Desmoid tumor medical therapy: Difference between revisions
Sara Mohsin (talk | contribs) |
Sara Mohsin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}}{{S.M.}}{{Faizan}} | {{CMG}} {{AE}}{{S.M.}}{{Faizan}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Wait and watch strategy is applied to desmoid tumors which are asymptomatic, unresectable, non-life threatening, not causing any significant impairment, and resectable tumors with increased morbidity associated with surgery.Different drugs including chemotherapeutic agents, NSAIDs, anti-hormonal agents and tyrosine kinase inhibitors can be used to shrink or stabilize the tumor size and to improve the symptoms. Radiation therapy and tumor ablation with heat, cold, microwave and/or high-frequency ultrasound waves can also be of therapeutic use as required. | Wait and watch [[Strategy (NLP)|strategy]] is applied to [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]] which are [[asymptomatic]], unresectable, non-life threatening, not causing any significant [[impairment]], and resectable [[tumors]] with increased [[morbidity]] associated with [[surgery]].Different [[drugs]] including [[chemotherapeutic agents]], [[Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug|NSAIDs]], anti-hormonal agents and [[tyrosine kinase inhibitors]] can be used to shrink or [[Stabilizer (chemistry)|stabilize]] the [[tumor]] size and to improve the [[symptoms]]. [[Radiation therapy]] and [[tumor]] [[ablation]] with [[heat]], [[cold]], [[microwave]] and/or high-frequency [[Ultrasound|ultrasound waves]] can also be of [[therapeutic]] use as required. | ||
==Medical Therapy== | ==Medical Therapy== | ||
*Ideally, patients with desmoid tumors should be evaluated by a multi-disciplinary team which includes surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, geneticists and nurses | *Ideally, [[patients]] with [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]] should be evaluated by a multi-disciplinary team which includes [[surgeons]], [[medical]] [[oncologists]], [[Radiation Oncology|radiation]] [[oncologists]], [[geneticists]] and [[nurses]] | ||
*Patients with desmoid tumors should be evaluated in a hospital with expertise in sarcoma (usually such hospitals are designated as NCCN | *[[Patients]] with [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]] should be evaluated in a [[hospital]] with expertise in [[sarcoma]] (usually such [[hospitals]] are designated as [[National Comprehensive Cancer Network|NCCN [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] centers]]) | ||
*'''Wait and watch or observation''' of the tumor carefully with images and/or physical examination, is implied as a primary therapeutic option for desmoid | *'''Wait and watch or observation''' of the [[tumor]] carefully with [[images]] and/or [[physical examination]], is implied as a primary [[therapeutic]] option for [[desmoid tumor]]<nowiki/>[[desmoid tumor|s]] with following [[Features (pattern recognition)|features]]: | ||
**Potentially resectable but asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic | **Potentially resectable but [[asymptomatic]] or minimally [[symptomatic]] | ||
**Non-life threatening | **Non-life threatening | ||
**Not causing any significant impairment | **Not causing any [[Significant figure|significant]] [[impairment]] | ||
**Stable appearance on screening modalities | **Stable [[appearance]] on [[Screening test|screening modalities]] | ||
**Unresectable tumors | **Unresectable [[tumors]] | ||
**Resectable but surgery would lead to unacceptable morbidity | **Resectable but [[surgery]] would lead to unacceptable [[morbidity]] | ||
**How often scans and/or physical exams are needed during a “wait and watch” period varies with each situation | **How often [[Scan|scans]] and/or [[Physical examination|physical exams]] are needed during a “wait and watch” period varies with each situation | ||
*Treatment is recommended for extra-abdominal or abdominal desmoid tumors associated with: | *Treatment is recommended for extra-abdominal or [[abdominal]] [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]] associated with: | ||
