Dilated cardiomyopathy pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Dystrophin]] || [[DMD]] || | | [[Dystrophin]] || [[DMD]] || | ||
<ref name="pmid9683584">{{cite journal| author=Ferlini A, Galié N, Merlini L, Sewry C, Branzi A, Muntoni F| title=A novel Alu-like element rearranged in the dystrophin gene causes a splicing mutation in a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=Am J Hum Genet | year= 1998 | volume= 63 | issue= 2 | pages= 436-46 | pmid=9683584 | doi=10.1086/301952 | pmc=PMC1377294 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9683584 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9170407">{{cite journal| author=Ortiz-Lopez R, Li H, Su J, Goytia V, Towbin JA| title=Evidence for a dystrophin missense mutation as a cause of X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=Circulation | year= 1997 | volume= 95 | issue= 10 | pages= 2434-40 | pmid=9170407 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9170407 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12794683">{{cite journal| author=Todorova A, Constantinova D, Kremensky I| title=Dilated cardiomyopathy and new 16 bp deletion in exon 44 of the Dystrophin gene: the possible role of repeated motifs in mutation generation. | journal=Am J Med Genet A | year= 2003 | volume= 120A | issue= 1 | pages= 5-7 | pmid=12794683 | doi=10.1002/ajmg.a.10264 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12794683 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8789442">{{cite journal| author=Milasin J, Muntoni F, Severini GM, Bartoloni L, Vatta M, Krajinovic M et al.| title=A point mutation in the 5' splice site of the dystrophin gene first intron responsible for X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=Hum Mol Genet | year= 1996 | volume= 5 | issue= 1 | pages= 73-9 | pmid=8789442 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8789442 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8361506">{{cite journal| author=Muntoni F, Cau M, Ganau A, Congiu R, Arvedi G, Mateddu A et al.| title=Brief report: deletion of the dystrophin muscle-promoter region associated with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1993 | volume= 329 | issue= 13 | pages= 921-5 | pmid=8361506 | doi=10.1056/NEJM199309233291304 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8361506 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8123157">{{cite journal| author=Towbin JA, Ortiz-Lopez R| title=X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1994 | volume= 330 | issue= 5 | pages= 369-70 | pmid=8123157 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8123157 }} </ref><ref name="pmid7825571">{{cite journal| author=Muntoni F, Melis MA, Ganau A, Dubowitz V| title=Transcription of the dystrophin gene in normal tissues and in skeletal muscle of a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=Am J Hum Genet | year= 1995 | volume= 56 | issue= 1 | pages= 151-7 | pmid=7825571 | doi= | pmc=PMC1801315 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7825571 }} </ref> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Eyes absent homology 4]] || [[EYA4]] || | | [[Eyes absent homology 4]] || [[EYA4]] || | ||
Revision as of 18:40, 11 October 2013
|
Dilated cardiomyopathy Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Dilated cardiomyopathy pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Dilated cardiomyopathy pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Dilated cardiomyopathy pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sachin Shah, M.D., Jennifer Hall
Overview
Cardiomyopathies are defined as a heterogeneous group of diseases of the heart associated with a mechanical and/or electrical dysfunction that usually (but not always) exhibit inappropropriate ventricular hypertrophy or dilation and are due to a variety of causes that frequently are genetic.[1] Phenotypic characteristics typically include ventricular chamber enlargement and systolic dysfunction with normal wall thickness.[1] Patients with dilated cardiomyopathy may experience a progressive decline in left ventricular contractile function, ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias, conduction system problems, thromboembolism, sudden cardiac death and/or heart failure.[1] Dilated cardiomyopathy is the third most common cause of heart failure.[1]
Pathophysiology
Genetics
Our understanding of the role of genetics in dilated cardiomyopathy continues to grow. Inherited familial dilated cardiomyopathy has been associated with 50 mutations in genes encoding cytoskeletal, nucleoskeletal, mitochondrial and calcium handling proteins.[2] These mutations are listed below.
