Delirium resident survival guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (162 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="width: 80%;"> | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Delirium resident survival guide}} | |||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{PB}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{PB}} | ||
{| class="infobox" style="margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right; width: 100px; background: #A8A8A8; position: fixed; top: 250px; right: 21px; border-radius: 0 0 10px 10px;" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"; | |||
|- | |||
! style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 85%; background: #A8A8A8" align=center| {{fontcolor|#2B3B44|Delirium resident survival guide Microchapters}} | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Overview|Overview]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Classification|Classification]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Causes|Causes]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Diagnosis|Diagnosis]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Treatment|Treatment]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Prophylaxis|Prophylaxis]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Do's|Do's]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="font-size: 80%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | [[Delirium resident survival guide#Dont's|Dont's]] | |||
|} | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Delirium''' is characterized by acute onset (developing over hours to days), and a fluctuating decline in attention-focus, perception, and [[cognition]]. Infection, neurological diseases and metabolic derangement are the common causes of the delirium. Treatment of underlying etiology is crucial in the management of delirium. Delirium is managed conservatively. If non-pharmacological interventions fail, [[antipsychotic]] with a minimal [[anticholinergic]] profile, like [[haloperidol]] and [[olanzapine]] are used. Extremely agitated patients are managed by restrains and sedatives. | |||
== | ==Classification== | ||
''' | * '''Hyperactive:''' Increased psychomotor activity, which may co-occur with increased mood lability, agitation, and/or non-cooperative attitude towards medical treatment. | ||
* '''Hypoactive:''' Decreased level of psychomotor activity, which may exist along with increased sluggishness, [[lethargy]] or [[stupor]]. | |||
* '''Mixed level of activity:''' Normal level of psychomotor activity, individuals with rapidly fluctuating activity are also included in this category.<ref name="Inouye-2013">{{Cite journal | last1 = Inouye | first1 = SK. | last2 = Westendorp | first2 = RG. | last3 = Saczynski | first3 = JS. | title = Delirium in elderly people. | journal = Lancet | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Aug | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60688-1 | PMID = 23992774 }}</ref> | |||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
===Life Threatening Causes=== | ===Life Threatening Causes=== | ||
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. | Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Delirium by itself is not a life threatening condition. | ||
===Common Causes=== | ===Common Causes=== | ||
* Infections ([[pneumonia]], [[UTI]], [[sepsis]], [[CNS infection|CNS infections]]) | |||
* Neurological ([[stroke]], [[subdural haematoma]], [[epilepsy]]) | |||
*[[ | * Cardiovascular ([[myocardial infarction]], [[heart failure]]) | ||
*[[ | * Respiratory ([[pulmonary embolism]], [[hypoxia]]) | ||
*[[ | * Electrolyte imbalance (dehydration, [[renal failure]]) | ||
*[[ | * Endocrine & metabolic ([[diabetic ketoacidosis]], [[cachexia]], [[thiamine]] deficiency, thyroid dysfunction) | ||
*[[ | * Drugs ([[antidepressants]], antiparkinsonian drugs, [[sedatives]], [[lithium]]) | ||
==FIRE:Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation of Suspected Delirium== | |||
*[[ | A Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation (FIRE) should be performed to identify patients in need of immediate intervention. | ||
<br><span style="font-size:85%">Boxes in salmon color signify that an urgent management is needed.</span> | |||
{{Family tree/start}} | |||
|} | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | D01 | | | | | | | | | D01=<div style="width:22em"> Identify if,<br> | ||
== | ❑ '''The patient is extremely agitated and is harm to self or others''' </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|^|-|-|.| | | | |}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | C01 | | | | C02 | | | | C01=<div style=" background: #FA8072; text-align: left"> {{fontcolor| #F8F8FF|❑ '''Administer restrains, if patient can not be redirected''' <br> ❑ '''Use bezodiazepines''' to further curtail agitation|<span style="color:white;">hypotension</span>]])}}</div> | C02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 15em; padding:1em;"> '''[[Delirium resident survival guide#Complete Diagnostic Approach|Continue with the diagnostic approach]]''' </div> | border=0}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree |border=0|boxstyle=background: #FA8072; color: #FA8072;| | | | | | | | F01 | | | | | | | | | F01=<div style=" background: #FA8072; text-align: left; width: 22em"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF| '''Patients with severe agitation that does not improve: <br> ❑ Give Morphine, paralyze, and if required put on artificial respirator'''}}</div> |border=red}} | |||
{{Family tree/end}} | |||
<br> | |||
== | ==Complete Diagnostic Approach== | ||
A complete diagnostic approach should be carried out after a focused initial rapid evaluation is conducted and following initiation of any urgent intervention. Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the diagnostic approach to delirium based on the 1999-2000 APA (American Psychiatric Association) guideline, 2006 British Geriatric Scociety guideline and 2010 NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) guideline for the management of delirium. | |||
