|
|
| Line 44: |
Line 44: |
| <gallery perRow="5"> | | <gallery perRow="5"> |
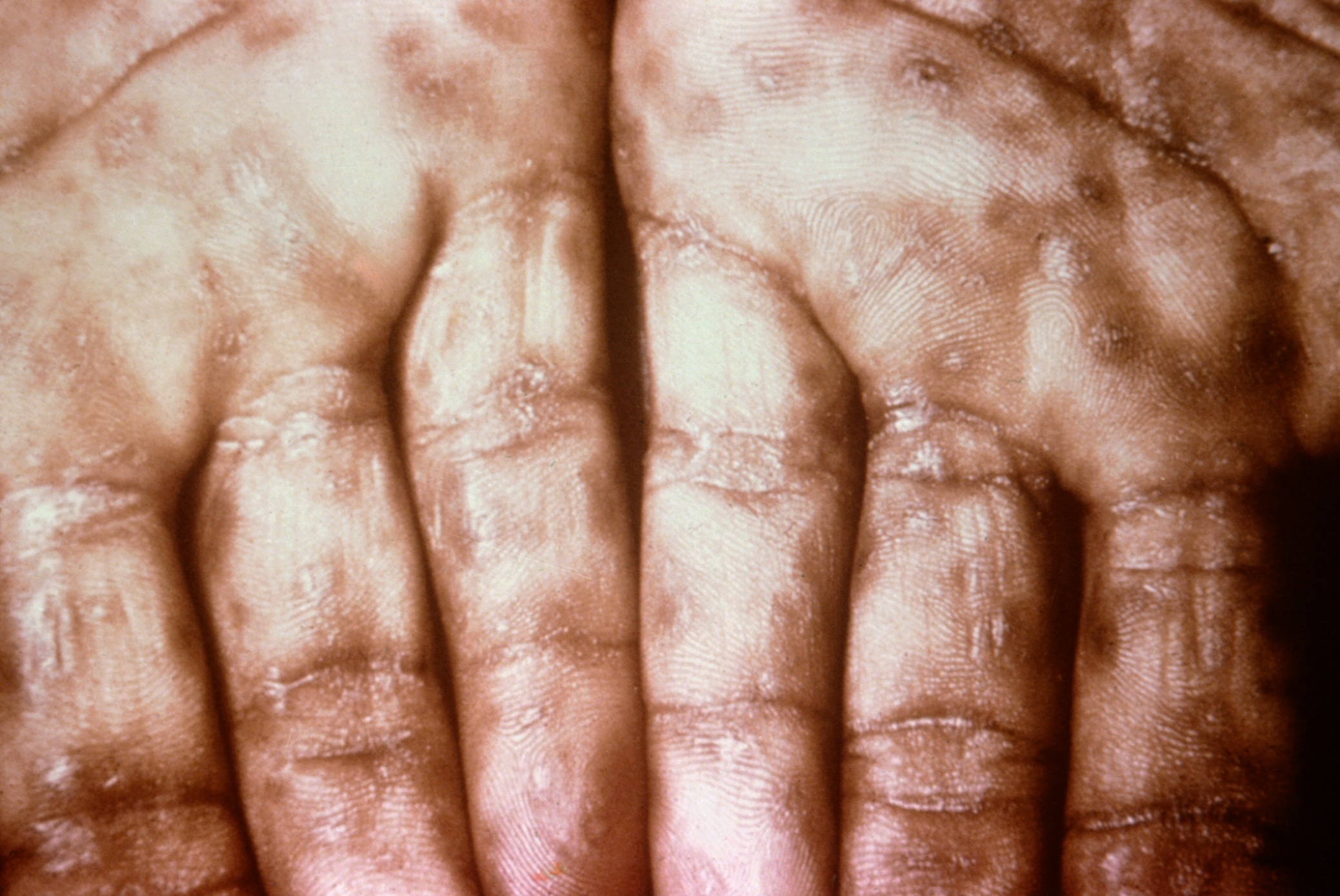
| Image:Secondary Syphilis on palms CDC 6809 lores rsh.jpg|Typical presentation of secondary syphilis rash on the palms of the hands and usually also seen on soles of feet | | Image:Secondary Syphilis on palms CDC 6809 lores rsh.jpg|Typical presentation of secondary syphilis rash on the palms of the hands and usually also seen on soles of feet |
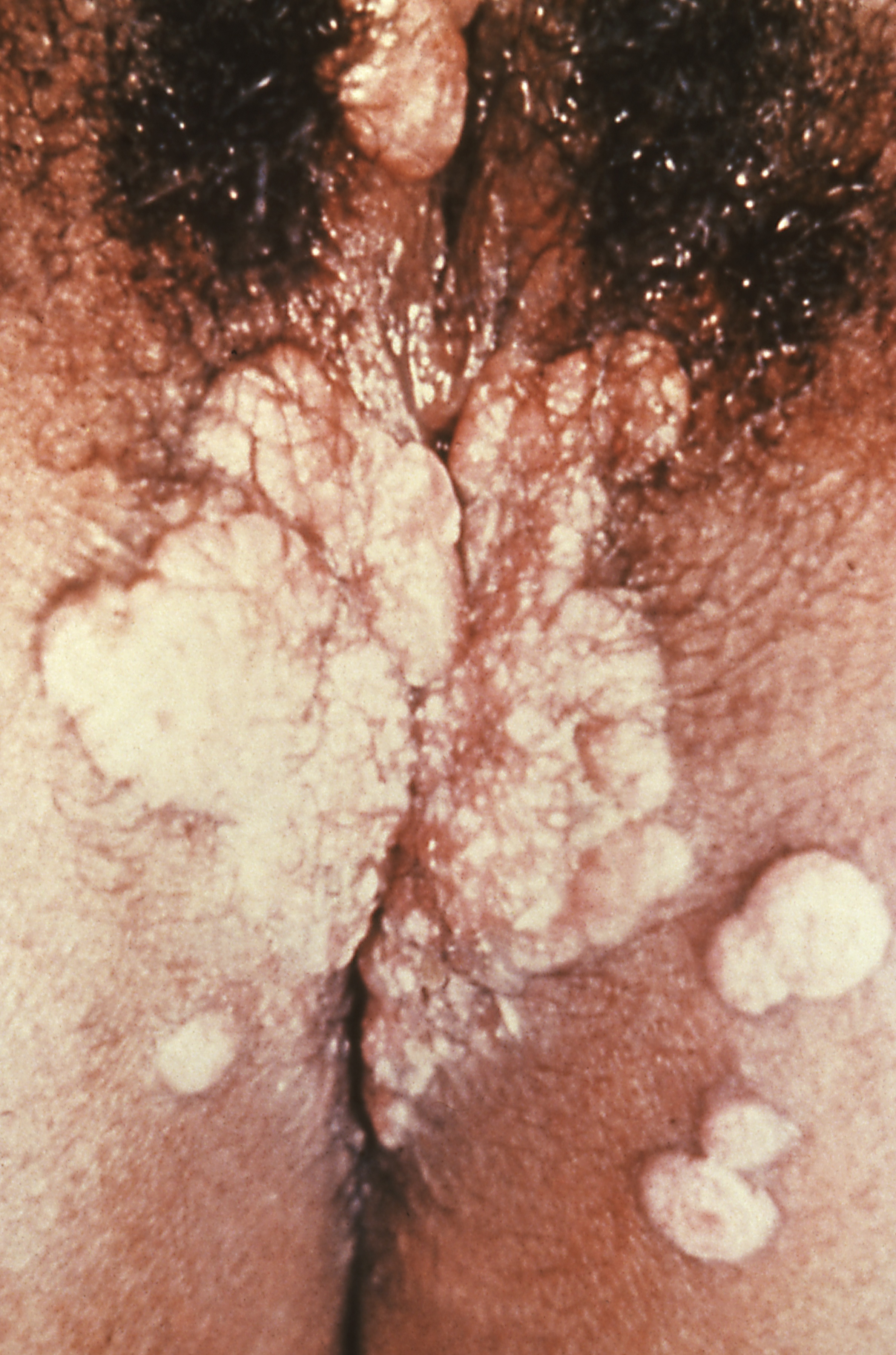
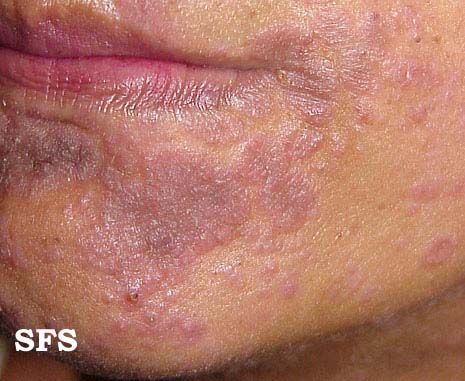
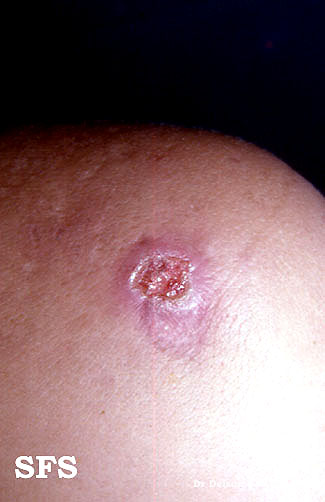
