Cirrhosis echocardiography or ultrasound: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Cirrhosis}} | {{Cirrhosis}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Cherry}} | |||
==Overview== | |||
On [[ultrasound|ultrasonography]], changes in the [[liver]] contour and increased [[Nodule (medicine)|nodularity]] may be evident. The echo texture may appear coarse along with an increase in echogenecity from focal fatty changes and irregular appearing areas. [[Medical ultrasonography|USG]] may also be used to screen for [[hepatocellular carcinoma]], [[portal hypertension]] and [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]. | |||
==Echocardiography== | |||
*[[Echocardiography|Echocardiograms]] may be helpful in the measurement of [[ejection fraction]] and identification of [[ischemia|ischemic]] and [[Hypokinesia|hypokinetic]] areas of the [[ventricle (heart)|ventricles]]. This is useful in establishing a diagnosis of [[congestive cardiac failure]] as a cause of liver cirrhosis. | |||
*[[Radiocontrast|Contrast]] [[echocardiography]] is a useful diagnostic test for [[hepatopulmonary syndrome]]: | |||
**Intravenous microbubbles (> 10 micrometers in diameter) from agitated [[normal saline]] that are normally obstructed by [[Lung|pulmonary]] [[Capillary|capillaries]] (normally <8 to 15 micrometers) rapidly transit the [[lung]] and appear in the [[left atrium]] of the heart within 7 heart beats. | |||
**Intravenous [[technetium]]-99m–labeled [[albumin]] may transit the [[Lung|lungs]] and appear in the [[kidney]] and [[brain]]. | |||
== | ==Ultrasound== | ||
* [[Medical ultrasonography|Ultrasonography]] may be routinely performed during the evaluation of cirrhosis. | |||
*[[Medical ultrasonography|USG]] is considered as the first-line investigation of choice due to the following advantages: | |||
**easy availability | |||
**low cost | |||
**absence of exposure to [[Contrast|intravenous contrast]] or [[Radiation (medicine)|radiation]] | |||
**high tolerabililty, safety due to non [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] nature | |||
*Findings on [[Medical ultrasonography|USG]] may be viewed in light of other signs of cirrhosis, such as findings on physical examination or laboratory investigations. | |||
*[[Ultrasound]] findings in cirrhosis are as follows:<ref name="pmid22357834">{{cite journal |vauthors=Udell JA, Wang CS, Tinmouth J, FitzGerald JM, Ayas NT, Simel DL, Schulzer M, Mak E, Yoshida EM |title=Does this patient with liver disease have cirrhosis? |journal=JAMA |volume=307 |issue=8 |pages=832–42 |year=2012 |pmid=22357834 |doi=10.1001/jama.2012.186 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3533689">{{cite journal |vauthors=Becker CD, Scheidegger J, Marincek B |title=Hepatic vein occlusion: morphologic features on computed tomography and ultrasonography |journal=Gastrointest Radiol |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=305–11 |year=1986 |pmid=3533689 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid2526349">{{cite journal |vauthors=Di Lelio A, Cestari C, Lomazzi A, Beretta L |title=Cirrhosis: diagnosis with sonographic study of the liver surface |journal=Radiology |volume=172 |issue=2 |pages=389–92 |year=1989 |pmid=2526349 |doi=10.1148/radiology.172.2.2526349 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3891495">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sanford NL, Walsh P, Matis C, Baddeley H, Powell LW |title=Is ultrasonography useful in the assessment of diffuse parenchymal liver disease? |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=89 |issue=1 |pages=186–91 |year=1985 |pmid=3891495 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3532188">{{cite journal |vauthors=Giorgio A, Amoroso P, Lettieri G, Fico P, de Stefano G, Finelli L, Scala V, Tarantino L, Pierri P, Pesce G |title=Cirrhosis: value of caudate to right lobe ratio in diagnosis with US |journal=Radiology |volume=161 |issue=2 |pages=443–5 |year=1986 |pmid=3532188 |doi=10.1148/radiology.161.2.3532188 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid10341686">{{cite journal |vauthors=Simonovský V |title=The diagnosis of cirrhosis by high resolution ultrasound of the liver surface |journal=Br J Radiol |volume=72 |issue=853 |pages=29–34 |year=1999 |pmid=10341686 |doi=10.1259/bjr.72.853.10341686 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22144108">{{cite journal |vauthors=Trinchet JC, Chaffaut C, Bourcier V, Degos F, Henrion J, Fontaine H, Roulot D, Mallat A, Hillaire S, Cales P, Ollivier I, Vinel JP, Mathurin P, Bronowicki JP, Vilgrain V, N'Kontchou G, Beaugrand M, Chevret S |title=Ultrasonographic surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a randomized trial comparing 3- and 6-month periodicities |journal=Hepatology |volume=54 |issue=6 |pages=1987–97 |year=2011 |pmid=22144108 |doi=10.1002/hep.24545 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22424438">{{cite journal |vauthors= |title=EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=56 |issue=4 |pages=908–43 |year=2012 |pmid=22424438 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001 |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Changes in [[liver]] contour: shrunken, irregular appearance | |||