{{Family tree/start}} | {{Family tree/start}} | ||
{{familytree | A01 | | A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left | {{familytree | A01 | | A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;"> '''Characterize the symptoms:''' <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ Impaired sleep awake cycle <br> | ||
❑ Change in psychomotor activity <br> | ❑ Change in psychomotor activity <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ Change in social behavior and emotional disturbances with rapid and unpredictable shifts from one emotional state to another e.g. from [[anxiety]], [[fear]], [[depression]], [[irritability]], [[anger]], [[euphoria]] to [[apathy]] <br> | ||
❑ Nonspecific neurological abnormalities like : <br> | |||
❑ Nonspecific neurological abnormalities: [[ | :❑ [[Tremor]] | ||
:❑ [[Myoclonus]] | |||
:❑ [[Asterixis]] | |||
:❑ Reflex and muscle tone changes | |||
❑ Change in perception and cognitive functions like memory, orientation, visuospatial ability, or language. <br> | |||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | |}} | {{familytree | |!| | |}} | ||
{{familytree | B01 | | B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; | {{familytree | B01 | | B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;"> '''Obtain detailed history:''' <br> | ||
❑ Collateral history from relatives, out patient care providers, case managers | ❑ Onset <br> | ||
❑ Previous intellectual function <br> | |||
❑ List of medications/drugs <br> | |||
:❑ [[Sedative]] | |||
:❑ [[Hypnotics]] | |||
:❑ [[Narcotic]] | |||
:❑ [[Anticholinergic]] | |||
:❑ [[Corticosteroid]] | |||
:❑ Polypharmacy | |||
:❑ Alcohol withdrawal or other drugs) | |||
❑ Collateral history from relatives, out patient care providers, case managers <br> | |||
❑ Baseline [[blood pressure]] <br> | ❑ Baseline [[blood pressure]] <br> | ||
❑ Previous medical history including psychiatric diagnosis <br> | ❑ Previous medical history including psychiatric diagnosis <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ Sensory deficits <br> | ||
❑ Hearing aids/glasses <br> | |||
❑ Symptoms suggestive of underlying infection | |||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Identify if patient is at high risk to develop delirium:'''<br> | '''Identify if patient is at high risk to develop delirium:'''<br> | ||
❑ | ❑ Underlying cognitive impairment <br> | ||
❑ Older age (>65 years) <br> | ❑ Older age (>65 years) <br> | ||
❑ History of delirium, stroke, neurological disease, falls or gait disorder <br> | ❑ History of delirium, [[stroke]], neurological disease, falls or gait disorder <br> | ||
❑ Associating multiple medical aliments <br> | ❑ Associating multiple medical aliments <br> | ||
❑ Male gender <br> | ❑ Male gender <br> | ||
❑ Sensory impairment (hearing or vision) <br> | ❑ Sensory impairment (hearing or vision) <br> | ||
❑ Immobilization (catheters or restraints) <br> | ❑ Immobilization (catheters or restraints) <br> | ||
❑ Acute neurological pathology ( | ❑ Acute neurological pathology (e.g. [[stroke|acute stroke]] usually involving right parieta region, [[intracranial hemorrhage]], [[meningitis]], [[encephalitis]]) <br> | ||
❑ Intercurrent illness (for example, infections, iatrogenic complications, severe acute illness, anemia, dehydration, poor nutritional status, fracture or trauma, HIV infection) <br> | ❑ Intercurrent illness (for example, infections, iatrogenic complications, severe acute illness, [[anemia]], [[dehydration]], poor nutritional status, fracture or trauma, [[HIV]] infection) <br> | ||
❑ Metabolic impairment <br> | ❑ Metabolic impairment <br> | ||
❑ Surgery <br> | ❑ Surgery especially orthoscopic surgeries of the hip <br> | ||
❑ Stressful surroundings (for example, admission to an intensive care unit) <br> | ❑ Stressful surroundings (for example, admission to an intensive care unit) <br> | ||
❑ Pain <br> | ❑ [[Pain]] <br> | ||
❑ Emotional stress <br> | ❑ Emotional stress <br> | ||
❑ Lack of sleep </div>}} | ❑ [[Sleep Disorder|Lack of sleep]] </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | | | | | |}} | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | |}} | ||
{{familytree | C01 |-|-|-|.| |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; | {{familytree | C01 |-|-|-|.| |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Diagnosis''' <br> | ||
❑ Diagnosis is made by DSM V criteria or in the ICU by CAM scale <br> | |||
❑ '''DSM V Diagnostic Criteria'''<br> | ❑ '''DSM V Diagnostic Criteria'''<br> | ||
# Diminished focus or concentration and lack of knowledge or perception of the surroundings<br> | # Diminished focus or concentration and lack of knowledge or perception of the surroundings<br> | ||
| Line 98: | Line 119: | ||
# Also, interference in faculties of cognition like, memory, orientation, visuospatial ability, or language<br> | # Also, interference in faculties of cognition like, memory, orientation, visuospatial ability, or language<br> | ||
# 1st and 3rd criteria are not a result of any previous, current, or developing neurocognitive disorder and is not related to a shift in arousal status e.g. coma<br> | # 1st and 3rd criteria are not a result of any previous, current, or developing neurocognitive disorder and is not related to a shift in arousal status e.g. coma<br> | ||
# The manifestation of the disturbances resulting as a | # The manifestation of the disturbances resulting as a<br> | ||
:* Physiological sequel of a medical condition<br> | :* Physiological sequel of a medical condition<br> | ||
:* Intoxication or | :* Intoxication or withdrawal of substance(s)/ medicine(s)/ toxin(s)<br> | ||
:* Is due to multiple etiologies<br> | :* Is due to multiple etiologies<br> | ||
:* As explained by the history, physical examination, or laboratory findings<br> | :* As explained by the history, physical examination, or laboratory findings<br> | ||
Specify if | ❑ Specify if<br> | ||
: '''Substance intoxication delirium'''<br> | :❑ '''Substance intoxication delirium''' or<br> | ||
: '''Substance withdrawal delirium'''<br> | :❑ '''Substance withdrawal delirium''' or<br> | ||