Genes Encoding Plasma Membrane Proteins
| Gene | Abbreviation | References |
| Laminin alpha 4 | LAMA4 | [3] |
| Sarcoglycan delta | SGCD | [4][5] |
Genes Encoding Cytoskeletal Proteins
Genes Encoding Calcium Handling Proteins
| Gene | Abbreviation | References |
| Phospholamban | PLN |
Genes Encoding Mitochondrial Proteins
| Gene | Abbreviation | References |
| Succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein | SDHA |
Genes Encoding Nuclear Proteins
The increase in whole exome and whole genome sequencing has significantly increased the number of rare variants that are associated with dilated cardiomyopathy [2]. A challenge in the field today is that many individuals without disease carry rare variants in their genome. Thus the task at hand is not in the sequencing but rather in the translation to define if the rare variants discovered are in fact pathophysiologic in nature. Secondly, evidence is accumulating that many patients with dilated cardiomyopathy may have many different mutations that contribute to or modify disease. [24]
Genetic Testing
Associated Conditions
A review of systems is also helpful in regards to connective tissue disease associated dilated cardiomyopathy. Some of the disease that can be associated with dilated cardiomyopathy are:
- SLE (systemic lupus erythematosis)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Connective tissue diseases
- Pericardial effusion - It may accompany myocarditis but this finding is not specific.
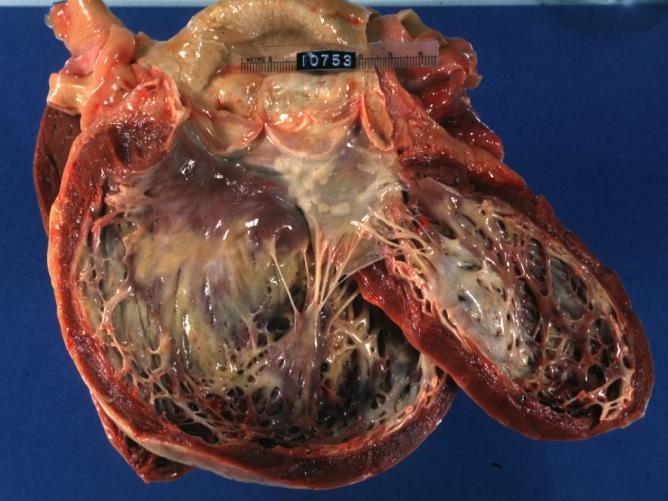
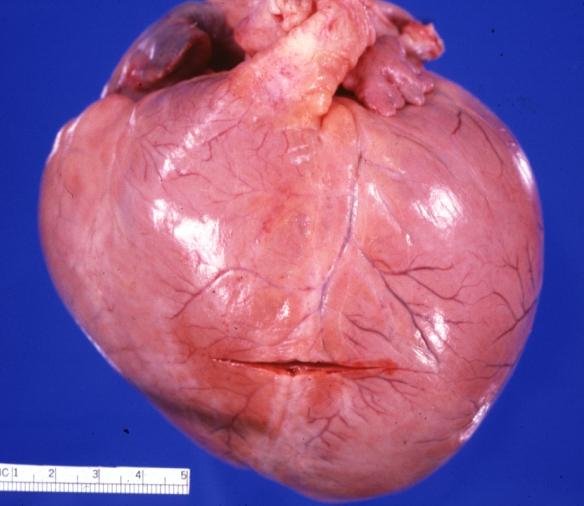
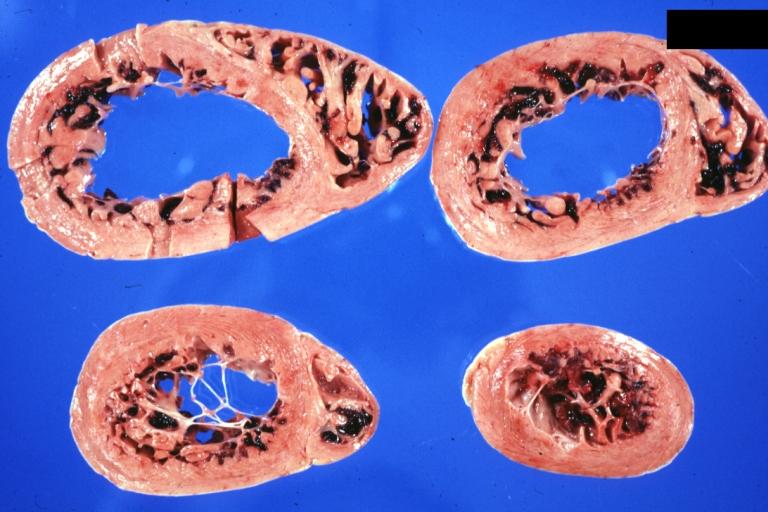
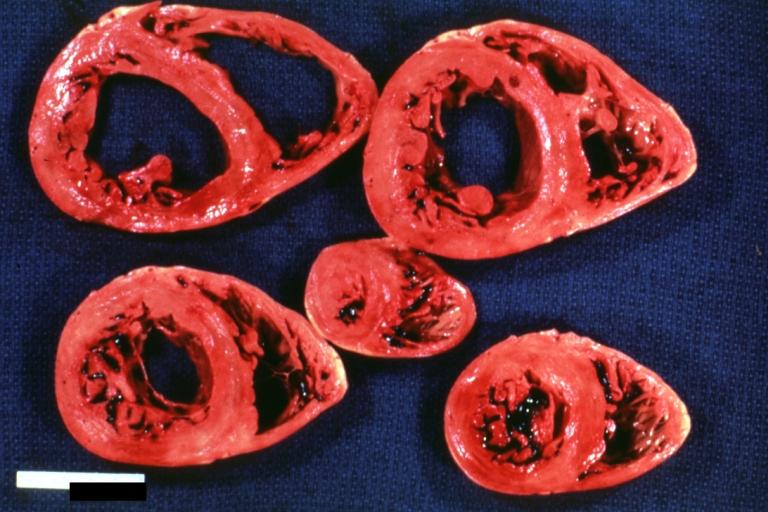
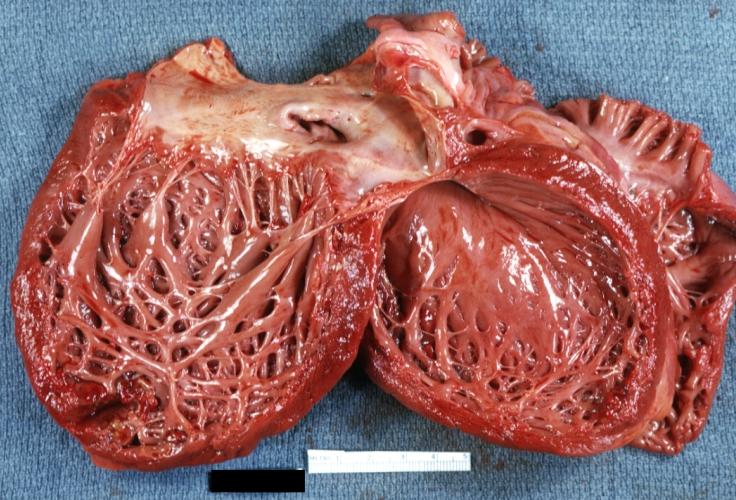
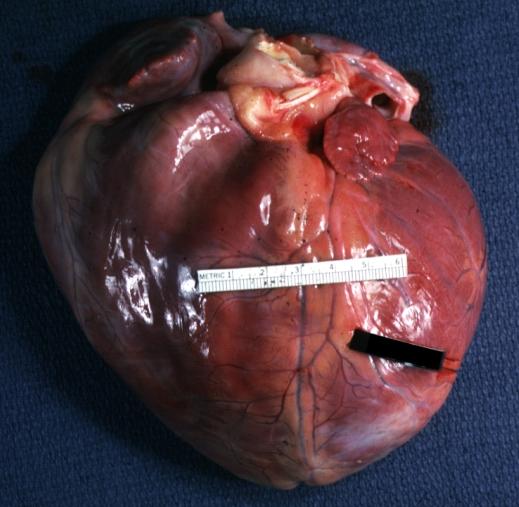
Gross Pathology
Images shown below are Courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
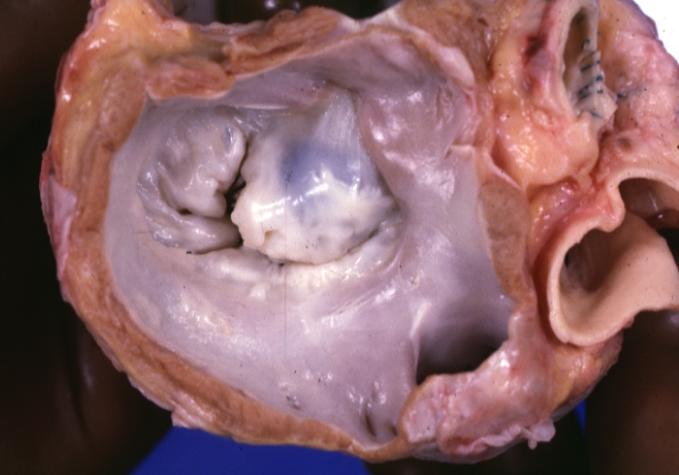
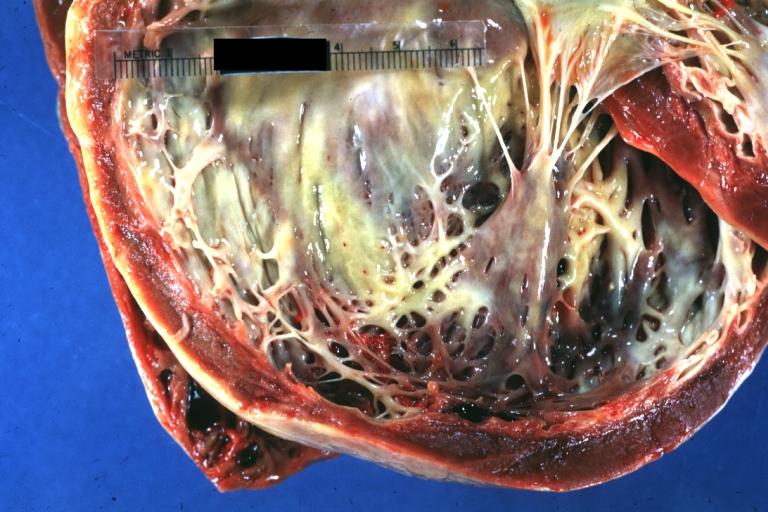
Cardiomyopathy: Gross excellent view of mitral valve from left atrium anterior leaflet appears to balloon a bit into the atrium
-
Cardiomyopathy: Gross excellent view of mitral and tricuspid valves from atria, appear normal anatomy.
-
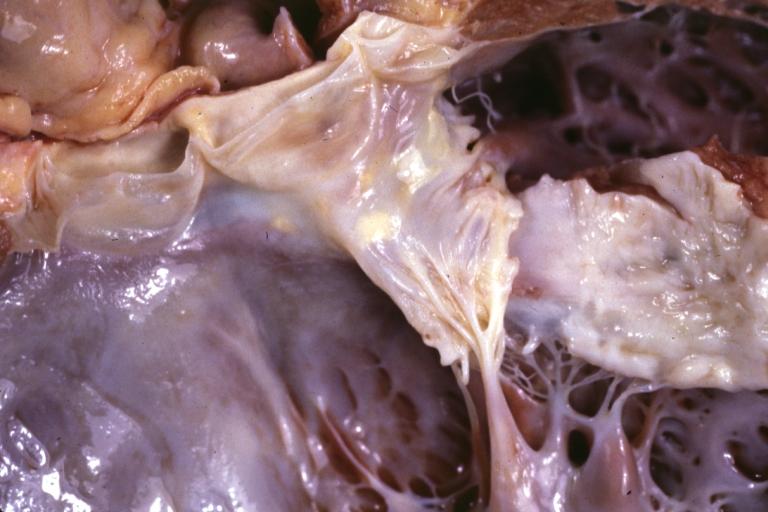
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross natural color close-up view of heart surgically removed for a transplantation shows aortic valve and anterior leaflet of mitral valve with cholesterol deposits endocardium of left ventricle is diffusely thickened
-
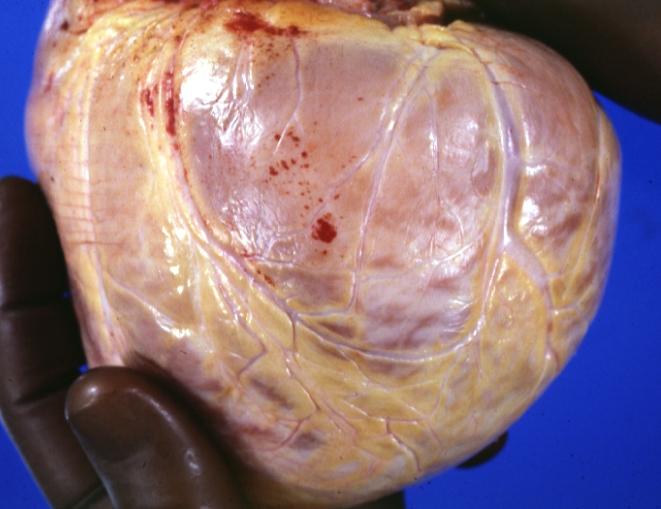
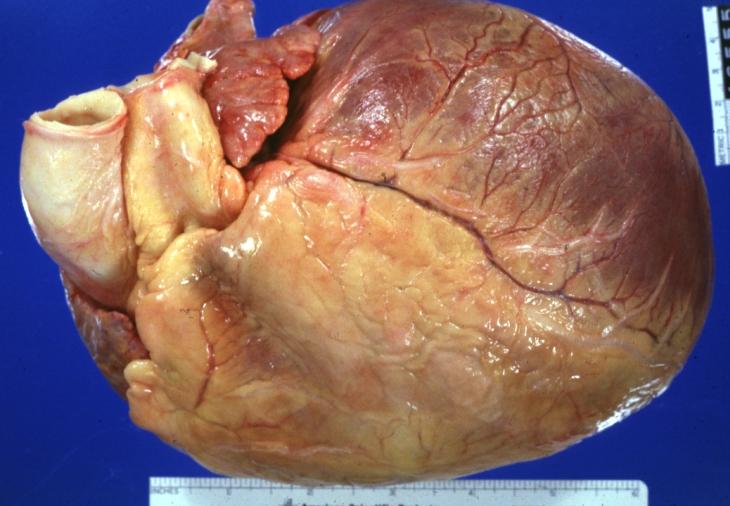
Cardiomyopathy: Gross external view of globular heart with patchy fibrosis seen through epicardium
-
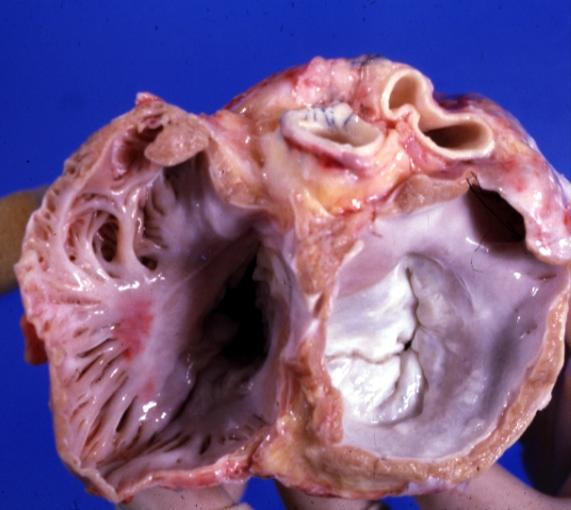
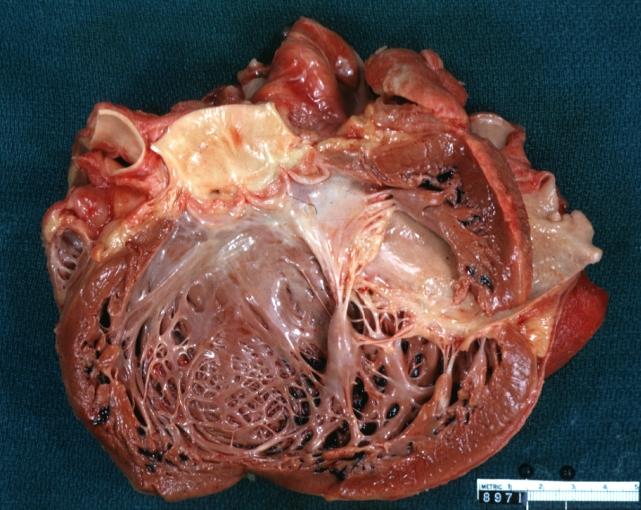
