Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
The mechanism of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase involves the formation of an [[enediol]] intermediate. | The mechanism of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase involves the formation of an [[enediol]] intermediate. | ||
==Other functions== | ==Other functions== | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 13 August 2012
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, or phosphoglucose isomerase, is an enzyme (EC 5.3.1.9) that catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate into fructose-6-phosphate in the second step of glycolysis. An unrelated enzyme, D-xylose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.5) catalyzes the isomerization of glucose to fructose, and is sometimes called "glucose isomerase".
The human variant of this enzyme is encoded by the GPI gene.
Function
This gene belongs to the GPI family whose members encode multifunctional phosphoglucose isomerase proteins involved in energy pathways. The protein encoded by this gene is a dimeric enzyme that catalyzes the reversible isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate.
glucose 6-phosphate <=> fructose 6-phosphate
The protein has different functions inside and outside the cell. In the cytoplasm, the protein is involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, while outside the cell it functions as a neurotrophic factor for spinal and sensory neurons. The same protein is also secreted by cancer cells, where it is called autocrine motility factor[1] and stimulates metastasis.[2] Defects in this gene are the cause of nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia and a severe enzyme deficiency can be associated with hydrops fetalis, immediate neonatal death and neurological impairment.[3]
In glycolysis
| α-D-Glucose 6-phosphate | {{{forward_enzyme}}} | β-D-Fructose 6-phosphate | |
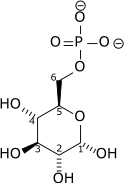
|
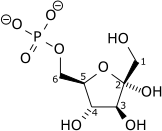
| ||
| {{{minor_forward_substrate(s)}}} | {{{minor_forward_product(s)}}} | ||
| [[image:Biochem_reaction_arrow_{{{reaction_direction_(forward/reversible/reverse)}}}_NNNN_horiz_med.svg|75px]] | |||
| Phosphoglucose isomerase | |||
As a glucose isomerase
| D-Glucose | {{{forward_enzyme}}} | D-Fructose | |
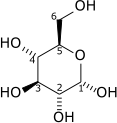
|
File:D-fructose wpmp.png | ||
| {{{minor_forward_substrate(s)}}} | {{{minor_forward_product(s)}}} | ||
| [[image:Biochem_reaction_arrow_{{{reaction_direction_(forward/reversible/reverse)}}}_NNNN_horiz_med.svg|75px]] | |||
| Phosphoglucose isomerase | |||
Mechanism
The mechanism of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase involves the formation of an enediol intermediate.
Other functions
There is evidence that phosphoglucose isomerase acts as a molecular messenger. It is produced and secreted by white blood cells, and acts to regulate the growth of several different cell types.
Pathology
A deficiency of phosphoglucose isomerase is responsible for 4% of the hemolytic anemias due to glycolytic enzyme deficiencies.
Other functions
There is evidence that phosphoglucose isomerase acts as a molecular messenger. It is produced and secreted by white blood cells, and acts to regulate the growth of several different cell types.
References
- ↑ Dobashi Y, Watanabe H, Sato Y; et al. (2006). "Differential expression and pathological significance of autocrine motility factor/glucose-6-phosphate isomerase expression in human lung carcinomas". J. Pathol. 210 (4): 431–40. doi:10.1002/path.2069. PMID 17029220. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Watanabe H, Takehana K, Date M, Shinozaki T, Raz A (1 July 1996). "Tumor cell autocrine motility factor is the neuroleukin/phosphohexose isomerase polypeptide". Cancer Res. 56 (13): 2960–3. PMID 8674049.
- ↑
ATP
ADP
ATP
ADP
+ +
NAD++ Pi
NADH + H+
NAD++ Pi
NADH + H+ H2O
H2O ADP
ATP
2 × Pyruvate 2 × File:Pyruvat.svg
|
| This isomerase article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |