Renal tubular acidosis
|
Renal tubular acidosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Renal tubular acidosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Renal tubular acidosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Renal tubular acidosis |
| Renal tubular acidosis | |
 | |
|---|---|
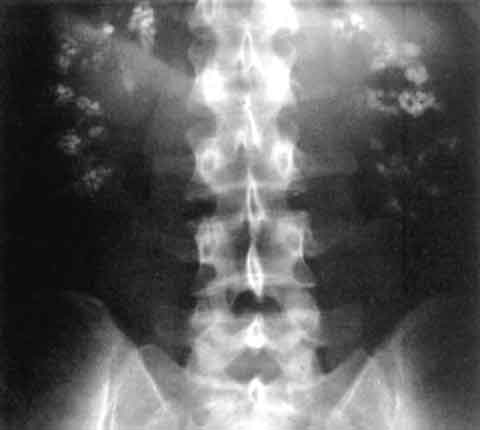
| Significant bilateral nephrocalcinosis (calcification of the kidneys) on a frontal X-ray (radiopacities (white) in the right upper and left upper quadrant of the image), as seen in distal renal tubular acidosis. | |
| ICD-10 | N25.8 |
| ICD-9 | 588.89 |
| OMIM | 179800 |
| DiseasesDB | 11687 Template:DiseasesDB2 Template:DiseasesDB2 |
| MeSH | D000141 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2] ; Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [3] Syed Ahsan Hussain, M.D.[4] Jogeet Singh Sekhon, M.D. [5]
For patient information, click here
Synonyms and keywords: RTA
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Renal tubular acidosis from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnostic study of choice | History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Electrocardiogram | X-Ray Findings | Echocardiography and Ultrasound | CT-Scan Findings | MRI Findings | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies