Bundle branch block: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Aditya Ganti (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} ; {{AE}} {{ADG}} | ||
{{SK}} BBB | {{SK}} BBB | ||
'''For detailed medical information on Left Bundle Branch Block click [[Left bundle branch block|here]].''' | |||
'''For detailed medical information on Right Bundle Branch Block click [[Right bundle branch block|here]].''' | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
A bundle branch block refers to a defect of the [[heart]]'s [[electrical conduction system of the heart|electrical conduction system]] below the level of the [[AV node]]. | A bundle branch block refers to a defect of the [[heart]]'s [[electrical conduction system of the heart|electrical conduction system]] below the level of the [[AV node]]. Depending upon the level and location of the block/defect in the conducting pathway bundle branch block can be classified into left bundle branch block and right bundle branch block. | ||
==Physiology== | |||
=== Normal Anatomy === | |||
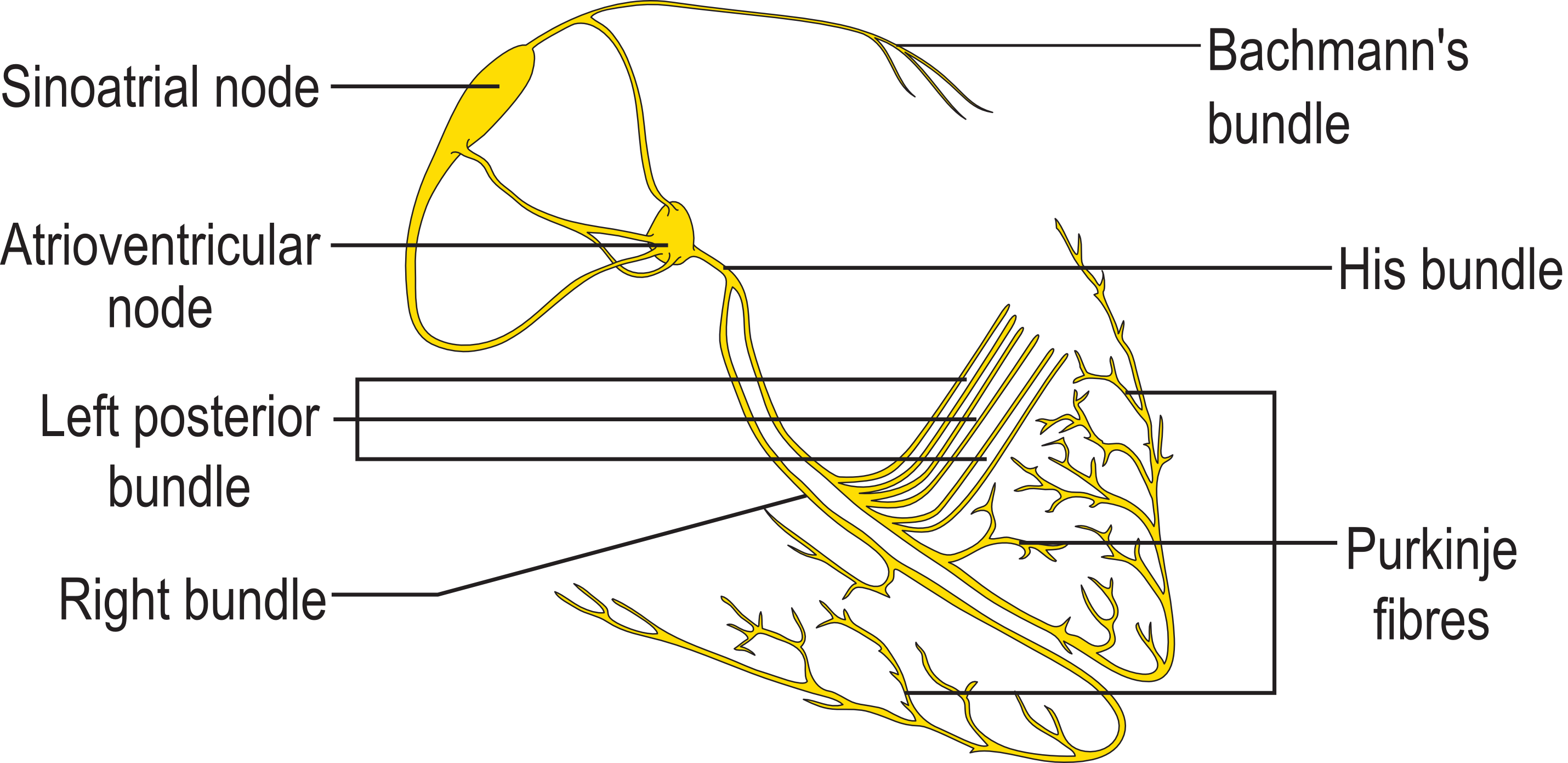
*The conduction system of the heart consists of specialized cells designed to conduct electrical impulse faster than the surrounding myocardial cells. | |||
*Anatomically, the AV node is divided into three regions as follows: | |||
**Transitional cell zone: This is the region where the internodal atrial pathways merge with the compact AV node. | |||
**Compact AV node: This region is located at the apex of the [[triangle of Koch]], which is formed by the ostium of [[coronary sinus]], tricuspid annulus and the [[tendon of Todaro]]. | |||
**Penetrating portion of the AV bundle: This region enters the [[tendon of Todaro]] and runs within the fibrous body of the [[Interventricular septum|membranous interventricular septum]] and eventually divides at the crest of the [[Interventricular septum|muscular interventricular septum]] into right and left branches. | |||
*The left bundle branch penetrates the membranous portion of the interventricular septum and divides into several smaller branches. Parts of the left bundle branch include a pre-divisional segment, anterior fascicle/hemibundle and posterior fascicle/hemibundle. Rarely a median fascicle is present in some hearts. | |||
**The anterior fascicle supplies the anterior [[papillary muscle]] and the Purkinje network of the antero-lateral surface of the left ventricle. | |||
**The posterior fascicle supplies the posterior papillary muscle and the Purkinje network of the postero-inferior surface of the left ventricle. | |||
**Left bundle branch receives its blood supply from [[left anterior descending artery]]. | |||
[[Image:AV node.png|thumb|600x600px|Structure of the heart's conduction system|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/File:AV_node.png|center]]<br /> | |||
=== Normal Physiology === | |||
*The normal cardiac conduction proceeds in a way so as to allow time for the [[atrium]] to relax during atrial [[diastole]]. | |||
*The electrical impulse generated in the [[SA node]] travels through the internodal pathways towards the [[AV node]]. | |||
*The conduction through the AV node is slowed down as it travels through it. This decrease in velocity of conduction allows time for the [[atrium]] to contract ahead of the ventricle so that the blood from the atria can fill up the ventricles through the atrio-ventricular valves. | |||
*As the impulse flows through the compact AV node, it rapidly conducts through the ventricular myocardial cells. Once the depolarization is complete, the ventricle relaxes during [[diastole]] in preparation for the next impulse. | |||
<br /> | |||
== Classification == | |||
</small> | |||
{{Family tree/start}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | |A01= Bundle Branch Block}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|.|}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | C01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | C02 |C01= Left Bundle Branch Block| C02= Right Bundle Branch Block}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | }} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|.| | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|-|-|-|.| |}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | | |!| | | | | | |!| | }} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | D01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | D02 | | | | D03 | | | | | D04 | | | | | D05 | | |D01=Based on Duration| D02= Based on Extent of Block|D03=Proximal RBB|D04=Intermediate RBB|D05= Distal RBB}} | |||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{Family tree | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|-|-|.| | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | | | | | |D01=Based on Duration| D02= Based on Extent of Block }} | |||
