EIF1AX
| Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1d7q. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | EIF1AX ; EIF1A; EIF4C; eIF-1A; eIF-4C | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 20364 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
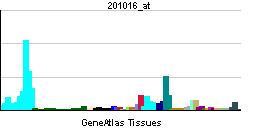 | |||||||||||||
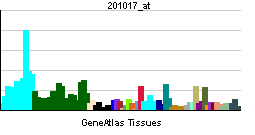 | |||||||||||||
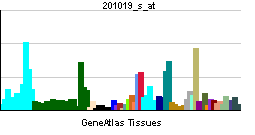 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked, also known as EIF1AX, is a human gene.[1]
This gene encodes an essential eukaryotic translation initiation factor. The protein is required for the binding of the 43S complex (a 40S subunit, eIF2/GTP/Met-tRNAi and eIF3) to the 5' end of capped RNA.[1]
References
Further reading
- Dever TE, Wei CL, Benkowski LA; et al. (1994). "Determination of the amino acid sequence of rabbit, human, and wheat germ protein synthesis factor eIF-4C by cloning and chemical sequencing". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (5): 3212–8. PMID 8106356.
- Lahn BT, Page DC (1997). "Functional coherence of the human Y chromosome". Science. 278 (5338): 675–80. PMID 9381176.
- Battiste JL, Pestova TV, Hellen CU, Wagner G (2000). "The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function". Mol. Cell. 5 (1): 109–19. PMID 10678173.
- Choi SK, Olsen DS, Roll-Mecak A; et al. (2000). "Physical and functional interaction between the eukaryotic orthologs of prokaryotic translation initiation factors IF1 and IF2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (19): 7183–91. PMID 10982835.
- Mingot JM, Kostka S, Kraft R; et al. (2001). "Importin 13: a novel mediator of nuclear import and export". EMBO J. 20 (14): 3685–94. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.14.3685. PMID 11447110.
- Sørensen HP, Hedegaard J, Sperling-Petersen HU, Mortensen KK (2002). "Remarkable conservation of translation initiation factors: IF1/eIF1A and IF2/eIF5B are universally distributed phylogenetic markers". IUBMB Life. 51 (5): 321–7. PMID 11699879.
- Bohnsack MT, Regener K, Schwappach B; et al. (2003). "Exp5 exports eEF1A via tRNA from nuclei and synergizes with other transport pathways to confine translation to the cytoplasm". EMBO J. 21 (22): 6205–15. PMID 12426392.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Olsen DS, Savner EM, Mathew A; et al. (2003). "Domains of eIF1A that mediate binding to eIF2, eIF3 and eIF5B and promote ternary complex recruitment in vivo". EMBO J. 22 (2): 193–204. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg030. PMID 12514125.
- Marintchev A, Kolupaeva VG, Pestova TV, Wagner G (2003). "Mapping the binding interface between human eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B: a new interaction between old partners". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (4): 1535–40. doi:10.1073/pnas.0437845100. PMID 12569173.
- Agate RJ, Choe M, Arnold AP (2004). "Sex differences in structure and expression of the sex chromosome genes CHD1Z and CHD1W in zebra finches". Mol. Biol. Evol. 21 (2): 384–96. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh027. PMID 14660691.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA; et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- Ross MT, Grafham DV, Coffey AJ; et al. (2005). "The DNA sequence of the human X chromosome". Nature. 434 (7031): 325–37. doi:10.1038/nature03440. PMID 15772651.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T; et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE; et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Kim S, Kim GJ, Miyoshi H; et al. (2007). "Efficiency of the elongation factor-1alpha promoter in mammalian embryonic stem cells using lentiviral gene delivery systems". Stem Cells Dev. 16 (4): 537–45. doi:10.1089/scd.2006.0088. PMID 17784828.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |