J chain: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
m (Bot: HTTP→HTTPS) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox_gene}} | |||
[[Image:IgM.png|thumb|Immunoglobulin M (IgM) [[pentamer]]ic antibody molecule (consisting of five base units).<br />1: Base unit. <br />2: [[Immunoglobulin heavy chain|Heavy chain]]s.<br />3: [[Immunoglobulin light chain|Light chain]]s.<br />4: '''J chain'''.<br />5: Intermolecular disulfide bonds.]] | |||
[[Image:Dimeric IgA schematic 01.svg|thumb|right|180 px|Schematic of immunoglobulin A [[protein dimer|dimer]] showing [[H-chain]] (blue), [[Immunoglobulin light chain|L-chain]] (red), '''[[J-chain]] (magenta)''' and [[secretory component]] (yellow).]] | |||
A '''J chain''' is a protein component of the [[antibodies]] [[IgM]] and [[IgA]].<ref name="Levinson Microbiology">{{cite book | publisher = McGrawHill | title = Medical Microbiology and Immunology | author = Levinson | edition = 11 | pages= 405–6}}</ref> It is a 137 [[amino acid|residue]] polypeptide,<ref name=Paul0804/> encoded by the ''IGJ'' [[gene]].<ref name="pmid3016707">{{cite journal |vauthors=Max EE, McBride OW, Morton CC, Robinson MA | title = Human J chain gene: chromosomal localization and associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms | journal = Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | volume = 83 | issue = 15 | pages = 5592–6 |date=Sep 1986 | pmid = 3016707 | pmc = 386334 | doi =10.1073/pnas.83.15.5592 }}</ref><ref name="pmid2984306">{{cite journal |vauthors=Max EE, Korsmeyer SJ | title = Human J chain gene. Structure and expression in B lymphoid cells | journal = J Exp Med | volume = 161 | issue = 4 | pages = 832–49 |date=May 1985 | pmid = 2984306 | pmc = 2189063 | doi =10.1084/jem.161.4.832 }}</ref><ref name="entrez">{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: IGJ immunoglobulin J polypeptide, linker protein for immunoglobulin alpha and mu polypeptides| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3512| accessdate = }}</ref> | |||
==Structure== | |||
The J Chain's molecular weight is approximately 15 kDa. It exhibits a standard [[immunoglobulin]] folding structure of two β-pleated sheets of four ribbons folded against one another. It has 8 [[cystine]] residues. Two of these residues link the [[Immunoglobulin heavy chain|α chains]] of [[IgA]] or the [[Immunoglobulin heavy chain|μ chains]] of [[IgM]] via [[disulfide bridge]]s, effectively serving as the "glue" between two Fc regions of the antibody.<ref name=Paul0831>{{cite book |last1=Kiyono |first1=Hiroshi |last2=Kunisawa |first2=Jaw |last3=McGhee |first3=Jerry |last4=Mestecky |first4=Jiri |editor1-first=William |editor1-last=Paul |title=Fundamental Immunology |type=Book |edition=6th |year=2008 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Philadelphia, PA |isbn=0-7817-6519-6 |pages=983–1030 |chapter=Chapter 31: The Mucosal Immune System}}</ref> | |||
The J-chain shows a large degree of homology between avian and human species, suggesting that it serves an important function.<ref name=Paul0831/> | |||
==Function== | |||
{{ | The J Chain is required for IgM or IgA to be secreted into mucosa.<ref name=Paul0804>{{cite book |last1=Schroeder |first1=Harry |last2=Wald |first2=David |last3=Greenspan |first3=Neil |editor1-first=William |editor1-last=Paul |title=Fundamental Immunology |type=Book |edition=6th |year=2008 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Philadelphia, PA |isbn=0-7817-6519-6 |pages=125–151 |chapter=Chapter 4: Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function}}</ref> As part of a polymeric immunoglobulin (pIg), the J-chain is essential for binding of pIg to the [[polymeric immunoglobulin receptor|pIgR]], which forms the [[secretory component]] upon excretion of the secretory pIg by epithelial cells.<ref name="Johansen2000">{{cite journal |vauthors=Johansen FE, Braathen R, Brandtzaeg P | title = Role of J Chain in Secretory Immunoglobulin Formation | journal = Scandinavian Journal of Immunology | volume = 52 | issue = 3 | pages = 240-248 |date=September 2000 | pmid = 10972899 | doi =10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00790.x }}</ref> This binding facilitates transport of the J-chain positive pIg molecules from the basal to the apical sides of epithelial cells. | ||