**Non homogeneous appearance of the [[Liver|hepatic]] tissue | |||
**Increased [[Liver|surface]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodularity]] | |||
**Increase in echogenecity from focal fatty [[Infiltration (medical)|infiltration]] | |||
**[[Atrophy]] of the right lobe and [[Hypertrophy (medical)|hypertrophy]] of the [[Caudate lobe of liver|caudate]] or left lobe | |||
**[[Splenomegaly]] | |||
**[[Ascites]] | |||
**[[Varices]] | |||
**[[Hepatic vein|Hepatic]] or [[portal vein]] [[thrombosis]] | |||
{| align="center" | |||
|[[image:Ascites11.jpg|thumb|400px|Ascites ultrasonography-Case courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel, via radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29199">rID: 29199</ref>]] | |||
|[[image:Splenomegaly-1.JPG|thumb|350px|Splenomegaly ultrasonography-Case courtesy of Dr Ian Bickle, via radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/52825">rID: 52825</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
*[[Vascular]] changes may be appreciated on ultrasound, particularly with color doppler imaging:<ref name="pmid25263492">{{cite journal |vauthors=Di Lelio A, Cestari C, Lomazzi A, Beretta L |title=Cirrhosis: diagnosis with sonographic study of the liver surface |journal=Radiology |volume=172 |issue=2 |pages=389–92 |year=1989 |pmid=2526349 |doi=10.1148/radiology.172.2.2526349 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11866220">{{cite journal |vauthors=Martínez-Noguera A, Montserrat E, Torrubia S, Villalba J |title=Doppler in hepatic cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis |journal=Semin. Ultrasound CT MR |volume=23 |issue=1 |pages=19–36 |year=2002 |pmid=11866220 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid12216750">{{cite journal |vauthors=Tchelepi H, Ralls PW, Radin R, Grant E |title=Sonography of diffuse liver disease |journal=J Ultrasound Med |volume=21 |issue=9 |pages=1023–32; quiz 1033–4 |year=2002 |pmid=12216750 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid12202712">{{cite journal |vauthors=Awaya H, Mitchell DG, Kamishima T, Holland G, Ito K, Matsumoto T |title=Cirrhosis: modified caudate-right lobe ratio |journal=Radiology |volume=224 |issue=3 |pages=769–74 |year=2002 |pmid=12202712 |doi=10.1148/radiol.2243011495 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid10334257">{{cite journal |vauthors=Albrecht T, Blomley MJ, Cosgrove DO, Taylor-Robinson SD, Jayaram V, Eckersley R, Urbank A, Butler-Barnes J, Patel N |title=Non-invasive diagnosis of hepatic cirrhosis by transit-time analysis of an ultrasound contrast agent |journal=Lancet |volume=353 |issue=9164 |pages=1579–83 |year=1999 |pmid=10334257 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(98)06373-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7718281">{{cite journal |vauthors=Zwiebel WJ |title=Sonographic diagnosis of hepatic vascular disorders |journal=Semin. Ultrasound CT MR |volume=16 |issue=1 |pages=34–48 |year=1995 |pmid=7718281 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Increased flow across both [[Portal venous system|portal]] and [[systemic circulation]] | |||
**Increase in r[[Resistive index|esistive index]] in end stage liver disease | |||
**Elongated and tortuous appearance of [[Blood vessel|vessels]], called "corkscrewing" | |||
**Spontaneous [[shunts]] seen on [[Doppler ultrasound]] | |||
**Re-canalization of [[umbilical vein]] -- [[pathognomonic]] of portal hypertension | |||
**Porto-systemic collaterals | |||
*Findings of [[portal hypertension]]:<ref name="urlPortal hypertension | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org" /> | |||
**Increased diameter of the [[portal vein]] | |||
** Presence of collateral veins | |||
** Decreased flow within the [[Portal venous system|portal circulation]] on [[Medical ultrasonography|Doppler]] imaging | |||
* Ultrasonography may be used as a screening test for [[hepatocellular carcinoma]] as [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] on ultrasonography warrant further evaluation. | |||
* Ultrasonography may also help rule out [[Cholestasis|biliary obstruction]] in cirrhotic patients with [[jaundice]]. | |||
{{#ev:youtube|AYb9NrZoSLs}} | |||
= | {| align="right" | ||
|{{#ev:youtube|lKkmWFm6xSw|500}} | |||
|} | |||
=== Echo-Doppler === | |||
*Findings on an [[Doppler echocardiography|echo-doppler]] suggestive of cirrhosis with portal hypertension include:<ref name="pmid1447502">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sabbà C, Ferraioli G, Buonamico P, Berardi E, Antonica G, Taylor KJ, Albano O |title=Echo-Doppler evaluation of acute flow changes in portal hypertensive patients: flow velocity as a reliable parameter |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=15 |issue=3 |pages=356–60 |year=1992 |pmid=1447502 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Lack of increase in [[portal vein]] diameter in response to meals | |||
