Cefdinir
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 16% to 21% (dose-dependent) |
| Protein binding | 60% to 70% |
| Metabolism | Negligible |
| Elimination half-life | 1.7 ± 0.6 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
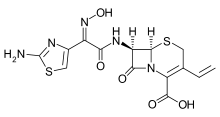
| Formula | C14H13N5O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 395.416 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Cefdinir |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Cefdinir |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Cefdinir at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Cefdinir at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Cefdinir
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Cefdinir Risk calculators and risk factors for Cefdinir
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Cefdinir |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Cefdinir (marketed by Abbott Laboratories under the brand name Omnicef) is a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum antibiotic in the third generation of the cephalosporin class, proven effective for common bacterial infections of the ear, sinus, throat, and skin. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December of 1997.
Mechanism of action
Indications
Therapeutic uses of cefdinir include otitis media, soft tissue infections, and respiratory tract infections, including sinusitis, strep throat, community-acquired pneumonia and acute exacerbations of bronchitis.
Susceptible organisms
Cefdinir is a bacteriocidal antibiotic. It can be used to treat infections caused by several Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, including:
Gram-negative
Gram-positive
Like most third-generation cephalosporins (except Ceftazidime), cefdinir is not an effective treatment against infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Side effects
According to the Omnicef website, side effects include "(...) diarrhea, vaginal infections or inflammation, nausea, headache, and abdominal pain."[1]
Available forms and dosage
Cefdinir is administered orally. It is available as capsules and a suspension. Dosage, schedule, and duration of therapy varies according to the type of infection. For adults, the average dosage is between 300 and 600 mg per 12 or 24 hour period, for the duration of between 5 and 10 days. Average pediatric dosage is between 7 and 14 mg/kg (schedule and duration the same as adult).
Notes
- Marketed by Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC in MENA region under the brand name Omnicef®
"Blood" in the Stool
The pediatric version of Omnicef® can bind to iron in the digestive tract. In rare cases, this creates a discoloration of the stool to a rust or red color. Some patients may interpret this as blood in the stool, although in reality blood appears dark brown or black in the stool. A doctor's office can perform a simple stool guaiac test on the stool to confirm that it does not have blood. If you simply wait one hour, the red color will remain red, (while real blood will turn black).
On the other hand, if the reddish stool is accompanied by abdominal pain, weight loss, diarrhea, etc., it could be a C. difficile (clostridium difficile) infection caused by the antibiotic. This infection can occur as a result of taking an antibiotic. Talk to your pediatrician immediately to see if you should stop using the antibiotic.
References
- ↑ "Omnicef® capsules Patient Information" (PDF). Abbott Laboratories. 2004. Retrieved 2006-11-24. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)
External links
- Pages with script errors
- Pages with citations using unsupported parameters
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Pages with broken file links
- Cephalosporin antibiotics
- Thiazoles