: '''Delirium caused by another medical condition'''<br> | :❑ '''Delirium caused by another medical condition''' or<br> | ||
: '''Delirium caused by multiple etiologies'''<br> | :❑ '''Delirium caused by multiple etiologies''' or<br> | ||
❑Specify if delirium is<br> | |||
: '''Acute'''<br> | :❑ '''Acute''' or<br> | ||
: '''Persistent'''<br> | :❑ '''Persistent'''<br> | ||
❑Specify if delirium is <br> | |||
: '''Hyperactive'''<br> | :❑ '''Hyperactive''' or<br> | ||
: '''Hypoactive'''<br> | :❑ '''Hypoactive''' or<br> | ||
: '''Mixed level of activity''' | :❑ '''Mixed level of activity''' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Or,<br> | Or,<br> | ||
❑ '''Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) | ❑ '''Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU)'''<br> | ||
Diagnosed if, feature 1 and 2 are present along with 3 | Diagnosed if, feature 1 and 2 are present along with 3 or 4 <br> | ||
# Onset of symptoms, is acute(change from baseline) or fluctuating | # Onset of symptoms, is acute(change from baseline) or fluctuating, calibrated by Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale or [[Glasgow Coma Scale]] | ||
# Inability to focus as measured by Attention Screening Examination | # Inability to focus as measured by Attention Screening Examination | ||
# Thinking is not organized | # Thinking is not organized | ||
# Altered level of consciousness if | # Altered level of consciousness if vigilant, [[Lethargy|lethargic]], [[stupor]], [[coma]] | ||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | {{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | ||
{{familytree | D01 | | | D02 |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; | {{familytree | D01 | | | D02 |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''If delirium is diagnosed, do focused examination to find out underlying etiology:''' <br> | ||
'''Vital signs''' <br> | '''Vital signs''' <br> | ||
❑ [[Blood pressure]] <br> | ❑ [[Blood pressure]] <br> | ||
:❑ If lower than baseline: Shock, drug overdose e.g. | :❑ If lower than baseline: [[Shock]], [[drug overdose]] e.g. [[opiate]] <br> | ||
:❑ If higher than baseline: Increased intracranial pressure, drug overdose e.g. cocaine, hypertensive crisis <br> | :❑ If higher than baseline: [[Increased intracranial pressure]], [[drug overdose]] e.g. [[cocaine]], [[hypertensive crisis]] <br> | ||
'''[[Pulse]]''' <br> | '''[[Pulse]]''' <br> | ||
:❑ [[Tachycardia]]:[[Shock]], drug overdose eg. cocaine <br> | :❑ [[Tachycardia]]:[[Shock]], [[drug overdose]] eg. [[cocaine]] <br> | ||
:❑ [[Bradycardia]]:[[Increased intracranial pressure]] <br> | :❑ [[Bradycardia]]:[[Increased intracranial pressure]] [[drug overdose]] eg. [[opiate]] <br> | ||
'''Respiratory rate''' <br> | '''[[Respiratory rate]]''' <br> | ||
:❑ If lower: | :❑ If lower: [[Drug overdose]] e.g. [[opiates]] <br> | ||
:❑ If higher: Pulmonary pathology like [[pneumonia]], [[asthma]], [[COPD]] <br> | :❑ If higher: Pulmonary pathology like [[pneumonia]], [[asthma]], [[COPD]] <br> | ||
'''Raised temperature''' <br> | '''[[Fever|Raised temperature]]''' <br> | ||
:❑ Suspect cholinergic drug overdose <br> | :❑ Suspect cholinergic drug overdose <br> | ||
:❑ Underlying infection <br> | :❑ Underlying infection <br> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 168: | ||
❑ [[Jaundice]]: Liver and biliary pathology <br> | ❑ [[Jaundice]]: Liver and biliary pathology <br> | ||
❑ Cherry red appearance: [[CO|CO poisoning]] <br> | ❑ Cherry red appearance: [[CO|CO poisoning]] <br> | ||
❑ [[Edema]]: [[Heart failure]], [[liver failure]], [[renal failure]], malnutrition <br> | ❑ [[Edema]]: [[Heart failure]], [[liver failure]], [[renal failure]], [[malnutrition]] <br> | ||
❑ [[Cyanosis]]:[[Heart failure]], lung pathology, drug overdose <br> | ❑ [[Cyanosis]]:[[Heart failure]], lung pathology, [[drug overdose]] <br> | ||
❑ Needle marks: | ❑ Needle marks: [[Drug overdose]] <br> | ||
'''Appearance''' <br> | '''[[Mental status examination#Appearance|Appearance]]''' <br> | ||
❑ Cherry red tongue, lip fissure etc suggestive of malnutrition <br> | ❑ Cherry red tongue, lip fissure etc suggestive of [[malnutrition]] <br> | ||
❑ Unkempt and | ❑ Unkempt and unhygienic: [[Schizophrenia]] | ||
''' | '''Neurological examination''' <br> | ||
❑ Emergence of new focal neurological signs: Cerebrovascular event <br> | ❑ Emergence of [[Focal neurologic signs|new focal neurological signs]]: [[Stroke|Cerebrovascular event]] <br> | ||
❑ Trauma to head: hemorrhage and increased intracranial pressure <br> | ❑ Trauma to head: hemorrhage and [[increased intracranial pressure]] <br> | ||
❑ Meningeal signs: [[Meningitis]] <br> | ❑ Meningeal signs: [[Meningitis]] <br> | ||
❑ Neurodegenerative diseases: | ❑ Neurodegenerative diseases: [[Parkinsonism]], [[alzheimer's disease]] etc. <br> | ||
❑ Mental status examination: [[Dementia]] <br> | ❑ Mental status examination: [[Dementia]] <br> | ||
'''Cardiovascular examination''' <br> | '''Cardiovascular examination''' <br> | ||
❑ New onset murmur: | ❑ New onset murmur: [[Myocardial infarction]] <br> | ||
❑ S3 and S4: Heart failure <br> | ❑ [[S3]] and [[S4]]: [[Heart failure]] <br> | ||
❑ Murmur: underlying shunts and cardiac valve pathology <br> | ❑ [[Murmur]]: underlying shunts and cardiac valve pathology <br> | ||
''' | '''Respiratory examination''' <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ [[Respiratory examination#Ausculation|Inspiratory crackles]]: Suggestive of [[congestive heart failure]] <br> | ||
❑ Wheeze may be because of asthma or COPD <br> | ❑ [[Respiratory examination#Ausculation|Wheeze]] may be because of [[asthma]] or [[COPD]] <br> | ||
❑ Increased tactile vocal fermitus, egophony and dull on percussion may indicate underlying pneumonia <br> | ❑ [[Respiratory examination#Ausculation|Increased tactile vocal fermitus]], [[egophony]] and dull on percussion may indicate underlying [[pneumonia]] <br> | ||
'''Abdominal examination''' <br> | '''Abdominal examination''' <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ [[Ascites]]: [[Liver failure]], [[heart failure]], [[kidney failure]] <br> | ||
❑ Organomegaly: Liver failure, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy <br> | ❑ Organomegaly: [[Liver failure]], [[portal hypertension]], [[hepatic encephalopathy]] <br> | ||
❑ Distended bladder: | ❑ Distended bladder: Urinary obstruction leading [[urinary tract infection]]. | ||
</div>|D02=<div style="float: right; text-align: left; | </div>|D02=<div style="float: right; text-align: left; padding:1em;"> '''If delirium is not diagnosed''', <br> | ||
❑ Re-access patient multiple times a day, diagnosis of delirium may be missed because of it's fluctuating course<br> | ❑ Re-access patient multiple times a day, diagnosis of delirium may be missed because of it's fluctuating course <br> | ||
❑ When delirium can not be differentiated from dementia or delirium and dementia co-exists, provide treatment delirium <br> | |||
❑ Consider following differential diagnosis, <br> | ❑ Consider following differential diagnosis, <br> | ||
#'''Psychiatric illness''': <br> | #'''Psychiatric illness''': <br> | ||
#*Psychotic disorders like, brief psychotic disorder, schizophrenia, schizophreniform disorder, bipolar etc. <br> | #* [[Psychosis|Psychotic disorders]] like, [[brief psychotic disorder]], [[schizophrenia]], [[schizophreniform disorder]], [[bipolar disorder]] etc. <br> | ||
#* Acute stress disorder <br> | #* [[Acute stress disorder]] <br> | ||
#* Malingering and factitious disorder <br> | #* [[Malingering]] and [[factitious disorder]] <br> | ||
#* Confusional states <br> | #* [[Altered mental status classification#Classification|Confusional states]] <br> | ||
#* Other neurocognitive disorders. | #* Other neurocognitive disorders e.g. [[dementia]] | ||
# '''Neurological Disorders''': <br> | # '''Neurological Disorders''': <br> | ||
#* Frontal lobe disorders such as tumor <br> | #* Frontal lobe disorders such as [[Brain tumor|tumor]] <br> | ||
#* Cerebral contusion <br> | #* [[Cerebral contusion]] <br> | ||
#* Bacterial | #* [[Meningitis|Bacterial meningitis]] <br> | ||
#* Parital lobe disorders like | #* Parital lobe disorders like [[wernicke's aphasia]] <br> | ||
#* Nonconvulsive epileptic episodes <br> | #* Nonconvulsive epileptic episodes <br> | ||
#* Hepatic encephalopathy <br> | #* [[Hepatic encephalopathy]] <br> | ||
#* Sundowning <br> | #* [[Differentiating confusion from other symptoms|Sundowning]] <br> | ||
#* Viral encephalitis | #* [[Viral encephalitis]] | ||
</div>}} | |||
{{familytree | |!| | | | | | |}} | |||
{{familytree | E01 | | | | |E01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Investigations''' <br> | |||
❑ Delirium is a clinical diagnosis, investigations are aimed to reveal underlying etiology.<br> | |||
❑ '''Lab investigations''':<br> | |||
* [[Complete blood count]] ([[CBC]]) <br> | |||
* [[Glucose]] <br> | |||
* [[Calcium]] <br> | |||
* [[Urinalysis]] <br> | |||
* [[Electrolyte]] <br> | |||
* [[Blood urea nitrogen]] ([[BUN]]) / [[creatinine]] <br> | |||
* [[Arterial blood gases]] <br> | |||
* [[Pulse oximetry]] <br> | |||
* [[Vitamin B12 ]] <br> | |||
* [[Folate levels]] <br> | |||
* [[Thyroid function test]] <br> | |||
* [[Urine culture]] <br> | |||
* [[Blood culture]] <br> | |||
* Toxic screen of blood and urine <br> | |||
If indicated: <br> | |||
* [[Arterial blood gas]] <br> | |||
* Specific cultures e.g. [[sputum culture|sputum]] <br> | |||
*Lumbar puncture if,<br> | |||
:*[[Meningism]]<br> | |||
:*[[Headache]]<br> | |||
:*[[Fever|Unexplained fever]]<br> | |||
* [[EEG]] to rule out<br> | |||
:*[[Dementia]]<br> | |||
:* Non‑convulsive status epilepticus and temporal lobe epilepsy<br> | |||
:* Conditions that can be identified on EEG e.g. metabolic encephalopathy or infectious encephalitis<br> | |||
:* Focal intracranial lesion, or it's a global abnormality<br> | |||
❑ '''Imaging Studies'''<br> | |||
# CT scan of the brain: <br> | |||
#* [[Neurological examination|Focal neurological signs]] <br> | |||
#* [[Head injury]] <br> | |||
#* [[Increased intracranial pressure]]. <br> | |||
# MRI of brain: <br> | |||
#* [[Intracranial bleed]] <br> | |||
#* [[Brain tumor]] <br> | |||
#* [[Dementia]] etc. <br> | |||
</div>}} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | |||
==Treatment== | |||
{{Family tree/start}} | |||
{{familytree | F01 |-|-|-|.| |F01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 35em; padding:1em;">'''Treatment:''' <br> | |||
❑ Treat underlying etiology. <br> | |||
❑ Discontinue/ adjust dose of the offending drugs<br> | |||
:*[[Antiarrhythmic]] <br> | |||
:* [[Antihistamine]] <br> | |||
:* [[Antiparkinsonian]] drugs such as [[benzatropine]] <br> | |||
:* [[Antispasmodic]] <br> | |||
:* [[Benzodiazepine]]<br> | |||
:* [[Diuretic]] e.g. [[furosemide]]<br> | |||
:* [[Incontinence]] medicines e.g. [[oxybutynin]]<br> | |||
:* [[Opioid]] analgesics <br> | |||
:* [[Tricyclic antidepressant]] <br> | |||
*'''Non-pharmacological treatment''' <br> | |||
❑ Avoid unnecessary movement of the patient <br> | |||
❑ Maintain continuity of care from caring staff <br> | |||
❑ Avoid physical restraints<br> | |||
❑ Involve family members in care<br> | |||
❑ Have recognizable faces at the bedside<br> | |||
❑ Sensory aids should be available and working where necessary<br> | |||
❑ Maintenance or restoration of normal sleep patterns<br> | |||
❑ Avoid sudden and irritating noise (e.g. Pump alarms)<br> | |||
❑ Careful management of bowel and bladder elimination<br> | |||
❑ Having a means of orientation available (such as a clock and a calendar)<br> | |||
❑ Reassurance and explanation to the patient<br> | |||
❑ Verbal and non-verbal de-escalation techniques to calm the patient. <br> | |||
❑ T-A-DA Method (Tolerate, Anticipate, Don't Agitate)<br> | |||
:❑ Tolerate patient behavior, as long as the patient or other people are not in danger<br> | |||
:❑ Provide greater mobility by removing unnecessary attachments like catheter <br> | |||
:❑ Reduce agitation, do not reorient if reorientation causes agitation<br> | |||
:❑ Provide supervision, anticipate behavior to keep the patient safe.<br> | |||
❑ Wandering and rambling speech can be tackled with the following strategies <br> | |||
