Kidney stone physical examination: Difference between revisions
(→Heart) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
===Heart=== | ===Heart=== | ||
{| align="right" | {| align="right" | ||
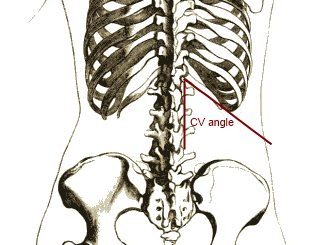
|[[File:CVangle.png|thumb|200px|Costovertebral angle -By Brainmachine, Source:Wikimedia commons<ref> https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=19887470</ref>]] | |[[File:CVangle.png|thumb|200px|Costovertebral angle -By Brainmachine, Source:Wikimedia commons<ref>https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=19887470</ref>]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
===Back=== | ===Back=== | ||
* Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally depending upon sides involved. | * [[Costovertebral angle|Costovertebral angle tenderness]](Murphy's punch sign, Pasternacki's sign, or Goldflam's sign) bilaterally/unilaterally depending upon sides involved. | ||
===Genitourinary=== | ===Genitourinary=== | ||
* | * [[Hematuria]] | ||
===Neuromuscular=== | ===Neuromuscular=== | ||
* Neuromuscular examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal. | * Neuromuscular examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal. | ||
Revision as of 19:39, 7 June 2018
|
Kidney stone Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Kidney stone physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Kidney stone physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Kidney stone physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance]. Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
Common physical examination findings of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually remarkable for
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with nephrolithiasis usually appear in pain.
- Patients tend to move constantly in order to achieve a comfortable position.
Vital Signs
- High-grade / low-grade fever.
- Tachycardia with regular pulse can be seen secondary to pain.
- Tachypnea can be seen.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
HEENT
- HEENT examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
Heart
 |
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
Abdomen
- Hypoactive bowel sounds as seen in ileus due to severe pain
- Additional findings, such as obturator test, psoas test, McBurney point test, Murphy test
Back
- Costovertebral angle tenderness(Murphy's punch sign, Pasternacki's sign, or Goldflam's sign) bilaterally/unilaterally depending upon sides involved.
Genitourinary
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.
Extremities
- Extremities examination of patients with nephrolithiasis is usually normal.