**Increased portal [[blood flow]] velocity | |||
**Decreased [[portal vein]] cross-sectional area | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
=== Color-Doppler Ultrasound === | |||
{| align="right" | |||
|[[image:Portal vein.jpg|thumb|400px|Portal vein color-doppler ultrasonography-Case courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel, via radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29199">rID: 29199</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
*Findings on an [[Doppler ultrasonography|color-doppler ultrasound]] suggestive of cirrhosis with portal hypertension include:<ref name="pmid11180179">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yin XY, Lu MD, Huang JF, Xie XY, Liang LJ |title=Color Doppler velocity profile assessment of portal hemodynamics in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension: correlation with esophageal variceal bleeding |journal=J Clin Ultrasound |volume=29 |issue=1 |pages=7–13 |year=2001 |pmid=11180179 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlPortal hypertension | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org">{{cite web |url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/portal-hypertension |title=Portal hypertension | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16052688">{{cite journal| author=Li FH, Hao J, Xia JG, Li HL, Fang H| title=Hemodynamic analysis of esophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis using color Doppler ultrasound. | journal=World J Gastroenterol | year= 2005 | volume= 11 | issue= 29 | pages= 4560-5 | pmid=16052688 | doi= | pmc=4398708 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16052688 }}</ref> | |||
**Diameter and velocity in [[left gastric vein]] are significantly associated with incident of [[esophageal varices]] | |||
**Increased diameter of [[left gastric vein]] | |||
**Increased diameter of [[portal vein]] | |||
**Increased flow velocity in [[left gastric vein]] | |||
**[[Biphasic]] and reverse flow in [[portal vein]] -- [[pathognomonic]] of portal hypertension | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==Transient Elastography== | |||
* Transient elastography and the Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) technique are well-established methods for the staging of [[fibrosis]] in various [[liver]] diseases: <ref name="pmid20581229">{{cite journal |vauthors=Castera L, Pinzani M |title=Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? |journal=Gut |volume=59 |issue=7 |pages=861–6 |year=2010 |pmid=20581229 |doi=10.1136/gut.2010.214650 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22239521">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M, Sporea I, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Strobel D, Takahashi H, Yoneda M, Suda T, Zeuzem S, Herrmann E |title=Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis |journal=J. Viral Hepat. |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=e212–9 |year=2012 |pmid=22239521 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01537.x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18395077">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, Sarrazin C, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, Herrmann E |title=Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=134 |issue=4 |pages=960–74 |year=2008 |pmid=18395077 |doi=10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.034 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15690481">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, de Lédinghen V, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M |title=Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C |journal=Hepatology |volume=41 |issue=1 |pages=48–54 |year=2005 |pmid=15690481 |doi=10.1002/hep.20506 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid14698338">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, Beaugrand M, Palau R |title=Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis |journal=Ultrasound Med Biol |volume=29 |issue=12 |pages=1705–13 |year=2003 |pmid=14698338 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23558397">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F, Cantisani V, Correas JM, D'Onofrio M, Drakonaki EE, Fink M, Friedrich-Rust M, Gilja OH, Havre RF, Jenssen C, Klauser AS, Ohlinger R, Saftoiu A, Schaefer F, Sporea I, Piscaglia F |title=EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: Basic principles and technology |journal=Ultraschall Med |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=169–84 |year=2013 |pmid=23558397 |doi=10.1055/s-0033-1335205 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25911335">{{cite journal |vauthors= |title=EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=63 |issue=1 |pages=237–64 |year=2015 |pmid=25911335 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.006 