{{Family tree | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{Family tree | | D05 | | | | D06 | | | | D07 | | | | D08 | | | | | | | | D09 | | | | D05=New LBB|D06=Old LBB|D07=LBB of unknown duration|D08=Complete LBB|D09=Incomplete LBB }} | |||
{{Family tree/end}} | |||
==Related Chapters== | ==Related Chapters== | ||
*[[Electrical conduction system of the heart]] | *[[Electrical conduction system of the heart]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:58, 8 June 2020
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: BBB
For detailed medical information on Left Bundle Branch Block click here.
For detailed medical information on Right Bundle Branch Block click here.
Overview
A bundle branch block refers to a defect of the heart's electrical conduction system below the level of the AV node. Depending upon the level and location of the block/defect in the conducting pathway bundle branch block can be classified into left bundle branch block and right bundle branch block.
Physiology
Normal Anatomy
- The conduction system of the heart consists of specialized cells designed to conduct electrical impulse faster than the surrounding myocardial cells.
- Anatomically, the AV node is divided into three regions as follows:
- Transitional cell zone: This is the region where the internodal atrial pathways merge with the compact AV node.
- Compact AV node: This region is located at the apex of the triangle of Koch, which is formed by the ostium of coronary sinus, tricuspid annulus and the tendon of Todaro.
- Penetrating portion of the AV bundle: This region enters the tendon of Todaro and runs within the fibrous body of the membranous interventricular septum and eventually divides at the crest of the muscular interventricular septum into right and left branches.
- The left bundle branch penetrates the membranous portion of the interventricular septum and divides into several smaller branches. Parts of the left bundle branch include a pre-divisional segment, anterior fascicle/hemibundle and posterior fascicle/hemibundle. Rarely a median fascicle is present in some hearts.
- The anterior fascicle supplies the anterior papillary muscle and the Purkinje network of the antero-lateral surface of the left ventricle.
- The posterior fascicle supplies the posterior papillary muscle and the Purkinje network of the postero-inferior surface of the left ventricle.
- Left bundle branch receives its blood supply from left anterior descending artery.
Normal Physiology
- The normal cardiac conduction proceeds in a way so as to allow time for the atrium to relax during atrial diastole.
- The electrical impulse generated in the SA node travels through the internodal pathways towards the AV node.
- The conduction through the AV node is slowed down as it travels through it. This decrease in velocity of conduction allows time for the atrium to contract ahead of the ventricle so that the blood from the atria can fill up the ventricles through the atrio-ventricular valves.
- As the impulse flows through the compact AV node, it rapidly conducts through the ventricular myocardial cells. Once the depolarization is complete, the ventricle relaxes during diastole in preparation for the next impulse.
Classification
| Bundle Branch Block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left Bundle Branch Block | Right Bundle Branch Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Based on Duration | Based on Extent of Block | Proximal RBB | Intermediate RBB | Distal RBB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New LBB | Old LBB | LBB of unknown duration | Complete LBB | Incomplete LBB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Chapters
- Electrical conduction system of the heart
- Cardiac pacemaker
- Heart blocks
- First degree AV block
- Second degree AV block
- Third degree AV block
- Right bundle branch block
- Left bundle branch block
- Bifascicular block
- Trifascicular block