F, Xia NS, Ijaz S, Izopet J et al.| title=Hepatitis E. | journal=Lancet | year= 2012 | volume= 379 | issue= 9835 | pages= 2477-88 | pmid=22549046 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61849-7 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22549046 }} </ref><ref name="pmid18992406">{{cite journal| author=Dalton HR, Bendall R, Ijaz S, Banks M| title=Hepatitis E: an emerging infection in developed countries. | journal=Lancet Infect Dis | year= 2008 | volume= 8 | issue= 11 | pages= 698-709 | pmid=18992406 | doi=10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70255-X | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18992406 }} </ref> | ||
{| style="border: 2px solid #DCDCDC; font-size: 90%; width: 50%;" | {| style="border: 2px solid #DCDCDC; font-size: 90%; width: 50%;" | ||
|+ ''' | |+ '''Genotypes''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="width: 75px; background: #4479BA; text-align: center;"|{{fontcolor|#FFF|Genotype}} | ! style="width: 75px; background: #4479BA; text-align: center;"|{{fontcolor|#FFF|Genotype}} | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px;"| | | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px;"| | ||
*Infects humans and other mammalian species, such as pigs | *Infects humans and other mammalian species, such as pigs | ||
*Responsible for autochthonous hepatitis E in developed and developing countries | *Responsible for autochthonous hepatitis E in developed and developing countries | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;"| '''HEV4''' | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;"| '''HEV4''' | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 26 August 2014
|
Hepatitis E Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Hepatitis E causes On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatitis E causes |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: João André Alves Silva, M.D. [2]
Overview
Taxonomy
Viruses; ssRNA viruses; ssRNA positive-strand viruses; Hepeviridae; Hepevirus; Hepatitis E virus[1]
Biology
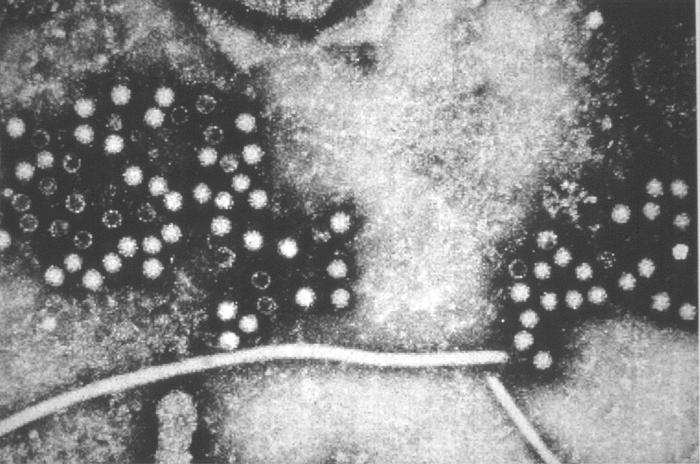 |
The viral particles are 27 to 34 nanometers in diameter, are non-enveloped and contain a single-strand of positive-sense RNA that is approximately 7200 bases in length, polyadenylated at the 3' terminus, and capped at the 5'terminus.[3][4][5]
The genome of HEV contains 3 Open Reading Frames:
- Protease
- Methyltransferase
- RNA helicase
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- ORF2 - encodes de protein of the viral capsid, responsible for:
- Assembly of virions[6]
- Target cell interaction[7]
- Immunogenicity[8]
- ORF3 - encodes a small protein involved in the morphogenesis and release of the virions.[9][10]
In order to study the biology of the virus and develop new treatment drugs, HEV must be grown in culture systems, such as:
- PLC/PRF/5 cell line of hepatic carcinoma, A549 cell line of lung carcinoma, and fecal samples from an infected patient[11]
- HepG2/C3A cell line of hepatoma[12]
Genotypes
Molecular studies of HEV lead to the classification of the virus into 4 genotypes:[3][13]
| Genotype | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| HEV1 |
|
| HEV2 |
|
| HEV3 |
|
| HEV4 |
Tropism
Natural Reservoir
The natural reservoir of HEV is yet to be identified. Different observations have suggested different reservoirs:
- Prolonged fecal shedding from patients with history of the disease has been suggested. However, the duration of viral shedding in feces is not compatible with this hypothesis.[14]
- Environmental reservoir was suggested following detection of HEV in sewages.[15]
- Continuous fecal shedding from asymptomatic patients was suggested as a form of maintenance of the virus, contaminating water supplies.[16]
- The existence of an animal reservoir is supported by the detection of anti-HEV antibodies in different species.[16]
References
- ↑ "Hepatitis E virus taxonomy".