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21205132">{{cite journal |vauthors=Castera L, Bedossa P |title=How to assess liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: serum markers or transient elastography vs. liver biopsy? |journal=Liver Int. |volume=31 Suppl 1 |issue= |pages=13–7 |year=2011 |pmid=21205132 |doi=10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02380.x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23732714">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chou R, Wasson N |title=Blood tests to diagnose fibrosis or cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=158 |issue=11 |pages=807–20 |year=2013 |pmid=23732714 |doi=10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00005 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26779260">{{cite journal |vauthors=Khallafi H, Qureshi K |title=Imaging Based Methods of Liver Fibrosis Assessment in Viral Hepatitis: A Practical Approach |journal=Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis |volume=2015 |issue= |pages=809289 |year=2015 |pmid=26779260 |pmc=4686715 |doi=10.1155/2015/809289 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23954643">{{cite journal |vauthors=Singh S, Fujii LL, Murad MH, Wang Z, Asrani SK, Ehman RL, Kamath PS, Talwalkar JA |title=Liver stiffness is associated with risk of decompensation, liver cancer, and death in patients with chronic liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis |journal=Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. |volume=11 |issue=12 |pages=1573–84.e1–2; quiz e88–9 |year=2013 |pmid=23954643 |pmc=3900882 |doi=10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.034 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* The '''FibroScan (transient elastography)''' uses elastic waves to determine [[liver]] stiffness which theoretically may be converted into a liver score. | |||
* The FibroScan produces an ultrasound image of the [[liver]] (from 20-80mm) along with a pressure reading (in kPa). | |||
* Transient elastography is much faster than a [[biopsy]] (usually lasts 2.5-5 minutes) and is completely painless. | |||
* Findings on transient elastography may show reasonable correlation with the severity of cirrhosis:<ref>{{cite journal |author=Foucher J, Chanteloup E, Vergniol J, ''et al'' |title=Diagnosis of cirrhosis by transient elastography (FibroScan): a prospective study |journal=Gut |volume=55|issue=3 |pages=403-8 |year=2006 |pmid=16020491 |doi=10.1136/gut.2005.069153}}</ref><ref name="pmid22733854">{{cite journal |author=Xie L, Chen X, Guo Q, Dong Y, Guang Y, Zhang X |title=Real-time elastography for diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B |journal=[[Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine : Official Journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine]] |volume=31 |issue=7 |pages=1053–60 |year=2012|pmid=22733854 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** Increasing [[Scar|scarring]] of the [[liver]] is associated with increasing "stiffness" of the [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:51, 13 December 2017
|
Cirrhosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Cirrhosis echocardiography or ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cirrhosis echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cirrhosis echocardiography or ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sudarshana Datta, MD [2]
Overview
On ultrasonography, changes in the liver contour and increased nodularity may be evident. The echo texture may appear coarse along with an increase in echogenecity from focal fatty changes and irregular appearing areas. USG may also be used to screen for hepatocellular carcinoma, portal hypertension and Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Echocardiography
- Echocardiograms may be helpful in the measurement of ejection fraction and identification of ischemic and hypokinetic areas of the ventricles. This is useful in establishing a diagnosis of congestive cardiac failure as a cause of liver cirrhosis.
- Contrast echocardiography is a useful diagnostic test for hepatopulmonary syndrome:
- Intravenous microbubbles (> 10 micrometers in diameter) from agitated normal saline that are normally obstructed by pulmonary capillaries (normally <8 to 15 micrometers) rapidly transit the lung and appear in the left atrium of the heart within 7 heart beats.
- Intravenous technetium-99m–labeled albumin may transit the lungs and appear in the kidney and brain.
Ultrasound
- Ultrasonography may be routinely performed during the evaluation of cirrhosis.
- USG is considered as the first-line investigation of choice due to the following advantages:
- easy availability
- low cost
- absence of exposure to intravenous contrast or radiation
- high tolerabililty, safety due to non invasive nature
- Findings on USG may be viewed in light of other signs of cirrhosis, such as findings on physical examination or laboratory investigations.