**Symptoms | **[[Symptoms]] | ||
**Progressively enlarging tumors irrespective of symptoms | **Progressively enlarging [[tumors]] irrespective of [[symptoms]] | ||
**Imminent risk to adjacent structures | **Imminent risk to adjacent structures | ||
**Tumor creating cosmetic concerns | **[[Tumor]] creating cosmetic concerns | ||
*'''Goals of medical therapy''' are: | *'''Goals of medical therapy''' are: | ||
**Shrinkage of tumor size | **Shrinkage of [[tumor]] size | ||
**Stabilization of tumor | **[[Stabilization (medicine)|Stabilization]] of [[tumor]] | ||
**Improvement in symptoms after a very wide variety of treatments | **Improvement in [[symptoms]] after a very wide variety of [[treatments]] | ||
*Following table shows drugs used in medical therapy for desmoid tumors:<ref name="pmid22359346">{{cite journal |author=Wilkinson MJ, Fitzgerald JE, Thomas JM, Hayes AJ, Strauss DC|title=Surgical resection for non-familial adenomatous polyposis-related intra-abdominal fibromatosis |journal=BJS. |volume=99 |issue=5 |pages=706–13|year=2012 |doi=10.1002/bjs.8703 |pmid=22359346}}</ref><ref name="pmid22370045">{{cite journal| author=Rammohan A, Wood JJ| title=Desmoid tumour of the breast as a manifestation of Gardner's syndrome. | journal=Int J Surg Case Rep | year= 2012 | volume= 3 | issue= 5 | pages= 139-42 | pmid=22370045 | doi=10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.01.004 | pmc=PMC3312056 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22370045 }} </ref> | *Following table shows [[drugs]] used in [[Medical therapy template|medical therapy]] for [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]]:<ref name="pmid22359346">{{cite journal |author=Wilkinson MJ, Fitzgerald JE, Thomas JM, Hayes AJ, Strauss DC|title=Surgical resection for non-familial adenomatous polyposis-related intra-abdominal fibromatosis |journal=BJS. |volume=99 |issue=5 |pages=706–13|year=2012 |doi=10.1002/bjs.8703 |pmid=22359346}}</ref><ref name="pmid22370045">{{cite journal| author=Rammohan A, Wood JJ| title=Desmoid tumour of the breast as a manifestation of Gardner's syndrome. | journal=Int J Surg Case Rep | year= 2012 | volume= 3 | issue= 5 | pages= 139-42 | pmid=22370045 | doi=10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.01.004 | pmc=PMC3312056 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22370045 }} </ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+Different drugs used in medical therapy of desmoid tumors | |+Different drugs used in medical therapy of desmoid tumors | ||
!Drug class | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Drug class | ||
!Drug name | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Drug name | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Chemotherapeutic agents''' | |style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''Chemotherapeutic agents''' | ||
| | | | ||
* Doxorubicin (Adriamycin, Rubex) | * [[Doxorubicin]] ([[Adriamycin]], [[Doxorubicin hydrochloride|Rubex]]) | ||
* Doxil (liposomal doxorubicin) | * [[Doxorubicin liposome|Doxil (liposomal doxorubicin)]] | ||
* Dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome) | * [[Dacarbazine|Dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome)]] | ||
* Methotrexate | * [[Methotrexate]] | ||
* Vinorelbine | * [[Vinorelbine]] | ||
* Vinblastine | * [[Vinblastine]] | ||
* Carboplatin (Paraplatin) | * [[Carboplatin]] ([[Paraplatin]]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''NSAIDs''' | |style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''NSAIDs''' | ||
| | | | ||
* Sulindac | * [[Sulindac]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Anti-hormonal agents''' | |style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''Anti-hormonal agents''' | ||
| | | | ||
* Tamoxifen (Soltamox, Nolvadex) | * [[Tamoxifen]] ([[Soltamox]], [[Nolvadex]]) | ||
* Prostaglandin inhibitors | * [[Prostaglandin]] inhibitors | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Tyrosine kinase inhibitors''' | |style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''Tyrosine kinase inhibitors''' | ||
(Novel molecular targeted therapies) | (Novel [[molecular]] targeted therapies) | ||
| | | | ||
* Sorafenib | * [[Sorafenib]] | ||
* Imatinib (Gleevec) | * [[Imatinib]] ([[Gleevec]]) | ||
|} | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
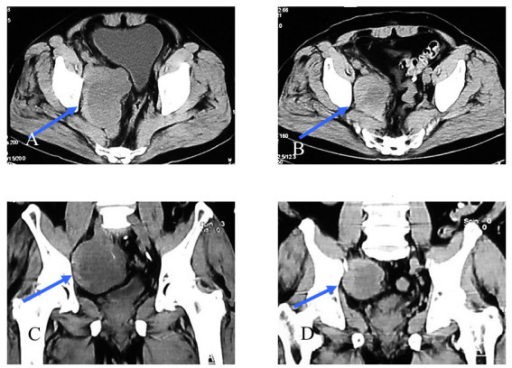
