Duchenne muscular dystrophy MRI: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Lower limb]] [[MRI]] may be helpful in the diagnosis of Duchenne [[muscular dystrophy]]. Findings on [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] suggestive of Duchenne [[muscular dystrophy]] include high T1-weighted signal in affected [[muscles]]. | |||
[ | |||
==MRI== | ==MRI== | ||
Lower limb MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Findings on MRI suggestive of Duchenne muscular dystrophy include:<ref name="SchreiberSmith1987">{{cite journal|last1=Schreiber|first1=A.|last2=Smith|first2=W. L.|last3=Ionasescu|first3=V.|last4=Zellweger|first4=H.|last5=Franken|first5=E. A.|last6=Dunn|first6=V.|last7=Ehrhardt|first7=J.|title=Magnetic resonance imaging of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy|journal=Pediatric Radiology|volume=17|issue=6|year=1987|pages=495–497|issn=0301-0449|doi=10.1007/BF02388288}}</ref> | [[Lower limb]] [[MRI]] may be helpful in the diagnosis of Duchenne [[muscular dystrophy]]. Findings on [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] suggestive of Duchenne [[muscular dystrophy]] include:<ref name="SchreiberSmith1987">{{cite journal|last1=Schreiber|first1=A.|last2=Smith|first2=W. L.|last3=Ionasescu|first3=V.|last4=Zellweger|first4=H.|last5=Franken|first5=E. A.|last6=Dunn|first6=V.|last7=Ehrhardt|first7=J.|title=Magnetic resonance imaging of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy|journal=Pediatric Radiology|volume=17|issue=6|year=1987|pages=495–497|issn=0301-0449|doi=10.1007/BF02388288}}</ref> | ||
*High T1-weighted signal in affected muscles such as: | *High T1-weighted signal in affected [[muscles]] such as: | ||
** | **[[Gastrocnemius muscle|Gastrocnemius]] | ||
**Gluteus maximus | **[[Gluteus maximus]] | ||
**Gluteus medius | **[[Gluteus medius]] | ||
**Adductor magnus | **[[Adductor magnus]] | ||
**Psoas | **[[Psoas]] | ||
**Iliacus | **[[Iliacus]] | ||
**Quadriceps | **[[Quadriceps]] | ||
**Rectus femoris | **[[Rectus femoris]] | ||
**Biceps femoris | **[[Biceps femoris]] | ||
**Peroneus longus | **[[Peroneus longus]] | ||
**Soleus muscles | **[[Soleus muscle|Soleus muscles]] | ||
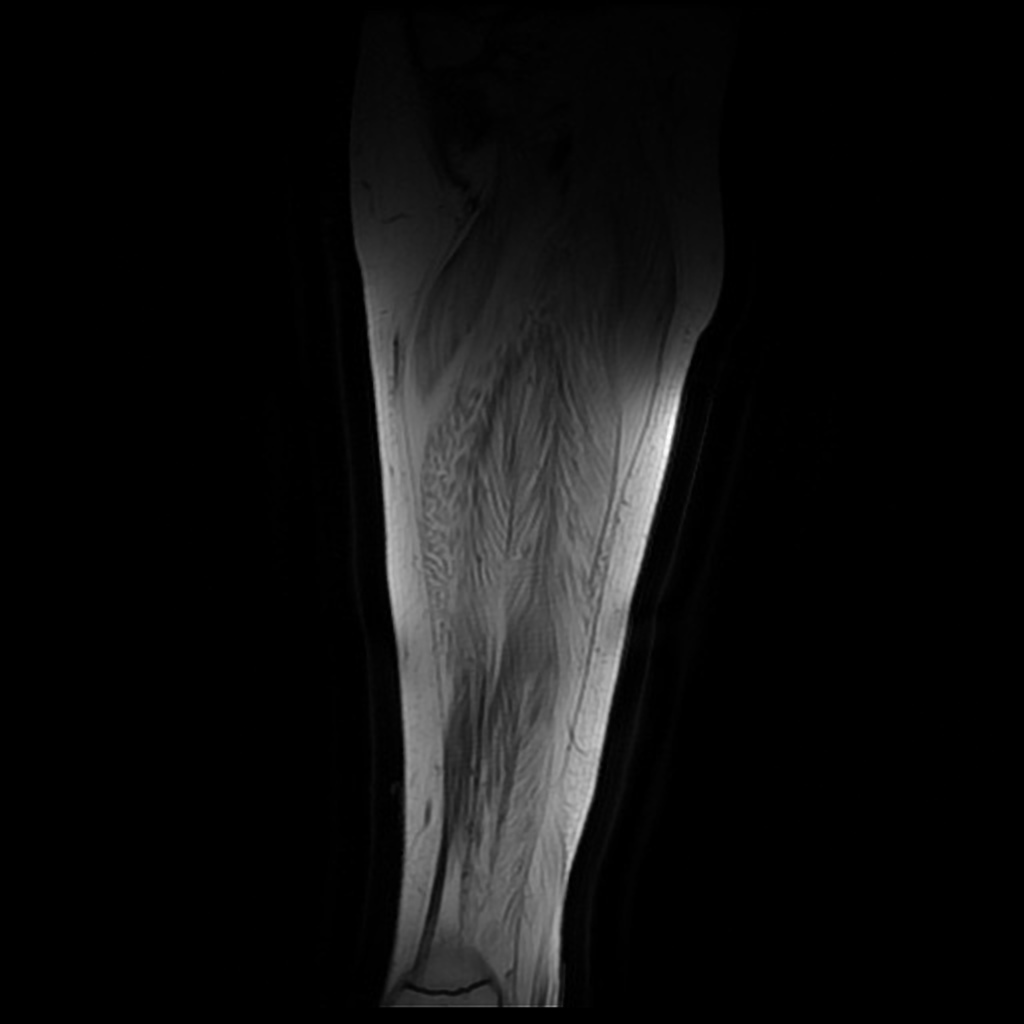
[[File:Duchenne-muscular-dystrophy.jpg|500px|none|thumb|Case courtesy of Kathryn Kinser, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/66153">rID: 66153</a>]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:23, 15 May 2019
|
Duchenne muscular dystrophy Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Duchenne muscular dystrophy from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Duchenne muscular dystrophy MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Duchenne muscular dystrophy MRI |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Duchenne muscular dystrophy MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Fahimeh Shojaei, M.D.
Overview
Lower limb MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Findings on MRI suggestive of Duchenne muscular dystrophy include high T1-weighted signal in affected muscles.
MRI
Lower limb MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Findings on MRI suggestive of Duchenne muscular dystrophy include:[1]
- High T1-weighted signal in affected muscles such as:
References
- ↑ Schreiber, A.; Smith, W. L.; Ionasescu, V.; Zellweger, H.; Franken, E. A.; Dunn, V.; Ehrhardt, J. (1987). "Magnetic resonance imaging of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy". Pediatric Radiology. 17 (6): 495–497. doi:10.1007/BF02388288. ISSN 0301-0449.