Chest pain x ray: Difference between revisions
Aisha Adigun (talk | contribs) (→X Ray) |
Aisha Adigun (talk | contribs) (→X Ray) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==X Ray== | ==X Ray== | ||
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of common causes of chest pain. Findings on an x-ray include: | An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of common causes of chest pain. Findings on an x-ray include: | ||
*'''Aortic dissection<ref>de Lacey G, Morley S et-al. The Chest X-Ray: A Survival Guide. Saunders Ltd. ISBN:0702030465. </ref><ref name="pmid22415593">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lai V, Tsang WK, Chan WC, Yeung TW |title=Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection |journal=Emerg Radiol |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=309–15 |date=August 2012 |pmid=22415593 |pmc=3396328 |doi=10.1007/s10140-012-1034-3 |url=}}</ref><ref> Gleeson CE, Spedding RL, Harding LA, et al The mediastinum—Is it wide? Emergency Medicine Journal 2001;18:183-185.</ref>''' | *'''Aortic dissection<ref>de Lacey G, Morley S et-al. The Chest X-Ray: A Survival Guide. Saunders Ltd. ISBN:0702030465. </ref><ref name="pmid22415593">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lai V, Tsang WK, Chan WC, Yeung TW |title=Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection |journal=Emerg Radiol |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=309–15 |date=August 2012 |pmid=22415593 |pmc=3396328 |doi=10.1007/s10140-012-1034-3 |url=}}</ref><ref> Gleeson CE, Spedding RL, Harding LA, et al The mediastinum—Is it wide? Emergency Medicine Journal 2001;18:183-185.</ref>''' | ||
**Widened mediastinum, (> 8cm at the level of the aortic knob on portable AP chest radiographs) | **[[Widened mediastinum]], (> 8cm at the level of the aortic knob on portable [[Chest X-ray|AP chest radiographs]]) | ||
**Left pleural effusion | **Left [[pleural effusion]] | ||
**double and irregular aortic contour | **double and irregular aortic contour | ||
**Displaced intimal calcification >5mm (ring sign) | **Displaced [[Tunica intima|intimal]] [[Calcification of the aorta|calcification]] >5mm (ring sign) | ||
**Esophageal and tracheal deviation to the right | **[[Esophagus|Esophageal]] and [[tracheal deviation]] to the right | ||
**Blurred aortic knob | **Blurred aortic knob | ||
**Depression of left mainstem bronchus | **Depression of left [[mainstem bronchus]] | ||
**Apical capping on the left | **Apical capping on the left | ||
**Loss of paratracheal stripe | **Loss of paratracheal stripe | ||
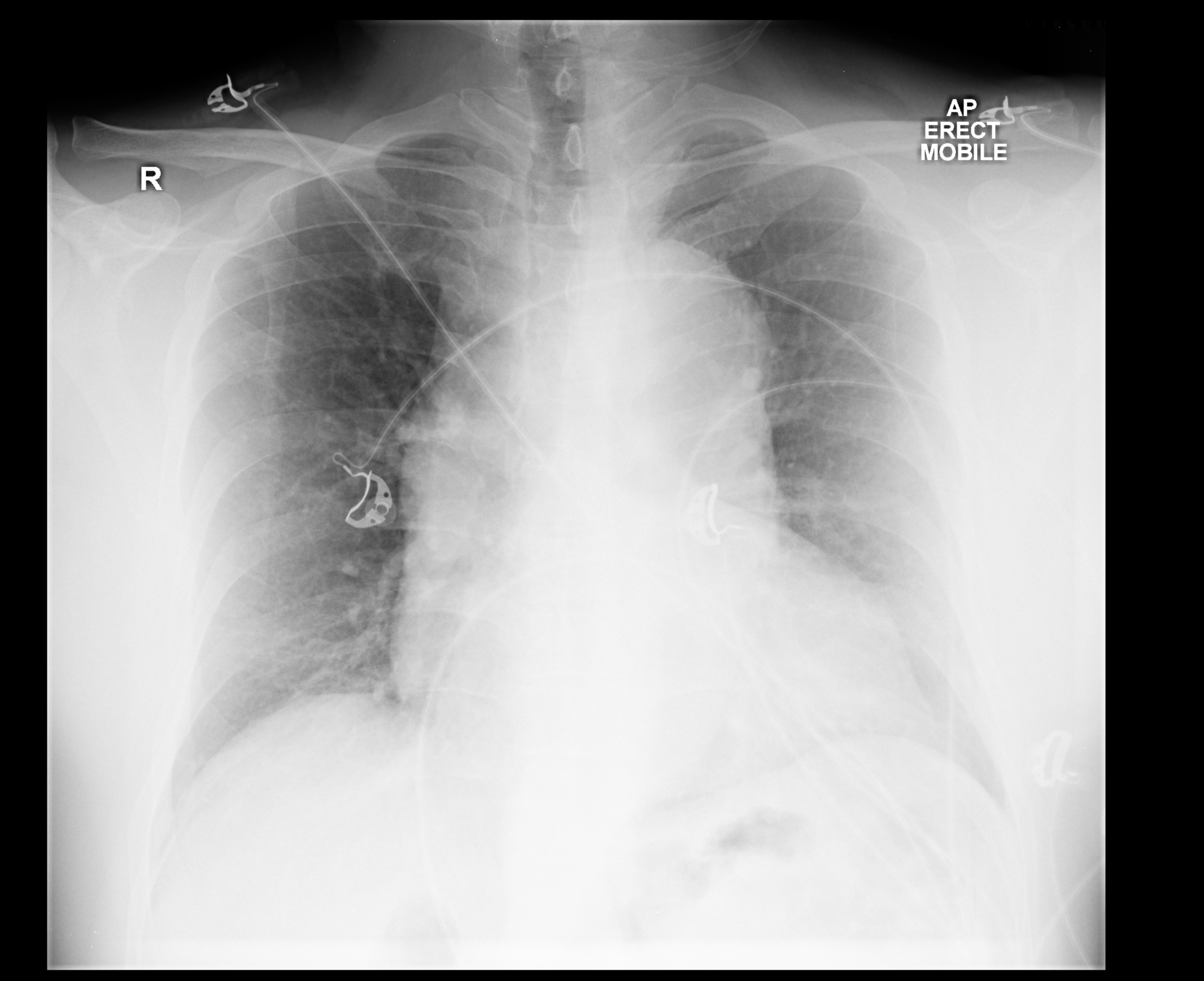
[[File:Aortic-dissection-23.png|thumb|left|500px|Aortic dissection with marked widening of the mediastinum<ref>Case courtesy of Dr Wayland Wang, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50763</ref>]] | [[File:Aortic-dissection-23.png|thumb|left|500px|Aortic dissection with marked widening of the mediastinum<ref>Case courtesy of Dr Wayland Wang, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50763</ref>]] | ||