:❑ Closely observe wandering patients<br> | |||
:❑ Distract agitated wandering patient, if required, seek help from relatives<br> | |||
:❑ Attain to the common stressors causing agitation, such as pain, and thirst<br> | |||
:❑ Do not agree with rambling talk, acknowledge the feelings expressed and ignore the content, or change the subject, or tactfully disagree if the topic is not sensitive.<br> | |||
❑ If non pharmacological techniques fail, or if de-escalation techniques are inappropriate, use pharmacological treatment to tackle delirium. <br> | |||
</div>|G02=<div style="float: right; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;"> '''Restrains:''' <br> | |||
*Used as a last resort in a severe delirium <br> | |||
*Must be avoided as it can increase agitation and risk of injury <br> | |||
*Local laws on restrains must be well known to care providers. <br> | |||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | {{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | ||
{{familytree | | {{familytree | G01 | | | G02 |G01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 35em; padding:1em;">'''Medical Management:''' <br> | ||
* [[ | ❑ [[Antipsychotic]] <br> | ||
* [[ | <span style="font-size:85%;color:red">Contraindicated in parkinson disease, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, dementia with lewy bodies.</span> <br> | ||
* [[ | :* [[Haloperidol]] is a gold standard, [[olanzepine]] can also be used. <br> | ||
:* Geriatric population, and seriously ill patients: 0.25 - 0.50mg four hourly <br> | |||
:* Healthier patients: 2mg - 3mg per day <br> | |||
:* Very agitated patients: 5mg - 10mg per hour iv <br> | |||
* [[ | :* IV route can reduce extrapyramidal side effects <br> | ||
* [[ | :* [[Droperidol]] can be given alone or after [[haloperidol]], if quicker results are desired <br> | ||
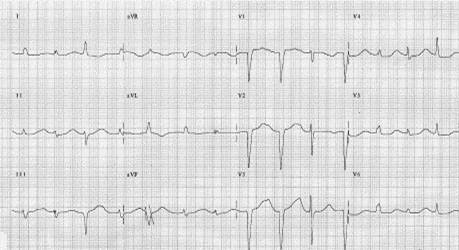
:* [[EKG]] monitoring may be needed to find out [[QT prolongation|QTc]] interval <br> | |||
[[Image:QT Prolongation3.jpg|center|300px]] <br> | |||
* [[ | ❑ [[Sedative]] such as [[benzodiazepine]]<br> | ||
<span style="font-size:85%;color:red">Contraindicated in hepatic encephalopathy, respiratory depression or compromised lung functions.</span> <br> | |||
:* To conduct required diagnostic procedures or to deliver treatment <br> | |||
:* If patient is danger to others or themselves<br> | |||
* [[ | :* Highly agitated or hallucinating patient<br> | ||
:* [[Alcohol withdrawal]] <br> | |||
:* [[Benzodiazepine withdrawal]] <br> | |||
</div>| | :* When [[antipsychotics]] are contraindicated, [[parkinson's disease]], [[neuroleptic malignant syndrome]], [[dementia with Lewy bodies]] <br> | ||
❑ [[Cholinergic]]: <br> | |||
:* [[Physostygmine]] is used if caused by [[anticholinergic]] medications <br> | |||
❑ [[Morphine]] and paralysis: <br> | |||
<span style="font-size:85%;color:red">Contraindicated in head trauma.</span> <br> | |||
:* Used in extremely agitated patients, unresponsive to other treatment, who may need sedation and ventilator support <br> | |||
:* It increases oxygenation and skeletal muscle exertion <br> | |||
:* [[Morphine]] is useful when pain is an important aggravating factor. But, [[opiates]] etc. can exacerbate delirium because of [[anticholinergic]] properties <br> | |||
</div>|G02=<div style="float: right; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;"> '''Restrains:''' <br> | |||
* Used as a last resort in a severe delirium <br> | |||
* Must be avoided as it can increase agitation and risk of injury <br> | |||
* Local laws on restrains must be well known to care providers. <br> | |||
</div>}} | |||
{{familytree | |!| | | | | | |}} | |||
{{familytree | H01 |-|-|-|.| |H01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 35em; padding:1em;">'''If Improvement:''' <br> | |||
❑ Continue the treatment <br> | |||
❑ Monitor the patient by CAM-ICU scale <br> | |||
❑ Avoid sedatives <br> | |||
❑ Avoid restrains. <br> | |||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | {{familytree | |!| | | | |!| |}} | ||
{{familytree | I01 | | | I02 |I01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 35em; padding:1em;">'''Discharge & Follow up''' <br> | |||
❑ Before Discharge: | |||
:* Housing and living issues like washing, dressing, medication etc. must be sorted out before the patient is relieved from the hospital <br> | |||
:* Cognitive and functional status (e.g. using standardized tools such as AMT and Barthel Index) must be accessed <br> | |||
:* Consult all relevant disciplines in the hospital and out patient care providers <br> | |||
:* Must be referred to a Geriatrician, Psychiatrist, Social Worker, etc. for further work up and management. <br> | |||
❑ Education and Reassurance: Explain transient nature of delirium to patients and their families help them cope <br> | |||
❑ Post Delirium Psychiatric Management: Patients may remember delirium after recovery, which can cause significant distress, and frightening recollections. Utilize standard psychiatric interventions used for traumatic experiences. <br> | |||
</div>|I02=<div style="float: right; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;"> '''If no Improvement''' <br> | |||
❑ Re-evaluate the patient<br> | |||
❑ Consider prolonged delirium syndrome<br> | |||
❑ Consider the diagnosis of [[dementia]].<br> | |||
</div>}} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | {{familytree/end}} | ||
{| border="2" | |||
|+ '''Dose of Haloperidol''' | |||
! Geriatric population, and seriously ill patients | |||
| 0.25 - 0.50mg four hourly|| | |||
|- | |||
! Healthier patients | |||
| 2mg - 3mg per day || | |||
|- | |||
! Very agitated patients | |||
|5mg - 10mg per hour iv | |||
|} | |||
{| style="cellpadding=0; cellspacing= 0; width: 600px;" | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 100%; background: #F5F5F5;" align=center | Reversible Causes of Delirium||style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 100%; background: #F5F5F5;" align=center | Offending Drugs causing Delirium | |||
|- | |||