- ↑ "http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/details.asp". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Kamar N, Bendall R, Legrand-Abravanel F, Xia NS, Ijaz S, Izopet J; et al. (2012). "Hepatitis E." Lancet. 379 (9835): 2477–88. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61849-7. PMID 22549046.
- ↑ Reyes GR, Purdy MA, Kim JP, Luk KC, Young LM, Fry KE; et al. (1990). "Isolation of a cDNA from the virus responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis". Science. 247 (4948): 1335–9. PMID 2107574.
- ↑ Tam AW, Smith MM, Guerra ME, Huang CC, Bradley DW, Fry KE; et al. (1991). "Hepatitis E virus (HEV): molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome". Virology. 185 (1): 120–31. PMID 1926770.
- ↑ Li TC, Yamakawa Y, Suzuki K, Tatsumi M, Razak MA, Uchida T; et al. (1997). "Expression and self-assembly of empty virus-like particles of hepatitis E virus". J Virol. 71 (10): 7207–13. PMC 192060. PMID 9311793.
- ↑ Kalia M, Chandra V, Rahman SA, Sehgal D, Jameel S (2009). "Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are required for cellular binding of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 capsid protein and for viral infection". J Virol. 83 (24): 12714–24. doi:10.1128/JVI.00717-09. PMC 2786843. PMID 19812150.
- ↑ Xing L, Wang JC, Li TC, Yasutomi Y, Lara J, Khudyakov Y; et al. (2011). "Spatial configuration of hepatitis E virus antigenic domain". J Virol. 85 (2): 1117–24. doi:10.1128/JVI.00657-10. PMC 3020005. PMID 21068233.
- ↑ Yamada K, Takahashi M, Hoshino Y, Takahashi H, Ichiyama K, Nagashima S; et al. (2009). "ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is essential for virion release from infected cells". J Gen Virol. 90 (Pt 8): 1880–91. doi:10.1099/vir.0.010561-0. PMID 19339479.
- ↑ Emerson SU, Nguyen HT, Torian U, Burke D, Engle R, Purcell RH (2010). "Release of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus from cultured hepatoma and polarized intestinal cells depends on open reading frame 3 protein and requires an intact PXXP motif". J Virol. 84 (18): 9059–69. doi:10.1128/JVI.00593-10. PMC 2937629. PMID 20610720.
- ↑ Tanaka T, Takahashi M, Kusano E, Okamoto H (2007). "Development and evaluation of an efficient cell-culture system for Hepatitis E virus". J Gen Virol. 88 (Pt 3): 903–11. doi:10.1099/vir.0.82535-0. PMID 17325363.
- ↑ Shukla P, Nguyen HT, Torian U, Engle RE, Faulk K, Dalton HR; et al. (2011). "Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 108 (6): 2438–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.1018878108. PMC 3038723. PMID 21262830.
- ↑ Dalton HR, Bendall R, Ijaz S, Banks M (2008). "Hepatitis E: an emerging infection in developed countries". Lancet Infect Dis. 8 (11): 698–709. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70255-X. PMID 18992406.
- ↑ Aggarwal R, Kini D, Sofat S, Naik SR, Krawczynski K (2000). "Duration of viraemia and faecal viral excretion in acute hepatitis E." Lancet. 356 (9235): 1081–2. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02737-9. PMID 11009149.
- ↑ Ippagunta SK, Naik S, Sharma B, Aggarwal R (2007). "Presence of hepatitis E virus in sewage in Northern India: frequency and seasonal pattern". J Med Virol. 79 (12): 1827–31. doi:10.1002/jmv.21017. PMID 17935174.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Aggarwal R, Jameel S (2011). "Hepatitis E." Hepatology. 54 (6): 2218–26. doi:10.1002/hep.24674. PMID 21932388.