Cardiomyopathy: Gross dilated left ventricle with marked endocardial thickening this is what has been called adult fibroelastosis
-
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross good example huge dilated left ventricle
-
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross dilated left ventricle with marked endocardial sclerosis (an excellent example)
-
Cardiomyopathy: Gross intact globular shaped heart
-
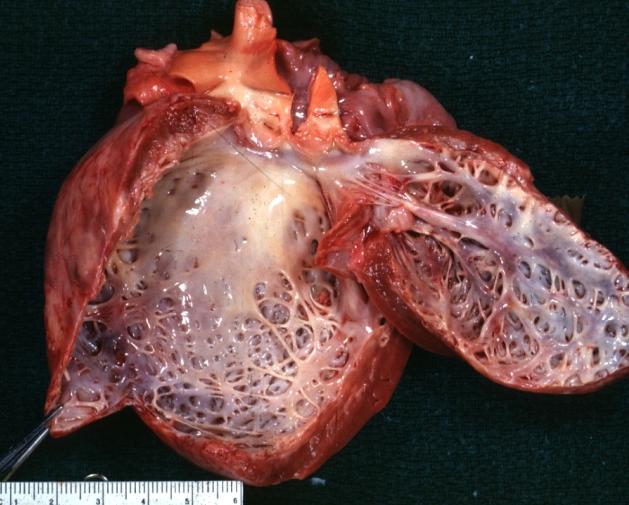
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross opened left ventricle dilated with endocardial thickening good example
-
Cardiomyopathy: Gross globular heart external view 10 year old girl with sickle cell anemia
-
Cardiomyopathy: Gross horizontal sections of ventricles dilation type 10 year old girl with sickle cell anemia
-
Cardiomyopathy: Intermediate between hypertrophic and dilated
-
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross opened globular left ventricle natural color (very good example)
-
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Gross natural color external view globular heart 500 gm 24yo female seven pregnancies
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Maron BJ, Towbin JA, Thiene G, Antzelevitch C, Corrado D, Arnett D; et al. (2006). "Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention". Circulation. 113 (14): 1807–16. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174287. PMID 16567565.