- Ultrasound findings in cirrhosis are as follows:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8]
- Changes in liver contour: shrunken, irregular appearance
- Non homogeneous appearance of the hepatic tissue
- Increased surface nodularity
- Increase in echogenecity from focal fatty infiltration
- Atrophy of the right lobe and hypertrophy of the caudate or left lobe
- Splenomegaly
- Ascites
- Varices
- Hepatic or portal vein thrombosis
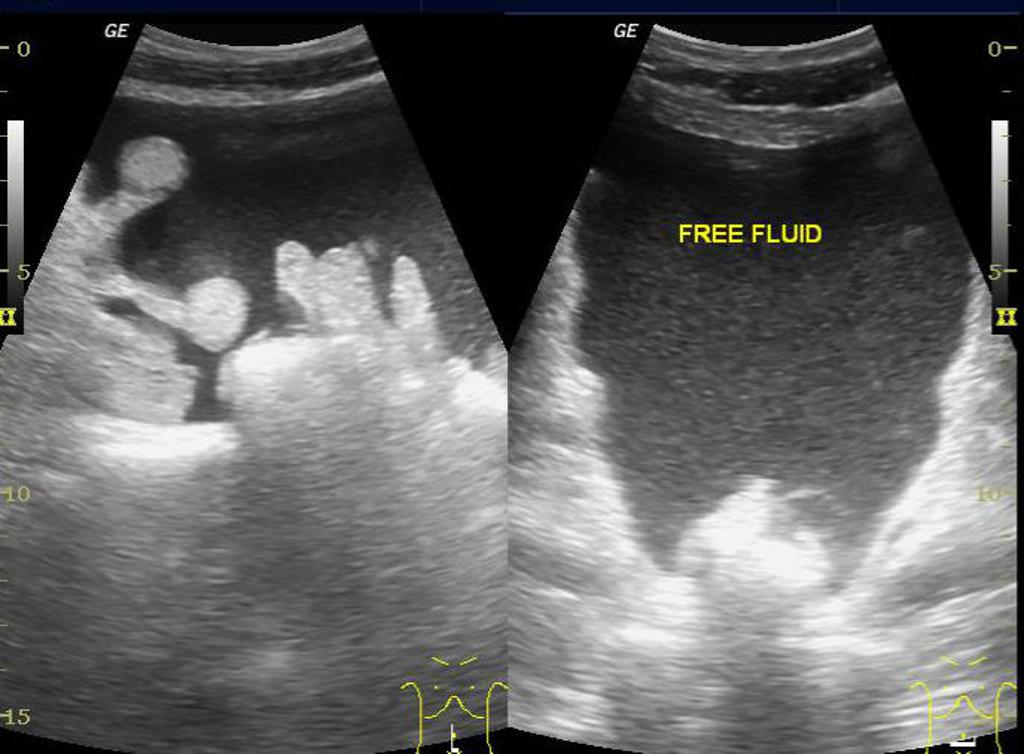 |
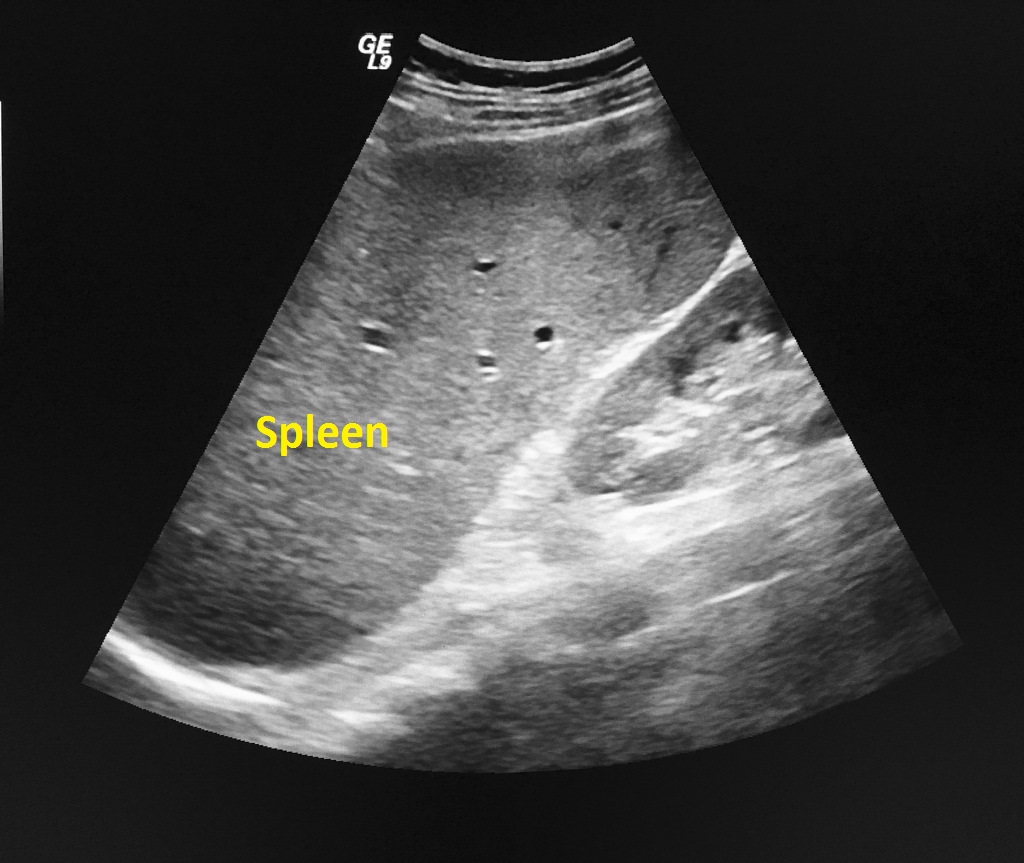 |
- Vascular changes may be appreciated on ultrasound, particularly with color doppler imaging:[10][11][12][13][14][15]
- Increased flow across both portal and systemic circulation
- Increase in resistive index in end stage liver disease
- Elongated and tortuous appearance of vessels, called "corkscrewing"
- Spontaneous shunts seen on Doppler ultrasound
- Re-canalization of umbilical vein -- pathognomonic of portal hypertension
- Porto-systemic collaterals
- Findings of portal hypertension:[16]
- Increased diameter of the portal vein
- Presence of collateral veins
- Decreased flow within the portal circulation on Doppler imaging
- Ultrasonography may be used as a screening test for hepatocellular carcinoma as nodules on ultrasonography warrant further evaluation.