[[File:Desmoid nsaid regression.png|thumb|600px|none|Desmoid tumour before (A, C) and 2 years after (B, D) the commencement of NSAID. Multi planner reformation (MPR)-CT demonstrates the sporadic desmoid tumours originating from the intra-abdominal cavity (arrows). Frontal (A, B) and axial (C, D) images are shown. The tumour has shown a remarkable shrinkage with a regression rate of 68.5% along with disappearance of intratumoural septa.[https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC2270274_1477-7819-6-17-1&query=desmoid%20tumor&it=xg&req=4&npos=13 Source: Tanaka K. et al, Department of Surgery, Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Hyogo, Japan]]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Radiation Therapy== | ==Radiation Therapy== | ||
*Desmoids are radiosensitive tumors | *[[Desmoid tumor|Desmoids]] are radiosensitive [[tumors]] | ||
*[[Radiation therapy]] uses high-energy [[waves]] such as [[X-rays]] to kill or shrink [[Tumor cell|tumor cells]] | |||
*Rarely, [[radiation therapy]] is used if: | *Rarely, [[radiation therapy]] is used if: | ||
**Patient is symptomatic | **[[Patient]] is [[symptomatic]] | ||
**Medical therapy fails | **[[Medical therapy template|Medical therapy]] fails | ||
**[[Surgery]] fails | **[[Surgery]] fails | ||
**Patient is not a good surgical candidate | **[[Patient]] is not a good surgical candidate | ||
**Patient declines surgery | **[[Patient]] declines [[surgery]] | ||
**Surgical morbidity would be excessive | **Surgical [[morbidity]] would be excessive | ||
**Margins are positive post-resection | **Margins are positive post-[[resection]] | ||
**Tumor recurrence post-resection | **[[Tumor]] [[Recurrence plot|recurrence]] post-[[resection]] | ||
*Depending on individual patient characteristics, the radiation may be applied by following two methods: | *Depending on individual [[patient]] characteristics, the [[Radiation therapy|radiation]] may be applied by following two methods: | ||
**Conventional linear accelerators (radiotherapy treatment machines) | **Conventional linear accelerators ([[radiotherapy]] treatment machines) | ||
**Proton beam therapy | **[[Proton]] beam [[therapy]] | ||
*Depending on the size and location of the [[tumor]], [[radiation]] is delivered either in low doses over the course of 5 to 6 weeks or in a single high dose | *Depending on the size and location of the [[tumor]], [[radiation]] is delivered either in low doses over the course of 5 to 6 weeks or in a single [[High doses of ionizing radiation|high dose]] | ||
*[[Radiation]] therapy is effective in approximately 30% of cases | *[[Radiation]] therapy is effective in approximately 30% of cases | ||
*Following complications can occur from radiation therapy due to late radiation effects: | *Following complications can occur from [[radiation therapy]] due to late [[radiation]] effects: | ||
**Secondary malignancies (especially in younger patients) | **Secondary [[malignancies]] (especially in younger patients) | ||
**Fibrosis associated with radiation therapy | **[[Fibrosis]] associated with [[radiation therapy]] | ||
==Tumor ablation== | ==Tumor ablation== | ||
*In some rare cases, ablation of desmoid tumors can be used as a therapeutic option | *In some rare cases, [[ablation]] of [[Desmoid tumor|desmoid tumors]] can be used as a [[therapeutic]] option | ||
*Following different kinds of ablation can be used: | *Following different kinds of [[ablation]] can be used: | ||
**Cold ablation | **[[Cold]] [[ablation]] | ||
**Heat/thermal ablation | **[[Heat]]/[[thermal ablation]] | ||
**Microwave ablation | **[[Microwave]] [[ablation]] | ||
**High-frequency ultrasound ablation | **High-frequency [[ultrasound]] [[ablation]] | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:38, 25 March 2019
|
Desmoid tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mohsin, M.D.[2]Faizan Sheraz, M.D. [3]
Overview
Wait and watch strategy is applied to desmoid tumors which are asymptomatic, unresectable, non-life threatening, not causing any significant impairment, and resectable tumors with increased morbidity associated with surgery.Different drugs including chemotherapeutic agents, NSAIDs, anti-hormonal agents and tyrosine kinase inhibitors can be used to shrink or stabilize the tumor size and to improve the symptoms. Radiation therapy and tumor ablation with heat, cold, microwave and/or high-frequency ultrasound waves can also be of therapeutic use as required.