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 McNally EM, Golbus JR, Puckelwartz MJ (2013). "Genetic mutations and mechanisms in dilated cardiomyopathy". J Clin Invest. 123 (1): 19–26. doi:10.1172/JCI62862. PMC 3533274. PMID 23281406.
- ↑ Knöll R, Postel R, Wang J, Krätzner R, Hennecke G, Vacaru AM; et al. (2007). "Laminin-alpha4 and integrin-linked kinase mutations cause human cardiomyopathy via simultaneous defects in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells". Circulation. 116 (5): 515–25. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.689984. PMID 17646580.
- ↑ {{cite journal| author=Tsubata S, Bowles KR, Vatta M, Zintz C, Titus J, Muhonen L et al.| title=Mutations in the human delta-sarcoglycan gene in familial and sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy. | journal=J Clin Invest | year= 2000 | volume= 106 | issue= 5 | pages= 655-62 | pmid=10974018 | doi=10.1172/JCI9224 | pmc=PMC381284 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10974018
- ↑ Trabelsi M, Kavian N, Daoud F, Commere V, Deburgrave N, Beugnet C; et al. (2008). "Revised spectrum of mutations in sarcoglycanopathies". Eur J Hum Genet. 16 (7): 793–803. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2008.9. PMID 18285821.
- ↑ Olson TM, Michels VV, Thibodeau SN, Tai YS, Keating MT (1998). "Actin mutations in dilated cardiomyopathy, a heritable form of heart failure". Science. 280 (5364): 750–2. PMID 9563954.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Mohapatra B, Jimenez S, Lin JH, Bowles KR, Coveler KJ, Marx JG; et al. (2003). "Mutations in the muscle LIM protein and alpha-actinin-2 genes in dilated cardiomyopathy and endocardial fibroelastosis". Mol Genet Metab. 80 (1–2): 207–15. PMID 14567970.
- ↑ Duboscq-Bidot L, Charron P, Ruppert V, Fauchier L, Richter A, Tavazzi L; et al. (2009). "Mutations in the ANKRD1 gene encoding CARP are responsible for human dilated cardiomyopathy". Eur Heart J. 30 (17): 2128–36. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp225. PMID 19525294.
- ↑ Norton N, Li D, Rieder MJ, Siegfried JD, Rampersaud E, Züchner S; et al. (2011). "Genome-wide studies of copy number variation and exome sequencing identify rare variants in BAG3 as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy". Am J Hum Genet. 88 (3): 273–82. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.01.016. PMC 3059419. PMID 21353195.
- ↑ Erdmann J, Hassfeld S, Kallisch H, Fleck E, Regitz-Zagrose V (2000). "Genetic variants in the promoter (g983G>T) and coding region (A92T) of the human cardiotrophin-1 gene (CTF1) in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy". Hum Mutat. 16 (5): 448. doi:10.1002/1098-1004(200011)16:5<448::AID-HUMU19>3.0.CO;2-D. PMID 11058912.