| style="font-size: 90%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left |❑ [[Hypoglycemia]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Hypoxia]] or [[anoxia]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Hyperthermia]] <br> | |||
❑ Severe hypertension <br> | |||
❑ Alcohol or sedative withdrawal <br> | |||
❑ [[Wernicke encephalopathy]] <br> | |||
| style="font-size: 90%; padding: 0 5px; background: #DCDCDC" align=left | ❑ [[Antiarrhythmic]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Antihistamine]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Antiparkinsonian]] drugs such as [[benzatropine]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Antispasmodic]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Benzodiazepine]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Diuretic]] e.g. [[furosemide]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Incontinence]] medicines e.g. [[oxybutynin]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Opioid]] Analgesics<br> | |||
❑ [[Tricyclic antidepressant]] | |||
|} | |||
<ref>{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://psychiatryonline.org/content.aspx?bookID=28§ionID=1663978 | url =http://psychiatryonline.org/content.aspx?bookID=28§ionID=1663978 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = Matching the Environment to Patients with Delirium: Lessons Learned from the Delirium Room, a Restraint‐Free Environment for Older Hospitalized Adults with Delirium - Flaherty-2011 - Journal of the American Geriatrics Society - Wiley Online Library | url = http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03678.x/abstract;jsessionid=AF673522CC21621BCB46B52E7E1ED850.f03t04 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref> | <ref>{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://psychiatryonline.org/content.aspx?bookID=28§ionID=1663978 | url =http://psychiatryonline.org/content.aspx?bookID=28§ionID=1663978 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = Matching the Environment to Patients with Delirium: Lessons Learned from the Delirium Room, a Restraint‐Free Environment for Older Hospitalized Adults with Delirium - Flaherty-2011 - Journal of the American Geriatrics Society - Wiley Online Library | url = http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03678.x/abstract;jsessionid=AF673522CC21621BCB46B52E7E1ED850.f03t04 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref> | ||
== | ==Prophylaxis== | ||
Targeted symptomatic intervention can help prevent the emergence of delirium, however, non pharmacological approach can curtail the incidence of delirium and not effective in preventing recurrence of delirium once delirium has set it. | |||
'''Non pharmacological approach''': | |||
== | ❑ Curtail cognitive decline: | ||
* Write names of care providers, the day’s schedule on board | |||
* Constantly reorient patients to surroundings | |||
* Activities to stimulate cognitive actions like discussion of current events, structured reminiscence, or word games | |||
❑ Curtail sleep impairment: | |||
* Reduce environmental noise | |||
* Relaxing activities such as music, back massage | |||
❑ Curtail immobility: | |||
* Minimal use of catheter or other aids which promotes immobility | |||
* Early mobilization | |||
* Incorporation of an exercise regiment | |||
❑ Manage difficulties in sight: | |||
* Use of visual aids | |||
* Use of large fluorescent tapes or objects with illuminations to help in vision | |||
❑ Manage difficulties in hearing: | |||
* Use of aids | |||
* Ear care | |||
❑ Avoid dehydration: | |||
* Regular hydration | |||
* Early recognition and prompt treatment.<ref>{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = MMS: Error | url = http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199903043400901 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref> | |||
❑ Delirium in ICU can be predicted by [[http://www.umcn.nl/Research/Departments/intensive%20care/Documents/Pre-deliric%20model.htm?language=english| PREDELIRIC]] model | |||
❑ Low dose [[haloperidol]], if given prophylactically in lower doses, have following benefits, | |||
* Lower mortality | |||
* Lower delirium incidence | |||
* More delirium free days | |||
* Patients are less likely to remove their tubes or catheters | |||
* Patients with a higher risk of developing delirium benefited more | |||
* ICU readmission rate was lower. | |||
Drawbacks for prophylactic treatment with Haloperidol: | |||
* Unnecessary treatment to patients who were not destined to develop delirium, | |||
* Side effects of treatment, however during clinical studies there was only a marginal [[QT prolongation|prolongation of QTc]] and no one developed [[ventricular arrhythmias]]. More studies neeeds to be done on prophylaxis of delirium.<ref name="www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = Practice guideline for the treatment of pati... [Am J Psychiatry. 1999] - PubMed - NCBI | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10327941 | publisher = | date = | accessdate = }}</ref> | |||
==Do's== | |||
*Access the patients multiple times a day, diagnosis of delirium can be missed because of transient nature of it's symptoms. | |||
*Use [[antipsychotic]]with caution, | |||
:*Give for a short period of time - approximately 1 week. | |||
:*Start with the lowest possible dose and titrated according to symptoms. | |||
:*Do [[EKG]] monitoring to calibrate [[QT prolongation|QTc]] interval which is one of the serious side effect of [[antipsychotic]], and order cardiology consult if [[QT prolongation|QTc]] interval is more than 450msec or it is greater than 25% baseline. Dose adjustment or discontinuation of [[antipsychotic]] medication may be warranted. | |||
:*Do watch for side effects: [[Haloperidol]] can cause sedation and [[hypotension]], lowering of [[seizure]] threshold, [[galactorrhea]], elevation in liver enzyme levels, inhibition of leukopoiesis, [[neuroleptic malignant syndrome]], and withdrawal movement disorders are rare side effects of [[antipsychotic]] medication. | |||
:*Do watch complications of anti psychotics in elderly, w.r.t. extra pyramidal side effects, falls, hip fracture. | |||
