Medetomidine hydrochloride
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Medetomidine hydrochloride is {{{aOrAn}}} sedative that is FDA approved for the procedure of sedation of non-intubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures.. Common adverse reactions include {{{adverseReactions}}}.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
None
Warnings
Drug Administration
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection should be administered only by persons skilled in the management of patients in the operating room setting. Due to the known pharmacological effects of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, patients should be continuously monitored while receiving dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection.
Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Sinus Arrest
Clinically significant episodes of bradycardia and sinus arrest have been reported with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection administration in young, healthy adult volunteers with high vagal tone or with different routes of administration including rapid intravenous or bolus administration.
Reports of hypotension and bradycardia have been associated with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection infusion. If medical intervention is required, treatment may include decreasing or stopping the infusion of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, increasing the rate of intravenous fluid administration, elevation of the lower extremities, and use of pressor agents. Because dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has the potential to augment bradycardia induced by vagal stimuli, clinicians should be prepared to intervene. The intravenous administration of anticholinergic agents (e.g., glycopyrrolate, atropine) should be considered to modify vagal tone. In clinical trials, glycopyrrolate or atropine were effective in the treatment of most episodes of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride-induced bradycardia. However, in some patients with significant cardiovascular dysfunction, more advanced resuscitative measures were required.
Caution should be exercised when administering dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection to patients with advanced heart block and/or severe ventricular dysfunction. Because dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection decreases sympathetic nervous system activity, hypotension and/or bradycardia may be expected to be more pronounced in patients with hypovolemia, diabetes mellitus, or chronic hypertension and in elderly patients.
In clinical trials where other vasodilators or negative chronotropic agents were coadministered with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection an additive pharmacodynamic effect was not observed. Nonetheless, caution should be used when such agents are administered concomitantly with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection.
Transient Hypertension
Transient hypertension has been observed primarily during the loading dose in association with the initial peripheral vasoconstrictive effects of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. Treatment of the transient hypertension has generally not been necessary, although reduction of the loading infusion rate may be desirable.
Arousability
Some patients receiving dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection have been observed to be arousable and alert when stimulated. This alone should not be considered as evidence of lack of efficacy in the absence of other clinical signs and symptoms.
Withdrawal
Procedural Sedation
In adult subjects, withdrawal symptoms were not seen after discontinuation of short term infusions of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection (< 6 hours).
Tolerance and Tachyphylaxis
Use of dexmedetomidine beyond 24 hours has been associated with tolerance and tachyphylaxis and a dose related increase in adverse reactions.
Hepatic Impairment
Since dexmedetomidine clearance decreases with severity of hepatic impairment, dose reduction should be considered in patients with impaired hepatic function
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has been associated with the following serious adverse reactions:
- Hypotension, bradycardia and sinus arrest.
- Transient hypertension
- Most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions, occurring in greater than 2% of patients in procedural sedation studies include hypotension, bradycardia and dry mouth.
Procedural Sedation
Adverse reaction information is derived from the two trials for procedural sedation in which 318 adult patients received dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. The mean total dose was 1.6 mcg/kg (range: 0.5 to 6.7), mean dose per hour was 1.3 mcg/kg/hr (range: 0.3 to 6.1) and the mean duration of infusion of 1.5 hours (range: 0.1 to 6.2). The population was between 18 to 93 years of age, 30% ≥ 65 years of age, 52% male and 61% Caucasian.
Treatment-emergent adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of > 2% are provided in Table 2. The most frequent adverse reactions were hypotension, bradycardia, and dry mouth. Pre-specified criteria for the vital signs to be reported as adverse reactions are footnoted below the table. The decrease in respiratory rate and hypoxia was similar between dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and comparator groups in both studies.