Because IgM and IgA are the only two types of antibody that [[polymerize]], initial hypotheses stated that J chain was required for polymerization. However, it was subsequently found that IgM is able to polymerize in the absence of J chain as both a [[pentamer]] and a [[hexamer]], however, both of these exist to lesser numbers in organisms lacking J chains. In such cases, there are also fewer IgA dimers.<ref name=Paul0804/> | |||
{{ | The J-chain also plays a role in the activation of complement. J-chain negative IgM hexamers are 15-20 times more effective at activating [[complement system|complement]] than J-chain positive IgM pentamers.<ref name="Johansen2000"/> A consequence of this lack of complement activation is it allows J-chain positive pIgM to bind antigens without causing excessive damage to epithelial membranes through complement activation. | ||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
==Further reading== | |||
{{refbegin | 2}} | |||
{{PBB_Further_reading | |||
| citations = | |||
*{{cite journal | author=Koshland ME |title=The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain. |journal=Annu. Rev. Immunol. |volume=3 |issue= |pages= 425–53 |year= 1986 |pmid= 2415140 |doi= 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Tartakoff A, Vassalli P |title=Plasma cell immunoglobulin M molecules. Their biosynthesis, assembly, and intracellular transport. |journal=J. Cell Biol. |volume=83 |issue= 2 Pt 1 |pages= 284–99 |year= 1980 |pmid= 115892 |doi=10.1083/jcb.83.2.284 | pmc=2111544 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Mole JE, Bhown AS, Bennett JC |title=Primary structure of human J chain: alignment of peptides from chemical and enzymatic hydrolyses. |journal=Biochemistry |volume=16 |issue= 16 |pages= 3507–13 |year= 1977 |pmid= 407930 |doi=10.1021/bi00635a002 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Bastian A, Kratzin H, Eckart K, Hilschmann N |title=Intra- and interchain disulfide bridges of the human J chain in secretory immunoglobulin A. |journal=Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler |volume=373 |issue= 12 |pages= 1255–63 |year= 1993 |pmid= 1292512 |doi= 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.1255}} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Frutiger S, Hughes GJ, Paquet N, etal |title=Disulfide bond assignment in human J chain and its covalent pairing with immunoglobulin M. |journal=Biochemistry |volume=31 |issue= 50 |pages= 12643–7 |year= 1993 |pmid= 1472500 |doi=10.1021/bi00165a014 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Moro I, Iwase T, Komiyama K, etal |title=Immunoglobulin A (IgA) polymerization sites in human immunocytes: immunoelectron microscopic study. |journal=Cell Struct. Funct. |volume=15 |issue= 2 |pages= 85–91 |year= 1990 |pmid= 2113434 |doi=10.1247/csf.15.85 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Alberini CM, Bet P, Milstein C, Sitia R |title=Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents. |journal=Nature |volume=347 |issue= 6292 |pages= 485–7 |year= 1990 |pmid= 2120591 |doi= 10.1038/347485a0 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Sumi Y, Nagura H, Kaneda T, Oka T |title=Immunoelectron microscopical localization of immunoglobulins, secretory component and J chain in the human minor salivary glands. |journal=J. Oral Pathol. |volume=17 |issue= 8 |pages= 390–5 |year= 1989 |pmid= 3146624 |doi=10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01303.x }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Hajdu I, Moldoveanu Z, Cooper MD, Mestecky J |title=Ultrastructural studies of human lymphoid cells. mu and J chain expression as a function of B cell differentiation. |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=158 |issue= 6 |pages= 1993–2006 |year= 1984 |pmid= 6417260 |doi=10.1084/jem.158.6.1993 | pmc=2187181 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Yasuda N, Kanoh T, Uchino H |title=J chain synthesis in human myeloma cells: light and electron microscopic studies. |journal=Clin. Exp. Immunol. |volume=40 |issue= 3 |pages= 573–80 |year= 1980 |pmid= 6774844 |doi= | pmc=1538946 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Harper SJ, Allen AC, Béné MC, etal |title=Increased dimeric IgA-producing B cells in tonsils in IgA nephropathy determined by in situ hybridization for J chain mRNA. |journal=Clin. Exp. Immunol. |volume=101 |issue= 3 |pages= 442–8 |year= 1995 |pmid= 7664491 |doi= 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03132.x| pmc=1553245 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Iwase T, Saito I, Takahashi T, etal |title=Early expression of human J chain and mu chain gene in the fetal liver. |journal=Cell Struct. Funct. |volume=18 |issue= 5 |pages= 297–302 |year= 1994 |pmid= 8168154 |doi=10.1247/csf.18.297 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Harper SJ, Pringle JH, Wicks AC, etal |title=Expression of J chain mRNA in duodenal IgA plasma cells in IgA nephropathy. |journal=Kidney Int. |volume=45 |issue= 3 |pages= 836–44 |year= 1994 |pmid= 8196286 |doi=10.1038/ki.1994.110 }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Bjercke S, Brandtzaeg P |title=Glandular distribution of immunoglobulins, J chain, secretory component, and HLA-DR in the human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. |journal=Hum. Reprod. |volume=8 |issue= 9 |pages= 1420–5 |year= 1994 |pmid= 8253928 |doi= }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Bertrand FE, Billips LG, Gartland GL, etal |title=The J chain gene is transcribed during B and T lymphopoiesis in humans. |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=156 |issue= 11 |pages= 4240–4 |year= 1996 |pmid= 8666793 |doi= }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Atkin JD, Pleass RJ, Owens RJ, Woof JM |title=Mutagenesis of the human IgA1 heavy chain tailpiece that prevents dimer assembly. |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=157 |issue= 1 |pages= 156–9 |year= 1996 |pmid= 8683109 |doi= }} | |||
*{{cite journal |vauthors=Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, etal |title=Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=99 |issue= 26 |pages= 16899–903 |year= 2003 |pmid= 12477932 |doi= 10.1073/pnas.242603899 | pmc=139241 }} | |||
}} | |||
{{refend}} | |||
<!-- The PBB_Controls template provides controls for Protein Box Bot, please see Template:PBB_Controls for details. --> | |||
{{PBB_Controls | |||
| update_page = yes | |||
| require_manual_inspection = no | |||
| update_protein_box = yes | |||
| update_summary = yes | |||
| update_citations = yes | |||
}} | |||
{{Immune proteins}} | |||
[[Category:Proteins]] | |||
[[Category:Antibodies]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:33, 1 September 2017
| VALUE_ERROR (nil) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Aliases | |||||||
| External IDs | GeneCards: [1] | ||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||
| Ensembl |
|
| |||||
| UniProt |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (protein) |
|
| |||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||
| Wikidata | |||||||
| |||||||
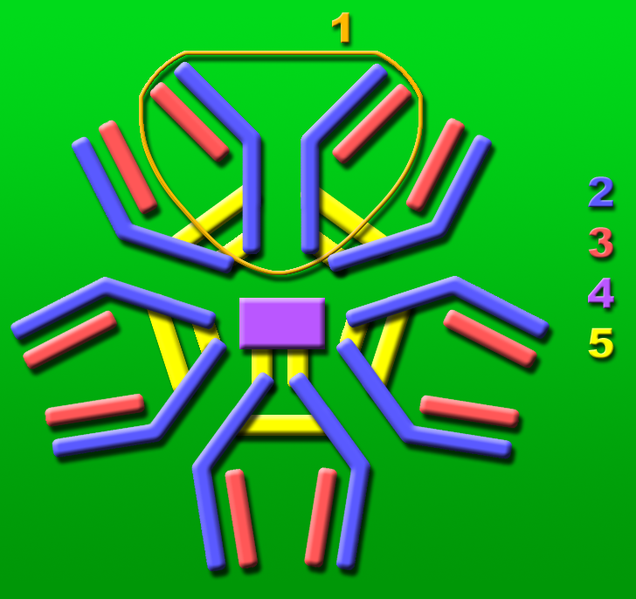
1: Base unit.