*Use sedatives must be used with caution with minimum possible dosage and discontinue if they are not required. | |||
*Use [[benzodiazepine]] with caution if liver functions are compromised. It can cause behavioral dis-inhibition, [[amnesia]], [[ataxia]], respiratory depression, physical dependence, rebound [[insomnia]], withdrawal reactions, and delirium. Adolescents and pediatric may suffer from dis-inhibition reactions, emotional lability, increased [[anxiety]], [[hallucinations]], aggression, [[insomnia]], [[euphoria]], and in-coordination. | |||
*Use [[anticholinergic]] with caution, It can cause [[bradycardia]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], salivation, and increased gastrointestinal acid. [[Physostigmine]] can cause [[seizure]]. | |||
*Be aware of medicolegal issues: | |||
:*Because of transient impairment in cognition, orientation and other higher functions, patient may not be able to provide consent or there can be impairment of competency. Delirium itself does not make patient incompetent by law. Emergency cases can be treated without obtaining consent, however non emergency cases pose an ethical dilemmas. | |||
:*Local laws on restrains must be well known to the care provider. | |||
*Educate family members and the patient to explain transient nature of delirium. Provide appropriate psychiatric care if the patient suffers distress and frightening recollection of delirium . | |||
==Don'ts == | |||
* Do not give sedatives in hypoactive delirium. | |||
* Do not catheterize, or use restraint | |||
* Do not acknowledge rambling speech and argue with the patients. | |||
* Do not discharge patients without setting up an appropriate outpatient care. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Psychiatry]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | |||
[[Category:Help]] | [[Category:Help]] | ||
[[Category:Projects]] | [[Category:Projects]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:52, 18 April 2014
Template:Delirium resident survival guide Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Pratik Bahekar, MBBS [2]
| Delirium resident survival guide Microchapters |
|---|
| Overview |
| Classification |
| Causes |
| Diagnosis |
| Treatment |
| Prophylaxis |
| Do's |
| Dont's |
Overview
Delirium is characterized by acute onset (developing over hours to days), and a fluctuating decline in attention-focus, perception, and cognition. Infection, neurological diseases and metabolic derangement are the common causes of the delirium. Treatment of underlying etiology is crucial in the management of delirium. Delirium is managed conservatively. If non-pharmacological interventions fail, antipsychotic with a minimal anticholinergic profile, like haloperidol and olanzapine are used. Extremely agitated patients are managed by restrains and sedatives.
Classification
- Hyperactive: Increased psychomotor activity, which may co-occur with increased mood lability, agitation, and/or non-cooperative attitude towards medical treatment.
- Hypoactive: Decreased level of psychomotor activity, which may exist along with increased sluggishness, lethargy or stupor.
- Mixed level of activity: Normal level of psychomotor activity, individuals with rapidly fluctuating activity are also included in this category.[1]
Causes
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Delirium by itself is not a life threatening condition.
Common Causes
- Infections (pneumonia, UTI, sepsis, CNS infections)
- Neurological (stroke, subdural haematoma, epilepsy)
- Cardiovascular (myocardial infarction, heart failure)
- Respiratory (pulmonary embolism, hypoxia)
- Electrolyte imbalance (dehydration, renal failure)
- Endocrine & metabolic (diabetic ketoacidosis, cachexia, thiamine deficiency, thyroid dysfunction)
- Drugs (antidepressants, antiparkinsonian drugs, sedatives, lithium)
FIRE:Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation of Suspected Delirium
A Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation (FIRE) should be performed to identify patients in need of immediate intervention.
Boxes in salmon color signify that an urgent management is needed.
Identify if, ❑ The patient is extremely agitated and is harm to self or others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
❑ Administer restrains, if patient can not be redirected ❑ Use bezodiazepines to further curtail agitation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Patients with severe agitation that does not improve: ❑ Give Morphine, paralyze, and if required put on artificial respirator | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Complete Diagnostic Approach
A complete diagnostic approach should be carried out after a focused initial rapid evaluation is conducted and following initiation of any urgent intervention. Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the diagnostic approach to delirium based on the 1999-2000 APA (American Psychiatric Association) guideline, 2006 British Geriatric Scociety guideline and 2010 NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) guideline for the management of delirium.
Characterize the symptoms: ❑ Impaired sleep awake cycle ❑ Change in perception and cognitive functions like memory, orientation, visuospatial ability, or language. | |||||||||||||||||
Obtain detailed history: ❑ Onset
❑ Collateral history from relatives, out patient care providers, case managers Identify if patient is at high risk to develop delirium: | |||||||||||||||||
Diagnosis ❑ Diagnosis is made by DSM V criteria or in the ICU by CAM scale
❑ Specify if
❑Specify if delirium is
❑Specify if delirium is
Or,
| |||||||||||||||||
If delirium is diagnosed, do focused examination to find out underlying etiology: Vital signs
Skin Appearance Neurological examination Cardiovascular examination Respiratory examination Abdominal examination | If delirium is not diagnosed, ❑ Re-access patient multiple times a day, diagnosis of delirium may be missed because of it's fluctuating course
| ||||||||||||||||
Investigations ❑ Delirium is a clinical diagnosis, investigations are aimed to reveal underlying etiology.
