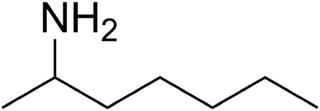
Tuaminoheptane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Heptan-2-amine[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 879: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 879: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | tuamine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H17N | |
| Molar mass | 115.22 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Tuaminoheptane |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Tuaminoheptane Most cited articles on Tuaminoheptane |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Tuaminoheptane |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Tuaminoheptane at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Tuaminoheptane Clinical Trials on Tuaminoheptane at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Tuaminoheptane NICE Guidance on Tuaminoheptane
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Tuaminoheptane Discussion groups on Tuaminoheptane Patient Handouts on Tuaminoheptane Directions to Hospitals Treating Tuaminoheptane Risk calculators and risk factors for Tuaminoheptane
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Tuaminoheptane |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Tuaminoheptane (or tuamine) is a nasal decongestant drug which is a sympathomimetic stimulant and vasoconstrictor.[2] However, it can cause skin irritation,[3] which limits its usefulness as a nasal decongestant. Oral preparations were once available, but are no longer produced. Side effects associated with the use of tuaminoheptane can include shortness of breath, tachycardia and hypertension.
Tuaminoheptane is on the 2011 list of prohibited substances published by the World Anti-Doping Agency.
See also
References
- ↑ "tuamine - Compound Summary". USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ↑ Delicado, E. G.; Fideu, M. D.; Miras-Portugal, M. T.; Pourrias, B.; Aunis, D. (1990). "Effect of tuamine, heptaminol and two analogues on uptake and release of catecholamines in cultured chromaffin cells". Biochemical Pharmacology. 40 (4): 821–825. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(90)90322-C. PMID 2386550.
- ↑ Raoux, M.; Colomban, C.; Delmas, P.; Crest, M. (2007). "The amine-containing cutaneous irritant heptylamine inhibits the volume-regulated anion channel and mobilizes intracellular calcium in normal human epidermal keratinocytes". Molecular Pharmacology. 71 (6): 1685–1694. doi:10.1124/mol.106.033324. PMID 17384225.
- Pages with script errors
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Chemical articles with multiple CAS registry numbers
- Chemical articles with multiple PubChem CIDs
- Articles without InChI source
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chembox having DSD data
- Chembox having GHS data
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Stimulants
- Amines
- Drug