| Image:Syphilis secondary 08.jpeg|Secondary syphilis | | Image:Vaginal syphilis (disturbing image).jpg|Secondary syphilis manifested perineal condylomata lata lesions |
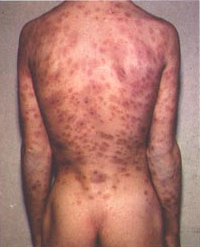
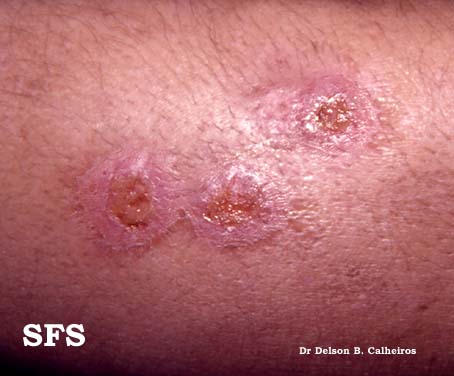
| Image:Syphilis lesions on back.jpg|Syphilis lesions on a patient's back | | Image:Syphilis lesions on back.jpg|Syphilis lesions on a patient's back |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 15.jpeg|Condymoata lata | | Image:Syphilis secondary 15.jpeg|Condymoata lata |
| Line 78: |
Line 78: |
| :*Cutaneous gumma: indurated, nodular, papulosquamous to ulcerative lesions with peripheral hyperpigmentation. | | :*Cutaneous gumma: indurated, nodular, papulosquamous to ulcerative lesions with peripheral hyperpigmentation. |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| ===Primary syphilis: Chancre===
| |
| *Afebrile
| |
|
| |
| *Chancre:
| |
| :*Single painless papule which rapidly progresses an ulcerated, indurated lesion with a surrounding red [[areola]].
| |
| :*Usually located on the [[penis]], [[cervix]], [[labia]], anal canal, [[rectum]], or [[oral cavity]].
| |
| :*Highly infectious lesion.
| |
|
| |
| *Regional [[lymphadenopathy]] accompanies primary lesion.
| |
| :*Onset within a week.
| |
| :*Unilateral or bilateral.
