Sandbox:Maneesha: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (313 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{M.N}} | {{WikiDoc CMG}}; {{AE}}, {{M.N}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
This section provides a short and straight to the point overview of the disease or symptom. The first sentence of the overview must contain the name of the disease.<ref name="pmid29067433">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lukacz ES, Santiago-Lastra Y, Albo ME, Brubaker L |title=Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Review |journal=JAMA |volume=318 |issue=16 |pages=1592–1604 |date=October 2017 |pmid=29067433 |doi=10.1001/jama.2017.12137 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Cardiology is | |||
===Causes=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
!Cardiac | |||
!Kidney | |||
! | |||
! | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
#Hallmark<ref name="pmid179495412">{{cite journal |vauthors=Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ |title=Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism |journal=J Can Dent Assoc |volume=73 |issue=8 |pages=727–30 |date=October 2007 |pmid=17949541 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|2. | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
#life | |||
#[[cardiac]] | |||
== | *cardiac arrest<ref name="pmid17949541">{{cite journal |vauthors=Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ |title=Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism |journal=J Can Dent Assoc |volume=73 |issue=8 |pages=727–30 |date=October 2007 |pmid=17949541 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*sudden infant death | |||
[[File:Pancreas 1.png|400px|right|thumb|Image of pancreas anatomy,Dr. Johannes Sobotta, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons,https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sobo_1906_393.png,https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1b/Sobo_1906_393.png]] | |||
==Risk factors== | |||
== | |||
* | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
!Smoking | |||
!Alchohol | |||
! | |||
! | |||
|- | |||
|*Risk factor | |||
|*Risk | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
{{ | *''Smoking''<ref name="pmid17949541">{{cite journal |vauthors=Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ |title=Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism |journal=J Can Dent Assoc |volume=73 |issue=8 |pages=727–30 |date=October 2007 |pmid=17949541 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Alchohol | |||
===Life Threatening Causes=== | |||
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated.<ref name="pmid31384377">{{cite journal |vauthors=Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA |title=Ebstein's Anomaly |journal=Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=138–144 |date=2019 |pmid=31384377 |pmc=6668741 |doi=10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22723533">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kilner PJ |title=Imaging congenital heart disease in adults |journal=Br J Radiol |volume=84 Spec No 3 |issue= |pages=S258–68 |date=December 2011 |pmid=22723533 |pmc=3473918 |doi=10.1259/bjr/74240815 |url=}}</ref><ref name="ChoongEmberton2000">{{cite journal|last1=Choong|first1=S.|last2=Emberton|first2=M.|title=Acute urinary retention|journal=BJU International|volume=85|issue=2|year=2000|pages=186–201|issn=14644096|doi=10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00409.x}}</ref><ref name="MacedoMacedo2014">{{cite journal|last1=Macedo|first1=Cristiane R|last2=Macedo|first2=Elizeu C|last3=Torloni|first3=Maria R|last4=Silva|first4=Ademir B|last5=Prado|first5=Gilmar F|last6=Macedo|first6=Cristiane R|title=Pharmacotherapy for sleep bruxism|year=2014|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD005578.pub2}}</ref> | |||
#[[Pregnancy]] | |||
#[[Urinary]] | |||
#Life | |||
[[File:Gallbladder (organ).png|500px|none|thumb|Gallbladder image showing duct, https://www.google.com/search?q=gallbladder&rlz=1C1CHBF_enUS833US833&sxsrf=ALeKk01butIe1QFo3P4CKO5mV5r7NnUsmA:1599229639711&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwix9trU2s_rAhVnoXIEHbL9AG4Q_AUoAXoECBEQAw&biw=1280&bih=539&dpr=1.5&safe=active#imgrc=B2pKDDEl92qKKM]] | |||
[[File:Pancreatic-ductal-carcinoma.jpg|300px|none|thumb|CT scan showing pancreatic adenocarcinoma, Case courtesy of Dr Mohammad Taghi Niknejad, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 20874,Case courtesy of Dr Mohammad Taghi Niknejad, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/20874">rID: 20874</a>]] | |||
===Common Causes=== | |||
*UTI <ref name="CappellePans2016">{{cite journal|last1=Cappelle|first1=Sarah|last2=Pans|first2=Steven|last3=Sciot|first3=Raf|title=Imaging features of chondromyxoid fibroma: report of 15 cases and literature review|journal=The British Journal of Radiology|volume=89|issue=1064|year=2016|pages=20160088|issn=0007-1285|doi=10.1259/bjr.20160088}}</ref><ref name="pmid31625673">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sussman RD, Syan R, Brucker BM |title=Guideline of guidelines: urinary incontinence in women |journal=BJU Int |volume=125 |issue=5 |pages=638–655 |date=May 2020 |pmid=31625673 |doi=10.1111/bju.14927 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17949541">{{cite journal |vauthors=Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ |title=Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism |journal=J Can Dent Assoc |volume=73 |issue=8 |pages=727–30 |date=October 2007 |pmid=17949541 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Heart]] | |||