- Ultrasonography may also help rule out biliary obstruction in cirrhotic patients with jaundice.
{{#ev:youtube|AYb9NrZoSLs}}
| lKkmWFm6xSw|500}} |
Echo-Doppler
- Findings on an echo-doppler suggestive of cirrhosis with portal hypertension include:[17]
- Lack of increase in portal vein diameter in response to meals
- Increased portal blood flow velocity
- Decreased portal vein cross-sectional area
Color-Doppler Ultrasound
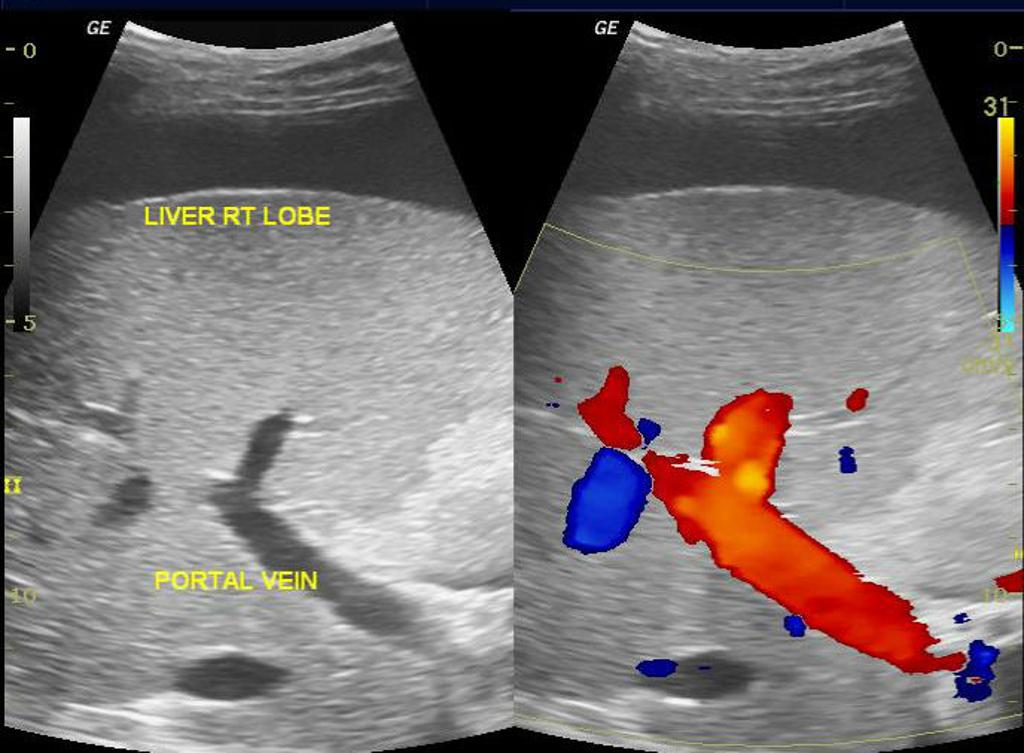 |
- Findings on an color-doppler ultrasound suggestive of cirrhosis with portal hypertension include:[18][16][19]
- Diameter and velocity in left gastric vein are significantly associated with incident of esophageal varices
- Increased diameter of left gastric vein
- Increased diameter of portal vein
- Increased flow velocity in left gastric vein
- Biphasic and reverse flow in portal vein -- pathognomonic of portal hypertension
Transient Elastography
- Transient elastography and the Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) technique are well-established methods for the staging of fibrosis in various liver diseases: [20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30]
- The FibroScan (transient elastography) uses elastic waves to determine liver stiffness which theoretically may be converted into a liver score.