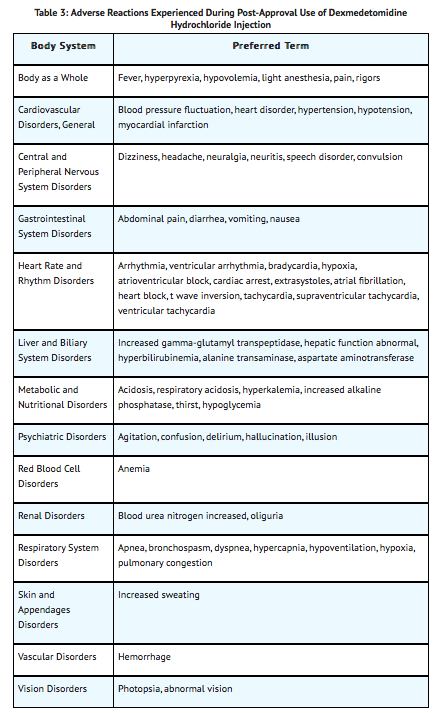
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypotension and bradycardia were the most common adverse reactions associated with the use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection during post approval use of the drug.
Drug Interactions
Anesthetics, Sedatives, Hypnotics, Opioids
Coadministration of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection with anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, and opioids is likely to lead to an enhancement of effects. Specific studies have confirmed these effects with sevoflurane, isoflurane, propofol, alfentanil, and midazolam. No pharmacokinetic interactions between dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and isoflurane, propofol, alfentanil and midazolam have been demonstrated. However, due to possible pharmacodynamic interactions, when coadministered with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection or the concomitant anesthetic, sedative, hypnotic or opioid may be required.
Neuromuscular Blockers
In one study of ten healthy adult volunteers, administration of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection for 45 minutes at a plasma concentration of one ng/mL resulted in no clinically meaningful increases in the magnitude of neuromuscular blockade associated with rocuronium administration
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C There are no adequate and well controlled studies of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection use in pregnant women. In an in vitro human placenta study, placental transfer of dexmedetomidine occurred. In a study in the pregnant rat, placental transfer of dexmedetomidine was observed when radiolabeled dexmedetomidine was administered subcutaneously. Thus, fetal exposure should be expected in humans, and dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus.
Teratogenic effects were not observed in rats following subcutaneous administration of dexmedetomidine during the period of fetal organogenesis (from gestation day 5 to 16) with doses up to 200 mcg/kg (representing a dose approximately equal to the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on body surface area) or in rabbits following intravenous administration of dexmedetomidine during the period of fetal organogenesis (from gestation day 6 to 18) with doses up to 96 mcg/kg (representing approximately half the human exposure at the maximum recommended dose based on plasma area under the time-curve comparison). However, fetal toxicity, as evidenced by increased post-implantation losses and reduced live pups, was observed in rats at a subcutaneous dose of 200 mcg/kg. The no-effect dose in rats was 20 mcg/kg (representing a dose less than the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on a body surface area comparison). In another reproductive toxicity study when dexmedetomidine was administered subcutaneously to pregnant rats at 8 and 32 mcg/kg (representing a dose less than the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on a body surface area comparison) from gestation day 16 through weaning, lower offspring weights were observed. Additionally, when offspring of the 32 mcg/kg group were allowed to mate, elevated fetal and embryocidal toxicity and delayed motor development was observed in second generation offspring.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Medetomidine hydrochloride in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
The safety of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection during labor and delivery has not been studied.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Radiolabeled dexmedetomidine administered subcutaneously to lactating female rats was excreted in milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy have not been established for Procedural Sedation in pediatric patients. Additional information describing clinical studies in a different indication in which efficacy was not demonstrated in pediatric patients is approved for Hospira’s dexmedetomidine injection. However, due to Hospira’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information. The use of dexmedetomidine for procedural sedation in pediatric patients has not been evaluated.
Geriatic Use
A total of 131 patients in the clinical studies were 65 years of age and over. A total of 47 patients were 75 years of age and over. Hypotension occurred in a higher incidence in dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection-treated patients 65 years or older (72%) and 75 years or older (74%) as compared to patients < 65 years (47%). A reduced loading dose of 0.5 mcg/kg given over 10 minutes is recommended and a reduction in the maintenance infusion should be considered for patients greater than 65 years of age.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Medetomidine hydrochloride with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Medetomidine hydrochloride with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
Since dexmedetomidine clearance decreases with increasing severity of hepatic impairment, dose reduction should be considered in patients with impaired hepatic function.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Medetomidine hydrochloride in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Medetomidine hydrochloride and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Medetomidine hydrochloride |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Medetomidine hydrochloride |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Medetomidine hydrochloride interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Medetomidine hydrochloride Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.