Fox-Fordyce disease: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}})) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
'''Fox-Fordyce disease''' is a [[chronic]] blockage of the [[sweat gland]] ducts with a secondary, non[[bacteria]]l inflammatory response to the [[secretion]]s and [[cell (biology)|cell]]ular debris in the [[cyst]]s. [[Hidradenitis]] is very similar but tends to have a secondary bacterial infection so that pus-draining sinuses are formed. It is a very devastating [[skin]] disease that does not have universally curative treatments. | '''Fox-Fordyce disease''' is a [[chronic]] blockage of the [[sweat gland]] ducts with a secondary, non[[bacteria]]l inflammatory response to the [[secretion]]s and [[cell (biology)|cell]]ular debris in the [[cyst]]s. [[Hidradenitis]] is very similar but tends to have a secondary bacterial infection so that pus-draining sinuses are formed. It is a very devastating [[skin]] disease that does not have universally curative treatments. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 10: | ||
==Eponym== | ==Eponym== | ||
It is named for George Henry Fox and John Fordyce.<ref>{{WhoNamedIt|synd|1512}}</ref><ref>G. H. Fox, J. A. Fordyce. Two cases of a rare papular disease affecting the axillary region. Journal of Cutaneous and Genitourinary Diseases, Chicago, 1902, 20: 1-5.</ref> | It is named for George Henry Fox and John Fordyce.<ref>{{WhoNamedIt|synd|1512}}</ref><ref>G. H. Fox, J. A. Fordyce. Two cases of a rare papular disease affecting the axillary region. Journal of Cutaneous and Genitourinary Diseases, Chicago, 1902, 20: 1-5.</ref> | ||
==Physical examination== | |||
===Gallery=== | |||
====Extremities==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
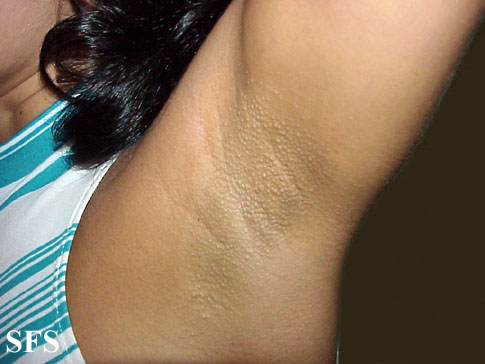
Image: Fox_fordyce disease_01.jpeg|Fox_fordyce disease. <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=12 With permission from Dermatology Atlas.]''<ref name="www.atlasdermatologico.com.br">{{Cite web | title = Dermatology Atlas | url = http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=158> | |||
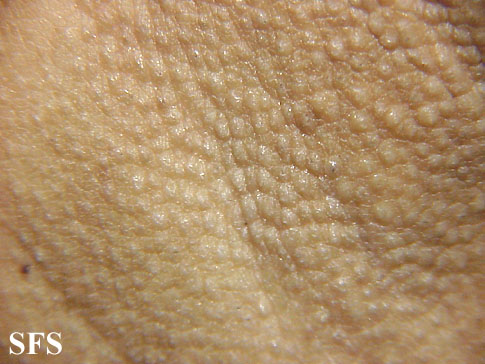
Image: Fox_fordyce disease_02.jpeg|Fox_fordyce disease. <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=12 With permission from Dermatology Atlas.]''<ref name="www.atlasdermatologico.com.br">{{Cite web | title = Dermatology Atlas | url = http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=158> | |||
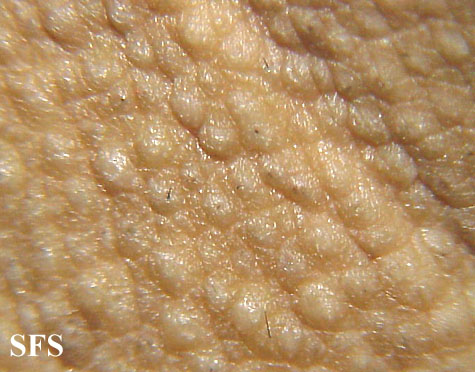
Image: Fox_fordyce disease_03.jpeg|Fox_fordyce disease. <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=12 With permission from Dermatology Atlas.]''<ref name="www.atlasdermatologico.com.br">{{Cite web | title = Dermatology Atlas | url = http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=158> | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 27 August 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Fox-Fordyce disease is a chronic blockage of the sweat gland ducts with a secondary, nonbacterial inflammatory response to the secretions and cellular debris in the cysts. Hidradenitis is very similar but tends to have a secondary bacterial infection so that pus-draining sinuses are formed. It is a very devastating skin disease that does not have universally curative treatments.
Eponym
It is named for George Henry Fox and John Fordyce.[1][2]
Physical examination
Gallery
Extremities
Treatment
The mainstay treatment is surgical removal of the skin tissue containing affected sweat glands. Irradiation therapy may also be used and antibiotics are used to reduce the inflammatory response.
No treatment is required for Fordyce granules, except for cosmetic removal of labial lesions. Inflamed glands can be treated topically with clindamycin. When surgically excised, recurrence does not occur. Neoplastic transformation is very rare but has been reported.
References
- ↑ Template:WhoNamedIt
- ↑ G. H. Fox, J. A. Fordyce. Two cases of a rare papular disease affecting the axillary region. Journal of Cutaneous and Genitourinary Diseases, Chicago, 1902, 20: 1-5.
External links
- http://www.wdxcyber.com/nvulva03.htm
- http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/result.cfm?Diagnosis=271470151