| |
| :*[[Lymph node]]s are firm, painless, non-tender and non-suppurative.
| |
|
| |
| *Primary [[chancre]] heals spontaneously within 4-6 weeks; however, regional lymphadenopathy may persist for longer periods.
| |
|
| |
| <gallery>
| |
|
| |
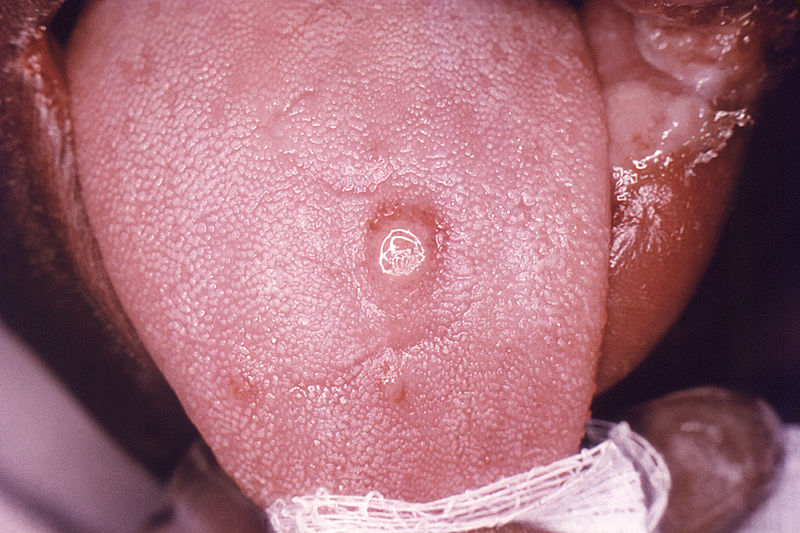
| File:800px-Primary stage syphilis sore (chancre) on the surface of a tongue-CDC.jpg| Primary stage syphilis sore (chancre) on the surface of a tongue.
| |
|
| |
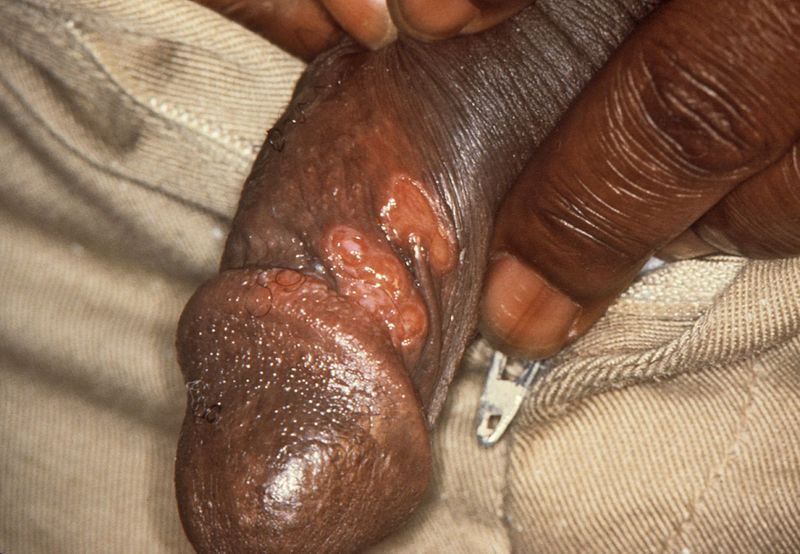
| File:800px-Chancres on the penile shaft due to a primary syphilitic infection caused by Treponema pallidum 6803 lores.jpg|Chancres on the penile shaft due to a primary syphilitic infection
| |
|
| |
| File:Chancre-penile-1.jpg|Primary stage syphilis sore (chancre) on glans (head) of the penis.
| |
|
| |
| File:Syphilis primary chancre 01.jpeg| Syphilis primary chancre.
| |
| File:Syphilis primary chancre 02.jpeg| Syphilis primary chancre.
