Guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |"'''6.''' In patients treated with statins, it is recommended to measure creatine kinase levels in individuals with severe statin-associated muscle symptoms, and objective muscle weakness, and to measure liver transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase) as well as total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (hepatic panel) if there are symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C-LD]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | | bgcolor="LightGreen" |"'''6.''' In patients treated with statins, it is recommended to measure creatine kinase levels in individuals with severe statin-associated muscle symptoms, and objective muscle weakness, and to measure liver transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase) as well as total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (hepatic panel) if there are symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C-LD]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | bgcolor="LightGreen" |"'''7.''' In patients at increased ASCVD risk with chronic, stable liver disease (including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) when appropriately indicated, it is reasonable to use statins after obtaining baseline measurements and determining a schedule of monitoring and safety checks (Level of Evidence B-R)<nowiki>''</nowiki> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==[[ACC AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol|2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce ASCV Risk in Adults]]== | ==[[ACC AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol|2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce ASCV Risk in Adults]]== | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 2 December 2022
Template:Hypercholesterolemia Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
2018 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol.
Statin and adverse effects
| Class I |
| "1. A clinician-patient risk discussion is recommended before initiation of statin therapy to review net clinical benefit, weighing the potential for ASCVD risk reduction against the potential for statin-associated side effects, statin–drug interactions, and safety, while emphasizing that side effects can be addressed successfully (Level of Evidence: A) " |
| "2. In patients with statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), a thorough assessment of symptoms is recommended, in addition to an evaluation for nonstatin causes and predisposing factors(Level of Evidence: A) " |
| "3. In patients with indication for statin therapy, identification of potential predisposing factors for statin-associated side effects, including new-onset diabetes mellitus and SAMS, is recommended before initiation of treatment(Level of Evidence: B-R) " |
| "4. In patients with a recent or remote history of MI or acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and LVEF ≤40%, evidence-based beta blockers should be used to reduce mortality (Level of Evidence: B-R) " |
| "5. In patients with increased diabetes mellitus risk or new-onset diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to continue statin therapy, with added emphasis on adherence, net clinical benefit, and the core principles of regular moderate-intensity physical activity, maintaining a healthy dietary pattern, and sustaining modest weight loss (Level of Evidence: B-R) " |
| "6. In patients treated with statins, it is recommended to measure creatine kinase levels in individuals with severe statin-associated muscle symptoms, and objective muscle weakness, and to measure liver transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase) as well as total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (hepatic panel) if there are symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity. (Level of Evidence: C-LD) " |
| "7. In patients at increased ASCVD risk with chronic, stable liver disease (including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) when appropriately indicated, it is reasonable to use statins after obtaining baseline measurements and determining a schedule of monitoring and safety checks (Level of Evidence B-R)'' |
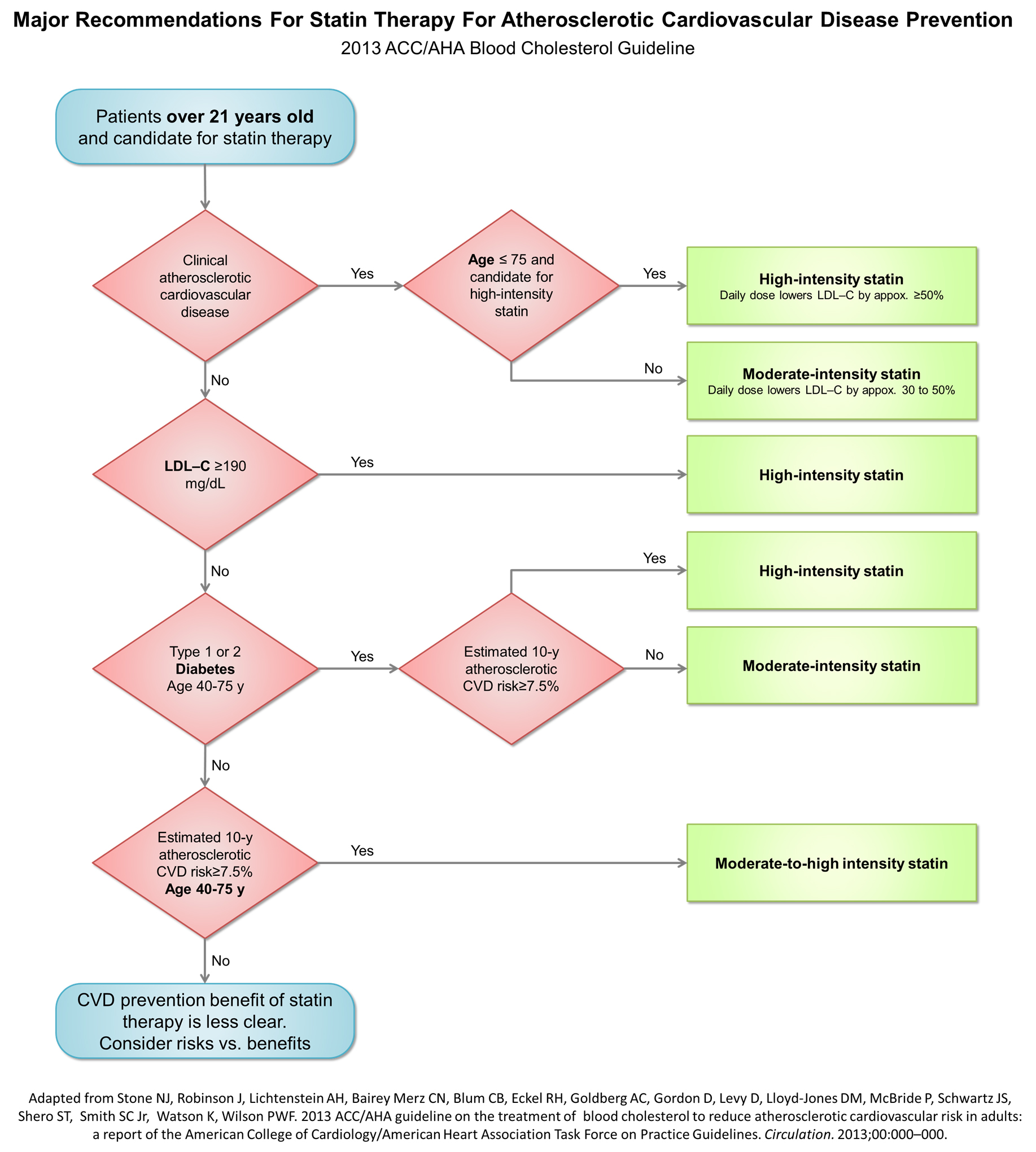
2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce ASCV Risk in Adults
Statin Treatment
Intensity of Statin Therapy | LDL and Non-HDL Treatment Goals | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Heart Failure and Hemodialysis
Safety
Managing Statin Therapy
Monitoring Statin Therapy | Optimizing statin therapy | Insufficient Response