2: Heavy chains.
3: Light chains.
4: J chain.
5: Intermolecular disulfide bonds.
A J chain is a protein component of the antibodies IgM and IgA.[1] It is a 137 residue polypeptide,[2] encoded by the IGJ gene.[3][4][5]
Structure
The J Chain's molecular weight is approximately 15 kDa. It exhibits a standard immunoglobulin folding structure of two β-pleated sheets of four ribbons folded against one another. It has 8 cystine residues. Two of these residues link the α chains of IgA or the μ chains of IgM via disulfide bridges, effectively serving as the "glue" between two Fc regions of the antibody.[6]
The J-chain shows a large degree of homology between avian and human species, suggesting that it serves an important function.[6]
Function
The J Chain is required for IgM or IgA to be secreted into mucosa.[2] As part of a polymeric immunoglobulin (pIg), the J-chain is essential for binding of pIg to the pIgR, which forms the secretory component upon excretion of the secretory pIg by epithelial cells.[7] This binding facilitates transport of the J-chain positive pIg molecules from the basal to the apical sides of epithelial cells.
Because IgM and IgA are the only two types of antibody that polymerize, initial hypotheses stated that J chain was required for polymerization. However, it was subsequently found that IgM is able to polymerize in the absence of J chain as both a pentamer and a hexamer, however, both of these exist to lesser numbers in organisms lacking J chains. In such cases, there are also fewer IgA dimers.[2]
The J-chain also plays a role in the activation of complement. J-chain negative IgM hexamers are 15-20 times more effective at activating complement than J-chain positive IgM pentamers.[7] A consequence of this lack of complement activation is it allows J-chain positive pIgM to bind antigens without causing excessive damage to epithelial membranes through complement activation.
References
- ↑ Levinson. Medical Microbiology and Immunology (11 ed.). McGrawHill. pp. 405–6.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Schroeder, Harry; Wald, David; Greenspan, Neil (2008). "Chapter 4: Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function". In Paul, William. Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 125–151. ISBN 0-7817-6519-6.
- ↑ Max EE, McBride OW, Morton CC, Robinson MA (Sep 1986). "Human J chain gene: chromosomal localization and associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 83 (15): 5592–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.15.5592. PMC 386334. PMID 3016707.
- ↑ Max EE, Korsmeyer SJ (May 1985). "Human J chain gene. Structure and expression in B lymphoid cells". J Exp Med. 161 (4): 832–49. doi:10.1084/jem.161.4.832. PMC 2189063. PMID 2984306.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: IGJ immunoglobulin J polypeptide, linker protein for immunoglobulin alpha and mu polypeptides".
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kiyono, Hiroshi; Kunisawa, Jaw; McGhee, Jerry; Mestecky, Jiri (2008). "Chapter 31: The Mucosal Immune System". In Paul, William. Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 983–1030. ISBN 0-7817-6519-6.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Johansen FE, Braathen R, Brandtzaeg P (September 2000). "Role of J Chain in Secretory Immunoglobulin Formation". Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 52 (3): 240–248. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00790.x. PMID 10972899.