If indicated:
❑ Imaging Studies
| |||||||||||||||||
Treatment
Treatment: ❑ Treat underlying etiology.
❑ Avoid unnecessary movement of the patient
❑ Wandering and rambling speech can be tackled with the following strategies
❑ If non pharmacological techniques fail, or if de-escalation techniques are inappropriate, use pharmacological treatment to tackle delirium. | |||||||||||||||||
Medical Management: ❑ Antipsychotic
 ❑ Sedative such as benzodiazepine
❑ Cholinergic:
❑ Morphine and paralysis:
| Restrains:
| ||||||||||||||||
If Improvement: ❑ Continue the treatment | |||||||||||||||||
Discharge & Follow up ❑ Before Discharge:
❑ Education and Reassurance: Explain transient nature of delirium to patients and their families help them cope | If no Improvement ❑ Re-evaluate the patient | ||||||||||||||||
| Geriatric population, and seriously ill patients | 0.25 - 0.50mg four hourly | |
|---|---|---|
| Healthier patients | 2mg - 3mg per day | |
| Very agitated patients | 5mg - 10mg per hour iv |
| Reversible Causes of Delirium | Offending Drugs causing Delirium |
| ❑ Hypoglycemia ❑ Hypoxia or anoxia |
❑ Antiarrhythmic ❑ Antihistamine |
Prophylaxis
Targeted symptomatic intervention can help prevent the emergence of delirium, however, non pharmacological approach can curtail the incidence of delirium and not effective in preventing recurrence of delirium once delirium has set it.
Non pharmacological approach:
❑ Curtail cognitive decline:
- Write names of care providers, the day’s schedule on board
- Constantly reorient patients to surroundings
- Activities to stimulate cognitive actions like discussion of current events, structured reminiscence, or word games
❑ Curtail sleep impairment:
- Reduce environmental noise
- Relaxing activities such as music, back massage
❑ Curtail immobility:
- Minimal use of catheter or other aids which promotes immobility
- Early mobilization
- Incorporation of an exercise regiment
❑ Manage difficulties in sight:
- Use of visual aids
- Use of large fluorescent tapes or objects with illuminations to help in vision
❑ Manage difficulties in hearing:
- Use of aids
- Ear care
❑ Avoid dehydration:
- Regular hydration
- Early recognition and prompt treatment.[4]
❑ Delirium in ICU can be predicted by [PREDELIRIC] model
❑ Low dose haloperidol, if given prophylactically in lower doses, have following benefits,
- Lower mortality
- Lower delirium incidence
- More delirium free days
- Patients are less likely to remove their tubes or catheters
- Patients with a higher risk of developing delirium benefited more
- ICU readmission rate was lower.
Drawbacks for prophylactic treatment with Haloperidol:
- Unnecessary treatment to patients who were not destined to develop delirium,
- Side effects of treatment, however during clinical studies there was only a marginal prolongation of QTc and no one developed ventricular arrhythmias. More studies neeeds to be done on prophylaxis of delirium.[5]
Do's
- Access the patients multiple times a day, diagnosis of delirium can be missed because of transient nature of it's symptoms.
- Use antipsychoticwith caution,
- Give for a short period of time - approximately 1 week.
- Start with the lowest possible dose and titrated according to symptoms.
- Do EKG monitoring to calibrate QTc interval which is one of the serious side effect of antipsychotic, and order cardiology consult if QTc interval is more than 450msec or it is greater than 25% baseline. Dose adjustment or discontinuation of antipsychotic medication may be warranted.
- Do watch for side effects: Haloperidol can cause sedation and hypotension, lowering of seizure threshold, galactorrhea, elevation in liver enzyme levels, inhibition of leukopoiesis, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and withdrawal movement disorders are rare side effects of antipsychotic medication.
- Do watch complications of anti psychotics in elderly, w.r.t. extra pyramidal side effects, falls, hip fracture.
- Use sedatives must be used with caution with minimum possible dosage and discontinue if they are not required.
- Use benzodiazepine with caution if liver functions are compromised. It can cause behavioral dis-inhibition, amnesia, ataxia, respiratory depression, physical dependence, rebound insomnia, withdrawal reactions, and delirium. Adolescents and pediatric may suffer from dis-inhibition reactions, emotional lability, increased anxiety, hallucinations, aggression, insomnia, euphoria, and in-coordination.
- Use anticholinergic with caution, It can cause bradycardia, nausea, vomiting, salivation, and increased gastrointestinal acid. Physostigmine can cause seizure.
- Be aware of medicolegal issues:
- Because of transient impairment in cognition, orientation and other higher functions, patient may not be able to provide consent or there can be impairment of competency. Delirium itself does not make patient incompetent by law. Emergency cases can be treated without obtaining consent, however non emergency cases pose an ethical dilemmas.
- Local laws on restrains must be well known to the care provider.
- Educate family members and the patient to explain transient nature of delirium. Provide appropriate psychiatric care if the patient suffers distress and frightening recollection of delirium .
Don'ts
- Do not give sedatives in hypoactive delirium.
- Do not catheterize, or use restraint
- Do not acknowledge rambling speech and argue with the patients.
- Do not discharge patients without setting up an appropriate outpatient care.
References
- ↑ Inouye, SK.; Westendorp, RG.; Saczynski, JS. (2013). "Delirium in elderly people". Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60688-1. PMID 23992774. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ "http://psychiatryonline.org/content.aspx?bookID=28§ionID=1663978". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ "Matching the Environment to Patients with Delirium: Lessons Learned from the Delirium Room, a Restraint‐Free Environment for Older Hospitalized Adults with Delirium - Flaherty-2011 - Journal of the American Geriatrics Society - Wiley Online Library".
- ↑ "MMS: Error".
- ↑ "Practice guideline for the treatment of pati... [Am J Psychiatry. 1999] - PubMed - NCBI".