- ↑ Li D, Tapscoft T, Gonzalez O, Burch PE, Quiñones MA, Zoghbi WA; et al. (1999). "Desmin mutation responsible for idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy". Circulation. 100 (5): 461–4. PMID 10430757.
- ↑ Bergman JE, Veenstra-Knol HE, van Essen AJ, van Ravenswaaij CM, den Dunnen WF, van den Wijngaard A; et al. (2007). "Two related Dutch families with a clinically variable presentation of cardioskeletal myopathy caused by a novel S13F mutation in the desmin gene". Eur J Med Genet. 50 (5): 355–66. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2007.06.003. PMID 17720647.
- ↑ Norgett EE, Hatsell SJ, Carvajal-Huerta L, Cabezas JC, Common J, Purkis PE; et al. (2000). "Recessive mutation in desmoplakin disrupts desmoplakin-intermediate filament interactions and causes dilated cardiomyopathy, woolly hair and keratoderma". Hum Mol Genet. 9 (18): 2761–6. PMID 11063735.
- ↑ Uzumcu A, Norgett EE, Dindar A, Uyguner O, Nisli K, Kayserili H; et al. (2006). "Loss of desmoplakin isoform I causes early onset cardiomyopathy and heart failure in a Naxos-like syndrome". J Med Genet. 43 (2): e5. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.032904. PMC 2564645. PMID 16467215.
- ↑ Rasmussen TB, Hansen J, Nissen PH, Palmfeldt J, Dalager S, Jensen UB; et al. (2013). "Protein expression studies of desmoplakin mutations in cardiomyopathy patients reveal different molecular disease mechanisms". Clin Genet. 84 (1): 20–30. doi:10.1111/cge.12056. PMID 23137101.
- ↑ Davey KM, Parboosingh JS, McLeod DR, Chan A, Casey R, Ferreira P; et al. (2006). "Mutation of DNAJC19, a human homologue of yeast inner mitochondrial membrane co-chaperones, causes DCMA syndrome, a novel autosomal recessive Barth syndrome-like condition". J Med Genet. 43 (5): 385–93. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.036657. PMC 2564511. PMID 16055927.
- ↑ Ferlini A, Galié N, Merlini L, Sewry C, Branzi A, Muntoni F (1998). "A novel Alu-like element rearranged in the dystrophin gene causes a splicing mutation in a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". Am J Hum Genet. 63 (2): 436–46. doi:10.1086/301952. PMC 1377294. PMID 9683584.
- ↑ Ortiz-Lopez R, Li H, Su J, Goytia V, Towbin JA (1997). "Evidence for a dystrophin missense mutation as a cause of X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". Circulation. 95 (10): 2434–40. PMID 9170407.
- ↑ Todorova A, Constantinova D, Kremensky I (2003). "Dilated cardiomyopathy and new 16 bp deletion in exon 44 of the Dystrophin gene: the possible role of repeated motifs in mutation generation". Am J Med Genet A. 120A (1): 5–7. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.10264. PMID 12794683.
- ↑ Milasin J, Muntoni F, Severini GM, Bartoloni L, Vatta M, Krajinovic M; et al. (1996). "A point mutation in the 5' splice site of the dystrophin gene first intron responsible for X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". Hum Mol Genet. 5 (1): 73–9. PMID 8789442.
- ↑ Muntoni F, Cau M, Ganau A, Congiu R, Arvedi G, Mateddu A; et al. (1993). "Brief report: deletion of the dystrophin muscle-promoter region associated with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". N Engl J Med. 329 (13): 921–5. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309233291304. PMID 8361506.
- ↑ Towbin JA, Ortiz-Lopez R (1994). "X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". N Engl J Med. 330 (5): 369–70. PMID 8123157.
- ↑ Muntoni F, Melis MA, Ganau A, Dubowitz V (1995). "Transcription of the dystrophin gene in normal tissues and in skeletal muscle of a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy". Am J Hum Genet. 56 (1): 151–7. PMC 1801315. PMID 7825571.
- ↑ Golbus JR, Puckelwartz MJ, Fahrenbach JP, Dellefave-Castillo LM, Wolfgeher D, McNally EM (2012). "Population-based variation in cardiomyopathy genes". Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 5 (4): 391–9. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.112.962928. PMC 3495587. PMID 22763267.