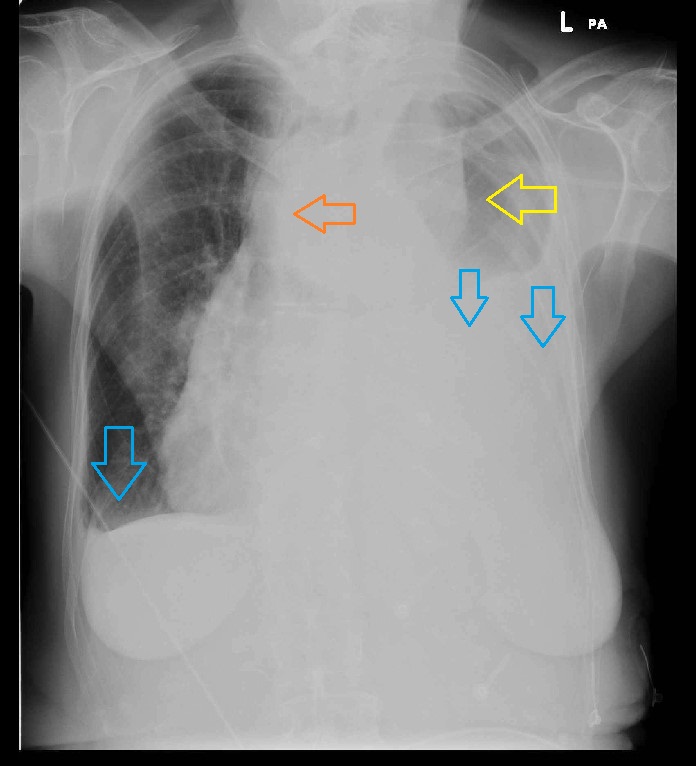
[[File:Aortic-dissection-34.jpeg|thumb|center|400px|Aortic dissection with marked pleural effusion (blue arrow), left upper mediastinal mass (yellow arrow), and tracheal deviation (orange arrow)<ref>Case courtesy of Dr Devanshi Pathania, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 68763</ref>]] | [[File:Aortic-dissection-34.jpeg|thumb|center|400px|Aortic dissection with marked pleural effusion (blue arrow), left upper mediastinal mass (yellow arrow), and tracheal deviation (orange arrow)<ref>Case courtesy of Dr Devanshi Pathania, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 68763</ref>]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name]. However, an x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include: | There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name]. However, an x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include: | ||
*[Complication 1] | *[Complication 1] | ||
*[Complication 2] | *[Complication 2] | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 29 August 2020
|
Chest pain Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chest pain x ray On the Web |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aisha Adigun, B.Sc., M.D.[2]
Overview
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name].
OR
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of [disease name]. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of/diagnostic of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name]. However, an x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include [complication 1], [complication 2], and [complication 3].
X Ray
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of common causes of chest pain. Findings on an x-ray include:
- Aortic dissection[1][2][3]
- Widened mediastinum, (> 8cm at the level of the aortic knob on portable AP chest radiographs)
- Left pleural effusion
- double and irregular aortic contour
- Displaced intimal calcification >5mm (ring sign)
- Esophageal and tracheal deviation to the right
- Blurred aortic knob
- Depression of left mainstem bronchus
- Apical capping on the left
- Loss of paratracheal stripe
OR
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name]. However, an x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include:
- [Complication 1]
- [Complication 2]
- [Complication 3]
References
- ↑ de Lacey G, Morley S et-al. The Chest X-Ray: A Survival Guide. Saunders Ltd. ISBN:0702030465.
- ↑ Lai V, Tsang WK, Chan WC, Yeung TW (August 2012). "Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection". Emerg Radiol. 19 (4): 309–15. doi:10.1007/s10140-012-1034-3. PMC 3396328. PMID 22415593.
- ↑ Gleeson CE, Spedding RL, Harding LA, et al The mediastinum—Is it wide? Emergency Medicine Journal 2001;18:183-185.
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Wayland Wang, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50763
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Devanshi Pathania, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 68763