Further reading
- Koshland ME (1986). "The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain". Annu. Rev. Immunol. 3: 425–53. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. PMID 2415140.
- Tartakoff A, Vassalli P (1980). "Plasma cell immunoglobulin M molecules. Their biosynthesis, assembly, and intracellular transport". J. Cell Biol. 83 (2 Pt 1): 284–99. doi:10.1083/jcb.83.2.284. PMC 2111544. PMID 115892.
- Mole JE, Bhown AS, Bennett JC (1977). "Primary structure of human J chain: alignment of peptides from chemical and enzymatic hydrolyses". Biochemistry. 16 (16): 3507–13. doi:10.1021/bi00635a002. PMID 407930.
- Bastian A, Kratzin H, Eckart K, Hilschmann N (1993). "Intra- and interchain disulfide bridges of the human J chain in secretory immunoglobulin A.". Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler. 373 (12): 1255–63. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.1255. PMID 1292512.
- Frutiger S, Hughes GJ, Paquet N, et al. (1993). "Disulfide bond assignment in human J chain and its covalent pairing with immunoglobulin M.". Biochemistry. 31 (50): 12643–7. doi:10.1021/bi00165a014. PMID 1472500.
- Moro I, Iwase T, Komiyama K, et al. (1990). "Immunoglobulin A (IgA) polymerization sites in human immunocytes: immunoelectron microscopic study". Cell Struct. Funct. 15 (2): 85–91. doi:10.1247/csf.15.85. PMID 2113434.
- Alberini CM, Bet P, Milstein C, Sitia R (1990). "Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents". Nature. 347 (6292): 485–7. doi:10.1038/347485a0. PMID 2120591.
- Sumi Y, Nagura H, Kaneda T, Oka T (1989). "Immunoelectron microscopical localization of immunoglobulins, secretory component and J chain in the human minor salivary glands". J. Oral Pathol. 17 (8): 390–5. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01303.x. PMID 3146624.
- Hajdu I, Moldoveanu Z, Cooper MD, Mestecky J (1984). "Ultrastructural studies of human lymphoid cells. mu and J chain expression as a function of B cell differentiation". J. Exp. Med. 158 (6): 1993–2006. doi:10.1084/jem.158.6.1993. PMC 2187181. PMID 6417260.
- Yasuda N, Kanoh T, Uchino H (1980). "J chain synthesis in human myeloma cells: light and electron microscopic studies". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 40 (3): 573–80. PMC 1538946. PMID 6774844.
- Harper SJ, Allen AC, Béné MC, et al. (1995). "Increased dimeric IgA-producing B cells in tonsils in IgA nephropathy determined by in situ hybridization for J chain mRNA". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 101 (3): 442–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03132.x. PMC 1553245. PMID 7664491.
- Iwase T, Saito I, Takahashi T, et al. (1994). "Early expression of human J chain and mu chain gene in the fetal liver". Cell Struct. Funct. 18 (5): 297–302. doi:10.1247/csf.18.297. PMID 8168154.
- Harper SJ, Pringle JH, Wicks AC, et al. (1994). "Expression of J chain mRNA in duodenal IgA plasma cells in IgA nephropathy". Kidney Int. 45 (3): 836–44. doi:10.1038/ki.1994.110. PMID 8196286.
- Bjercke S, Brandtzaeg P (1994). "Glandular distribution of immunoglobulins, J chain, secretory component, and HLA-DR in the human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle". Hum. Reprod. 8 (9): 1420–5. PMID 8253928.
- Bertrand FE, Billips LG, Gartland GL, et al. (1996). "The J chain gene is transcribed during B and T lymphopoiesis in humans". J. Immunol. 156 (11): 4240–4. PMID 8666793.
- Atkin JD, Pleass RJ, Owens RJ, Woof JM (1996). "Mutagenesis of the human IgA1 heavy chain tailpiece that prevents dimer assembly". J. Immunol. 157 (1): 156–9. PMID 8683109.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.