| |
|
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| <gallery perRow="5">
| |
| Image:Secondary Syphilis on palms CDC 6809 lores rsh.jpg|Typical presentation of secondary syphilis rash on the palms of the hands and usually also seen on soles of feet
| |
|
| |
| Image:condyoma lata (syphilis secondary).jpg|Condyoma lata (syphilis secondary)
| |
|
| |
| Image:TreponemaPallidum.jpg|Electron micrograph of Treponema pallidum
| |
|
| |
| Image:Syphilis lesions on back.jpg|Syphilis lesions on a patient's back
| |
|
| |
| Image:Syphilis lesions on chest.jpg|Syphilis lesions on a patient's chest
| |
|
| |
| Image:Penis syphilis.png|Chancres on the penile shaft due to a primary syphilitic infection
| |
|
| |
| Image:Vaginal syphilis (disturbing image).jpg|Secondary syphilis manifested perineal condylomata lata lesions, which presented as gray, raised papules that sometimes appear on the vulva or near the anus, or in any other warm intertriginous region.
| |
|
| |
| Image:Gumma of nose due to a long standing tertiary syphilitic Treponema pallidum infection 5330 lores.jpg|Gumma of the nose due to long standing tertiary syphilis
| |
|
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 01.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 02.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 03.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 04.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 05.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 06.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 07.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 08.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 09.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 10.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 11.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 12.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 13.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 14.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 15.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 16.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 17.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 18.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 19.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 20.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 21.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 22.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 23.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 24.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 25.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 26.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 27.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 28.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 29.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 30.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 31.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 32.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 33.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 34.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 35.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 36.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 37.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 38.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 39.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 40.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 41.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 42.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 44.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
| Image:Syphilis secondary 45.jpeg|Secondary syphilis
