Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include [[bone marrow aspiration]] and [[biopsy]], [[lumbar puncture]], and [[lymph node biopsy]]. | Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include [[bone marrow aspiration]] and [[biopsy]], [[lumbar puncture]], and [[lymph node biopsy]]. | ||
==Other diagnostic studies== | ==Other diagnostic studies== | ||
Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include: | Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include:<ref name="cancer.ca">Canadian Cancer Society.2015.http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/leukemia-chronic-myelogenous-cml/diagnosis/?region=ab</ref> | ||
*[[Bone marrow aspiration]] and [[biopsy]] | *[[Bone marrow aspiration]] and [[biopsy]] | ||
:*Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells | :*Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*[[Lymph node biopsy]] | *[[Lymph node biopsy]] | ||
:*Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells | :*Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells | ||
==Gallery== | ==Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=400px class="center"> | |||
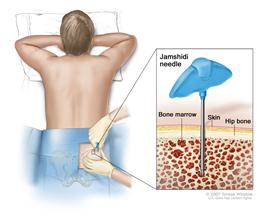
<gallery> | CDR554337-274.jpg| Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. After a small area of skin is numbed, a Jamshidi needle (a long, hollow needle) is inserted into the patient’s hip bone. Samples of blood, bone, and bone marrow are removed for examination under a microscope. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 9 October 2015
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Chronic myelogenous leukemia from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies |
|
FDA on Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies |
|
CDC on Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies |
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies in the news |
|
Blogs on Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Chronic myelogenous leukemia |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Chronic myelogenous leukemia other diagnostic studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamad Alkateb, MBBCh [2]
Overview
Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include bone marrow aspiration and biopsy, lumbar puncture, and lymph node biopsy.
Other diagnostic studies
Other diagnostic studies for chronic myelogenous leukemia include:[1]
- Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells
- Used to detect any metastasis to the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
- Used to detect and/or determine the type of leukemic cells
Gallery
-
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. After a small area of skin is numbed, a Jamshidi needle (a long, hollow needle) is inserted into the patient’s hip bone. Samples of blood, bone, and bone marrow are removed for examination under a microscope.
References
- ↑ Canadian Cancer Society.2015.http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/leukemia-chronic-myelogenous-cml/diagnosis/?region=ab