Medical Therapy
- Ideally, patients with desmoid tumors should be evaluated by a multi-disciplinary team which includes surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, geneticists and nurses
- Patients with desmoid tumors should be evaluated in a hospital with expertise in sarcoma (usually such hospitals are designated as NCCN [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] centers)
- Wait and watch or observation of the tumor carefully with images and/or physical examination, is implied as a primary therapeutic option for desmoid tumors with following features:
- Potentially resectable but asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic
- Non-life threatening
- Not causing any significant impairment
- Stable appearance on screening modalities
- Unresectable tumors
- Resectable but surgery would lead to unacceptable morbidity
- How often scans and/or physical exams are needed during a “wait and watch” period varies with each situation
- Treatment is recommended for extra-abdominal or abdominal desmoid tumors associated with:
- Goals of medical therapy are:
- Shrinkage of tumor size
- Stabilization of tumor
- Improvement in symptoms after a very wide variety of treatments
- Following table shows drugs used in medical therapy for desmoid tumors:[1][2]
| Drug class | Drug name |
|---|---|
| Chemotherapeutic agents | |
| NSAIDs | |
| Anti-hormonal agents |
|
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(Novel molecular targeted therapies) |
 |
Radiation Therapy
- Desmoids are radiosensitive tumors
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy waves such as X-rays to kill or shrink tumor cells
- Rarely, radiation therapy is used if:
- Patient is symptomatic
- Medical therapy fails
- Surgery fails
- Patient is not a good surgical candidate
- Patient declines surgery
- Surgical morbidity would be excessive
- Margins are positive post-resection
- Tumor recurrence post-resection
- Depending on individual patient characteristics, the radiation may be applied by following two methods:
- Conventional linear accelerators (radiotherapy treatment machines)
- Proton beam therapy
- Depending on the size and location of the tumor, radiation is delivered either in low doses over the course of 5 to 6 weeks or in a single high dose
- Radiation therapy is effective in approximately 30% of cases
- Following complications can occur from radiation therapy due to late radiation effects:
- Secondary malignancies (especially in younger patients)
- Fibrosis associated with radiation therapy
Tumor ablation
- In some rare cases, ablation of desmoid tumors can be used as a therapeutic option
- Following different kinds of ablation can be used:
- Cold ablation
- Heat/thermal ablation
- Microwave ablation
- High-frequency ultrasound ablation
Reference
- ↑ Wilkinson MJ, Fitzgerald JE, Thomas JM, Hayes AJ, Strauss DC (2012). "Surgical resection for non-familial adenomatous polyposis-related intra-abdominal fibromatosis". BJS. 99 (5): 706–13. doi:10.1002/bjs.8703. PMID 22359346.
- ↑ Rammohan A, Wood JJ (2012). "Desmoid tumour of the breast as a manifestation of Gardner's syndrome". Int J Surg Case Rep. 3 (5): 139–42. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.01.004. PMC 3312056. PMID 22370045.