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| </gallery>
| |
|
| |
| ===Tertiary syphilis: Gumma===
| |
| *[[Gumma]]:
| |
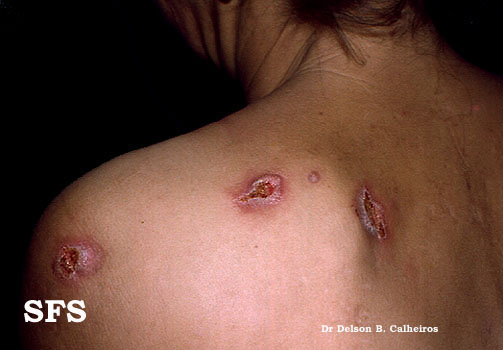
| :*Soft, asymmetric, coalscent [[granuloma|granulomatous]] lesion
| |
| :*Solitary lesions less than a centimeter in diameter
| |
| :*Appear almost anywhere in the body including in the skeleton
| |
| :*Cutaneous gumma: indurated, nodular, papulosquamous to ulcerative lesions with peripheral hyperpigmentation
| |
|
| |
| <gallery> | | <gallery> |
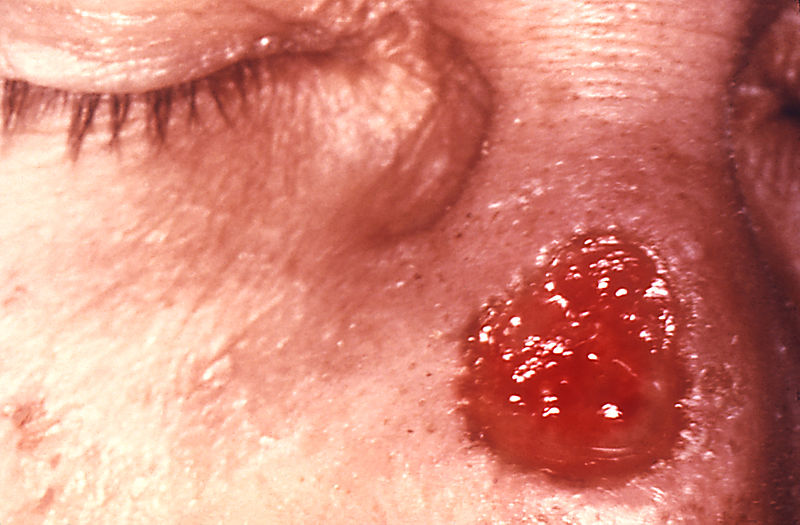
| File:800px-Gumma of nose due to a long standing tertiary syphilitic Treponema pallidum infection 5330 lores.jpg|A gumma of nose due to a long standing tertiary syphilitic Treponema pallidum infection. | | File:800px-Gumma of nose due to a long standing tertiary syphilitic Treponema pallidum infection 5330 lores.jpg|A gumma of nose due to a long standing tertiary syphilitic Treponema pallidum infection. |
| Line 188: |
Line 86: |
| Image:Syphilis tertiary 03.jpeg| Tertiary syphilis | | Image:Syphilis tertiary 03.jpeg| Tertiary syphilis |
| </gallery> | | </gallery> |
| *Cardiovascular manifestation secondary to aortic dilation with resultant [[Aortic insufficiency physical findings|aortic regurgitation]]:
| | |- |
| :*[[Diastolic murmur]]
| | |} |
| :*[[De Musset's sign]]<ref>{{cite journal | author=Sapira JD | title="Quincke, de Musset, Duroziez, and Hill: some aortic regurgitations" | journal=South Med J. | date=1981 Apr | volume=74 | issue=4 | pages=459-67 }}</ref> a bobbing of the head that de Musset first noted in Parisian prostitutes
| |
| | |
| *Neurological manifestation:
| |
| :*Asymptomatic meningitis
| |
| ::*Asymptomatic neurosyphilis usually has no signs or symptoms and is diagnosed exclusively with the presence of CSF abnormalities notably pleocytosis, elevated protein, decreased glucose or a positive VDRL test.
| |
| | |
| :*Symptomatic meningitis
| |
| ::*Develops within 6-months to several years of primary infection
| |
| ::*Typical meningitis symptoms present
| |
| ::*Cranial nerve abnormalities may be observed
| |
| | |
| :*Meningovascular syphilis
| |
| ::*Occurs a few months to 10 years (average, 7 years) after the primary infection
| |
| ::*Associated with [[prodromal]] symptoms lasting weeks to months before focal deficits are identifiable
| |
| ::*Focal deficits initially are intermittent or progress slowly over a few days
| |
| ::*Clinical present with CNS vascular insufficiency or [[stroke]] involving the middle cerebral artery
| |
| | |
| :*Parenchymatous neurosyphilis
| |
| ::*Develops 15-20 years after primary infection
| |
| ::*Clinical presents as [[general paresis]] or [[tabes dorsalis]] with resultant [[ataxia]]
| |
| ::*[[Argyll Robertson pupil]]: small irregular pupil
| |
| | |
| ===Ophthalmic Examination===
| |
| *Slit-lamp examination and ophthalmic examination may be helpful to differentiate between acquired and congenital syphilis.
| |
| | |
| *Presence of [[interstitial keratitis]] is suggestive of [[congenital syphilis]] with latent infection of unknown duration.
| |
| | |
| ===Clinical pearl: Syphilis detecting Handshake===
| |
| {{#ev:youtube|SAedwyzTMWA}}
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| Line 226: |
Line 95: |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |
|
| |
|
| [[Category:Disease]]
| | |
| [[Category:Gynecology]] | | [[Category:Gynecology]] |
| [[Category:Infectious disease]] | | [[Category:Infectious disease]] |
| [[Category:Primary care]] | | [[Category:Primary care]] |
| [[Category:Bacterial diseases]]
| |
| [[Category:Sexually transmitted diseases]]
| |
| [[Category:Needs overview]]
| |