*[[Common cause 3]] | |||
*[[Common cause 4]] | |||
*[[Common cause 5]] | |||
[[File:Pancreatic-ductal-carcinoma (1).jpg|400px|none|CT showing adenocarcinoma, Case courtesy of Dr Mohammad Taghi Niknejad, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 20874, Case courtesy of Dr Mohammad Taghi Niknejad, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/20874">rID: 20874</a>]] | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the diagnosis of <nowiki>[[disease name]]</nowiki> according the the [...] guidelines.<ref name="pmid31384377">{{cite journal |vauthors=Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA |title=Ebstein's Anomaly |journal=Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=138–144 |date=2019 |pmid=31384377 |pmc=6668741 |doi=10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138 |url=}}</ref> | |||
{{familytree/start |summary=PE diagnosis Algorithm.}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | A01 | | | A01= }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | |!| | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | B01 | | | B01= }} | |||
{{familytree | | |,|-|^|-|.| | }} | |||
{{familytree | | C01 | | C02 | C01= | C02= }} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | |||
==Treatment== | |||
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the treatment of <nowiki>[[disease name]]</nowiki> according the the [...] guidelines. | |||
{{familytree/start |summary=PE diagnosis Algorithm.}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | A01 |A01= }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|.| | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | B01 | | | | | | | | B02 | | |B01= |B02= }} | |||
{{familytree | | | |!| | | | | | | | | |!| }} | |||
{{familytree | | | C01 | | | | | | | | |!| |C01= }} | |||
{{familytree | |,|-|^|.| | | | | | | | |!| }} | |||
{{familytree | D01 | | D02 | | | | | | D03 |D01= |D02= |D03= }} | |||
{{familytree | |!| | | | | | | | | |,|-|^|.| }} | |||
{{familytree | E01 | | | | | | | E02 | | | E03 |E01= |E02= |E03= }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | |!| }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | F01 | | | F02 |F01= |F02= }} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | |||
==Do's== | |||
*The content in this section is in bullet points. | |||
==Don'ts== | |||
*The content in this section is in bullet points. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Help]] | |||
[[Category:Projects]] | |||
[[Category:Resident survival guide]] | |||
[[Category:Templates]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
<br /> | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Template:Ebstein's anomaly of the tricuspid valve}} | |||
[[File:79px-Life cycle of Rustic Butterfly (2663558308).jpg|800px|center|thumb|The Rustic (Cupha erymanthis) is a species of brush-footed butterfly found in tropical South Asia and Southeast Asia.https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Life_cycle_of_Rustic_Butterfly_(2663558308).jpg]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Onset | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Disease | |||
! colspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Symptoms | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Gold Standard | |||
Test | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |CT/MRI Findings | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Other Investigation Findings | |||
|- | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |'''Headache''' | |||
Characteristics | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Associated Features | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="2" |'''Sudden''' | |||
|Epidural hematoma | |||
| | |||
*Dull | |||
*Throbbing | |||
*One sided or all around | |||
| | |||
*[[Confusion]] | |||
*[[Drowsiness]] | |||
*[[Personality changes|Personality change]] | |||
*[[Seizure|Seizures]] | |||
*[[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]] | |||
*[[Headache|Loss of consciousness]] | |||
|[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] without [[Contrast medium|contrast]] | |||
|Biconvex lens shaped [[hematoma]] which expand inward toward the [[brain]] rather than along the inside of the [[skull]] | |||
| | |||
*The [[Glasgow Coma Scale]] is a tool for measuring degree of [[unconsciousness]] and is a useful tool for determining severity of [[injury]]. | |||
*The [[Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale]] is used in young [[children]]. | |||
|- | |||
|[[Meningitis]] | |||
|[[Headache]] is associated with: | |||
*[[Fever]] | |||
*[[Neck stiffness]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Photophobia]] | |||
*[[Phonophobia]] | |||
*[[Irritability]] | |||
*[[Altered mental status]] | |||
|[[Lumbar puncture]] for [[CSF]] | |||
| | |||
*[[CT]] scan of the [[head]] may be performed before [[Lumbar puncture|LP]] to determine the risk of [[herniation]]. | |||
| | |||
*[[Diagnosis]] is based on [[clinical]] presentation in combination with [[CSF]] analysis. | |||
*[[CSF]] analysis is the investigation of choice. | |||
*For more information on [[CSF]] analysis in [[meningitis]] please [[Meningitis#Diagnosis|click here.]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="1" |'''Gradual''' | |||
|[[Intracranial mass]] | |||
|[[Morning headache]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Nausea]] | |||
*[[Vomiting]] | |||
*[[Change in mental status]] | |||
*[[Seizures]] | |||
*[[Focal neurologic signs|Focal neurological deficits]] | |||
|[[MRI]] | |||
| | |||
*[[CT]] or [[MRI]] is the initial test to detect intracranial lesions (ring enhancing lesions). | |||
*These [[imaging]] tests determine the location of [[intracranial mass]] lesion(s) and help in guiding [[therapy]]. | |||
| | |||
*[[Biopsy]] of the [[lesion]] may be done to identify the nature of the lesion such as: | |||
**[[Tumor]] | |||
**[[Abscess]] | |||
*[[X-rays|X-ray]] of the [[skull]] is a non [[Specificity (tests)|specific]] test, but useful if any of the lesions are [[Calcified lesion|calcified]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 14:30, 8 May 2021
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: , Maneesha Nandimandalam, M.B.B.S.[2]
Overview
This section provides a short and straight to the point overview of the disease or symptom. The first sentence of the overview must contain the name of the disease.[1]
- Cardiology is
Causes
| Cardiac | Kidney | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| 2. | |||
- life
- cardiac
- cardiac arrest[3]
- sudden infant death

Risk factors
| Smoking | Alchohol | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| *Risk factor | *Risk | ||
- Smoking[3]
- Alchohol
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated.[4][5][6][7]


Common Causes
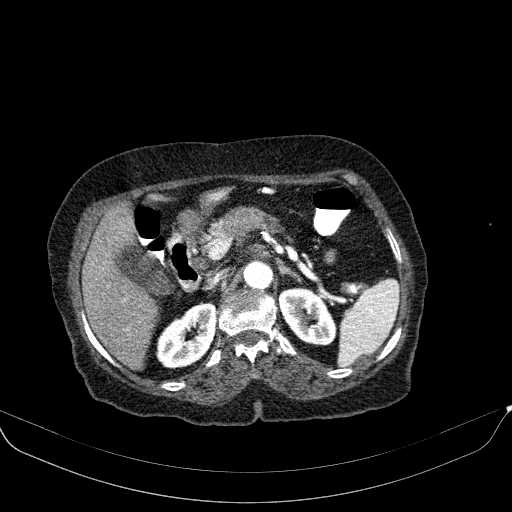
Diagnosis
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the diagnosis of [[disease name]] according the the [...] guidelines.[4]
Treatment
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the treatment of [[disease name]] according the the [...] guidelines.
Do's
- The content in this section is in bullet points.
Don'ts
- The content in this section is in bullet points.
References
- ↑ Lukacz ES, Santiago-Lastra Y, Albo ME, Brubaker L (October 2017). "Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Review". JAMA. 318 (16): 1592–1604. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.12137. PMID 29067433.
- ↑ Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ (October 2007). "Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism". J Can Dent Assoc. 73 (8): 727–30. PMID 17949541.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Huynh N, Manzini C, Rompré PH, Lavigne GJ (October 2007). "Weighing the potential effectiveness of various treatments for sleep bruxism". J Can Dent Assoc. 73 (8): 727–30. PMID 17949541.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA (2019). "Ebstein's Anomaly". Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 15 (2): 138–144. doi:10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138. PMC 6668741 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 31384377. - ↑ Kilner PJ (December 2011). "Imaging congenital heart disease in adults". Br J Radiol. 84 Spec No 3: S258–68. doi:10.1259/bjr/74240815. PMC 3473918. PMID 22723533.
- ↑ Choong, S.; Emberton, M. (2000). "Acute urinary retention". BJU International. 85 (2): 186–201. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00409.x. ISSN 1464-4096.
- ↑ Macedo, Cristiane R; Macedo, Elizeu C; Torloni, Maria R; Silva, Ademir B; Prado, Gilmar F; Macedo, Cristiane R (2014). "Pharmacotherapy for sleep bruxism". doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005578.pub2.
- ↑ Cappelle, Sarah; Pans, Steven; Sciot, Raf (2016). "Imaging features of chondromyxoid fibroma: report of 15 cases and literature review". The British Journal of Radiology. 89 (1064): 20160088. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160088. ISSN 0007-1285.
- ↑ Sussman RD, Syan R, Brucker BM (May 2020). "Guideline of guidelines: urinary incontinence in women". BJU Int. 125 (5): 638–655. doi:10.1111/bju.14927. PMID 31625673.
|
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|---|---|
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Sandbox:Maneesha On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Sandbox:Maneesha | |

| Onset | Disease | Symptoms | Gold Standard
Test |
CT/MRI Findings | Other Investigation Findings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Headache
Characteristics |
Associated Features | |||||
| Sudden | Epidural hematoma |
|
CT scan without contrast | Biconvex lens shaped hematoma which expand inward toward the brain rather than along the inside of the skull |
| |
| Meningitis | Headache is associated with: | Lumbar puncture for CSF |
|
| ||
| Gradual | Intracranial mass | Morning headache | MRI |
|
||