Volvulus
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
| Volvulus | |
 | |
|---|---|
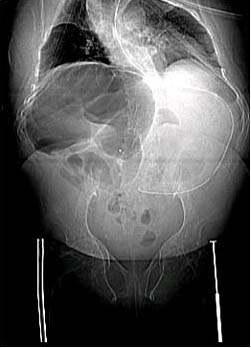
| CECAL VOLVULUS 27 year old female with osteogenesis imperfecta. Patient is complaining of abdominal pain. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology | |
| ICD-10 | K56.2 |
| ICD-9 | 537.3, 560.2 |
| DiseasesDB | 13996 |
| eMedicine | ped/2415 |
| MeSH | D045822 |
Template:Search infobox A volvulus is a loop of the bowel whose nose has twisted on itself.[1] The American Heritage Stedman's Medical Dictionary defines volvulus slightly differently as "abnormal twisting of the intestine causing obstruction," which adds obstruction in the definition, and would be more clinically significant term.[2]
Types
- Gastric volvulus (click on the link in blue to read more about this specific type of volvulus)
- Volvulus Neonatorum
- Volvulus Small Intestine
- Volvulus Caecum
- Volvulus Sigmoid Colon
Causes
Midgut volvulus occurs in patients (usually in infants) that are predisposed because of congenital intestinal malrotation. Segmental volvulus occurs in patients of any age, usually with a predisposition because of abnormal intestinal contents (e.g. meconium ileus) or adhesions. Volvulus of the cecum, transverse colon, or sigmoid colon occurs, usually in adults, with only minor predisposing factors such as redundant (excess, inadequately supported) intestinal tissue and constipation.
Presentation
Regardless of cause, volvulus causes symptoms by two mechanisms. One is bowel obstruction, manifested as abdominal distension and vomiting. The other is ischemia (loss of blood flow) to the affected portion of intestine. This causes severe pain and progressive injury to the intestinal wall, with accumulation of gas and fluid in the portion of the bowel obstructed.[3] Ultimately, this can result in necrosis of the affected intestinal wall, acidosis, and death. Acute volvulus therefore requires immediate surgical intervention to untwist the affected segment of bowel and possibly resect any unsalvageable portion.[4]
Volvulus occurs most frequently in middle-aged and elderly men.[5] Volvulus can also arise as a rare complication in persons with redundant colon, a normal anatomic variation resulting in extra colonic loops.[6]
Sigmoid volvulus is the most-common form of volvulus of the gastrointestinal tract and is responsible for 8% of all intestinal obstructions. Sigmoid volvulus is particularly common in elderly persons and constipated patient. Patients experience abdominal pain, distension, and absolute constipation.
Associated conditions
The volvulus can also occur in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to the smooth muscle dysfunction.
Investigations
Treatment
- Laparotomy
- Untwisting
- Transduodenal band of ladd is divided
See also
References
- ↑ Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005
- ↑ The American Heritage Stedman's Medical Dictionary. "KMLE Medical Dictionary Definition of volvulus".
- ↑ Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005
- ↑ Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005
- ↑ Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005
- ↑ Mayo Clinic Staff (2006-10-13). "Redundant colon: A health concern?". Ask a Digestive System Specialist. MayoClinic.com. Retrieved 2007-06-11.
Additional Resources
Template:SIB Template:Gastroenterology
Template:Skin and subcutaneous tissue symptoms and signs Template:Nervous and musculoskeletal system symptoms and signs Template:Urinary system symptoms and signs Template:Cognition, perception, emotional state and behaviour symptoms and signs Template:Speech and voice symptoms and signs Template:General symptoms and signs