- The FibroScan produces an ultrasound image of the liver (from 20-80mm) along with a pressure reading (in kPa).
- Transient elastography is much faster than a biopsy (usually lasts 2.5-5 minutes) and is completely painless.
- Findings on transient elastography may show reasonable correlation with the severity of cirrhosis:[31][32]
References
- ↑ Udell JA, Wang CS, Tinmouth J, FitzGerald JM, Ayas NT, Simel DL, Schulzer M, Mak E, Yoshida EM (2012). "Does this patient with liver disease have cirrhosis?". JAMA. 307 (8): 832–42. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.186. PMID 22357834.
- ↑ Becker CD, Scheidegger J, Marincek B (1986). "Hepatic vein occlusion: morphologic features on computed tomography and ultrasonography". Gastrointest Radiol. 11 (4): 305–11. PMID 3533689.
- ↑ Di Lelio A, Cestari C, Lomazzi A, Beretta L (1989). "Cirrhosis: diagnosis with sonographic study of the liver surface". Radiology. 172 (2): 389–92. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.2.2526349. PMID 2526349.
- ↑ Sanford NL, Walsh P, Matis C, Baddeley H, Powell LW (1985). "Is ultrasonography useful in the assessment of diffuse parenchymal liver disease?". Gastroenterology. 89 (1): 186–91. PMID 3891495.
- ↑ Giorgio A, Amoroso P, Lettieri G, Fico P, de Stefano G, Finelli L, Scala V, Tarantino L, Pierri P, Pesce G (1986). "Cirrhosis: value of caudate to right lobe ratio in diagnosis with US". Radiology. 161 (2): 443–5. doi:10.1148/radiology.161.2.3532188. PMID 3532188.
- ↑ Simonovský V (1999). "The diagnosis of cirrhosis by high resolution ultrasound of the liver surface". Br J Radiol. 72 (853): 29–34. doi:10.1259/bjr.72.853.10341686. PMID 10341686.
- ↑ Trinchet JC, Chaffaut C, Bourcier V, Degos F, Henrion J, Fontaine H, Roulot D, Mallat A, Hillaire S, Cales P, Ollivier I, Vinel JP, Mathurin P, Bronowicki JP, Vilgrain V, N'Kontchou G, Beaugrand M, Chevret S (2011). "Ultrasonographic surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a randomized trial comparing 3- and 6-month periodicities". Hepatology. 54 (6): 1987–97. doi:10.1002/hep.24545. PMID 22144108.
- ↑ "EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma". J. Hepatol. 56 (4): 908–43. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001. PMID 22424438.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29199">rID: 29199
- ↑ Di Lelio A, Cestari C, Lomazzi A, Beretta L (1989). "Cirrhosis: diagnosis with sonographic study of the liver surface". Radiology. 172 (2): 389–92. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.2.2526349. PMID 2526349.
- ↑ Martínez-Noguera A, Montserrat E, Torrubia S, Villalba J (2002). "Doppler in hepatic cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis". Semin. Ultrasound CT MR. 23 (1): 19–36. PMID 11866220.
- ↑ Tchelepi H, Ralls PW, Radin R, Grant E (2002). "Sonography of diffuse liver disease". J Ultrasound Med. 21 (9): 1023–32, quiz 1033–4. PMID 12216750.
- ↑ Awaya H, Mitchell DG, Kamishima T, Holland G, Ito K, Matsumoto T (2002). "Cirrhosis: modified caudate-right lobe ratio". Radiology. 224 (3): 769–74. doi:10.1148/radiol.2243011495. PMID 12202712.
- ↑ Albrecht T, Blomley MJ, Cosgrove DO, Taylor-Robinson SD, Jayaram V, Eckersley R, Urbank A, Butler-Barnes J, Patel N (1999). "Non-invasive diagnosis of hepatic cirrhosis by transit-time analysis of an ultrasound contrast agent". Lancet. 353 (9164): 1579–83. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)06373-9. PMID 10334257.
- ↑ Zwiebel WJ (1995). "Sonographic diagnosis of hepatic vascular disorders". Semin. Ultrasound CT MR. 16 (1): 34–48. PMID 7718281.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Portal hypertension | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org".
- ↑ Sabbà C, Ferraioli G, Buonamico P, Berardi E, Antonica G, Taylor KJ, Albano O (1992). "Echo-Doppler evaluation of acute flow changes in portal hypertensive patients: flow velocity as a reliable parameter". J. Hepatol. 15 (3): 356–60. PMID 1447502.
- ↑ Yin XY, Lu MD, Huang JF, Xie XY, Liang LJ (2001). "Color Doppler velocity profile assessment of portal hemodynamics in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension: correlation with esophageal variceal bleeding". J Clin Ultrasound. 29 (1): 7–13. PMID 11180179.
- ↑ Li FH, Hao J, Xia JG, Li HL, Fang H (2005). "Hemodynamic analysis of esophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis using color Doppler ultrasound". World J Gastroenterol. 11 (29): 4560–5. PMC 4398708. PMID 16052688.
- ↑ Castera L, Pinzani M (2010). "Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango?". Gut. 59 (7): 861–6. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.214650. PMID 20581229.
- ↑ Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M, Sporea I, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Strobel D, Takahashi H, Yoneda M, Suda T, Zeuzem S, Herrmann E (2012). "Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis". J. Viral Hepat. 19 (2): e212–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01537.x. PMID 22239521.
- ↑ Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, Sarrazin C, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, Herrmann E (2008). "Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis". Gastroenterology. 134 (4): 960–74. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.034. PMID 18395077.
- ↑ Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, de Lédinghen V, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M (2005). "Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C". Hepatology. 41 (1): 48–54. doi:10.1002/hep.20506. PMID 15690481.
- ↑ Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, Beaugrand M, Palau R (2003). "Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis". Ultrasound Med Biol. 29 (12): 1705–13. PMID 14698338.
- ↑ Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F, Cantisani V, Correas JM, D'Onofrio M, Drakonaki EE, Fink M, Friedrich-Rust M, Gilja OH, Havre RF, Jenssen C, Klauser AS, Ohlinger R, Saftoiu A, Schaefer F, Sporea I, Piscaglia F (2013). "EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: Basic principles and technology". Ultraschall Med. 34 (2): 169–84. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1335205. PMID 23558397.
- ↑ "EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis". J. Hepatol. 63 (1): 237–64. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.006. PMID 25911335.
- ↑ Castera L, Bedossa P (2011). "How to assess liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: serum markers or transient elastography vs. liver biopsy?". Liver Int. 31 Suppl 1: 13–7. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02380.x. PMID 21205132.
- ↑ Chou R, Wasson N (2013). "Blood tests to diagnose fibrosis or cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review". Ann. Intern. Med. 158 (11): 807–20. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00005. PMID 23732714.
- ↑ Khallafi H, Qureshi K (2015). "Imaging Based Methods of Liver Fibrosis Assessment in Viral Hepatitis: A Practical Approach". Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2015: 809289. doi:10.1155/2015/809289. PMC 4686715. PMID 26779260.
- ↑ Singh S, Fujii LL, Murad MH, Wang Z, Asrani SK, Ehman RL, Kamath PS, Talwalkar JA (2013). "Liver stiffness is associated with risk of decompensation, liver cancer, and death in patients with chronic liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11 (12): 1573–84.e1–2, quiz e88–9. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.034. PMC 3900882. PMID 23954643.
- ↑ Foucher J, Chanteloup E, Vergniol J; et al. (2006). "Diagnosis of cirrhosis by transient elastography (FibroScan): a prospective study". Gut. 55 (3): 403–8. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.069153. PMID 16020491.
- ↑ Xie L, Chen X, Guo Q, Dong Y, Guang Y, Zhang X (2012). "Real-time elastography for diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B". Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine : Official Journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 31 (7): 1053–60. PMID 22733854.