Cerebral palsy medical therapy: Difference between revisions
Iqra Qamar (talk | contribs) (Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Cerebral palsy}} {{CMG}}; {{AE}} ==Overview== There is no treatment for [disease name]; the mainstay of therapy is supportive care. OR Supportive therapy for [...") |
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Cerebral palsy}} | {{Cerebral palsy}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{AY}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Pharmacologic medical therapies for cerebral palsy include [[botulinum]] toxin, intrathecal [[baclofen]], and oral antispastics. The management of cerebral palsy should be individualized according to the patient's need and status of the disease. The disease itself is not progressive but the presentations might change with the maturation of the [[brain]] and the development of the [[skeletal system]]. Medical therapy aims at improvement of the motor function through relieving the spasticity of the [[limbs]] and preventing the occurrence of [[convulsions]]. | |||
==Medical Therapy== | |||
===Botulinum toxin=== | |||
*[[Botulinum toxin]] acts on the [[neuromuscular junction]] preventing the release of [[acetylcholine]].<ref name="pmid17606561">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bjornson K, Hays R, Graubert C, Price R, Won F, McLaughlin JF, Cohen M |title=Botulinum toxin for spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: a comprehensive evaluation |journal=Pediatrics |volume=120 |issue=1 |pages=49–58 |year=2007 |pmid=17606561 |pmc=1920182 |doi=10.1542/peds.2007-0016 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*It has a relaxant effect on the muscles undergoing contractures. | |||
*Primarily used if there are contractures causing [[deformity]] or jeopardizing the nearby joints.<ref name="pmid17606561">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bjornson K, Hays R, Graubert C, Price R, Won F, McLaughlin JF, Cohen M |title=Botulinum toxin for spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: a comprehensive evaluation |journal=Pediatrics |volume=120 |issue=1 |pages=49–58 |year=2007 |pmid=17606561 |pmc=1920182 |doi=10.1542/peds.2007-0016 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*The injections cause temporary improvement in the function of the affected limbs. | |||
*[[Botulinum toxin]] injections may decrease the [[joint]] and [[bone]] deformities resulting from the contractures especially if combined with casting.<ref name="pmid21629371">{{cite journal |vauthors=Molenaers G, Van Campenhout A, Fagard K, De Cat J, Desloovere K |title=The use of botulinum toxin A in children with cerebral palsy, with a focus on the lower limb |journal=J Child Orthop |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=183–95 |year=2010 |pmid=21629371 |pmc=2866843 |doi=10.1007/s11832-010-0246-x |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Children under four years in the early stages of contractures are the most category of patients to benefit from [[botulinum toxin]].<ref name="pmid12474176">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murphy NA, Irwin MC, Hoff C |title=Intrathecal baclofen therapy in children with cerebral palsy: efficacy and complications |journal=Arch Phys Med Rehabil |volume=83 |issue=12 |pages=1721–5 |year=2002 |pmid=12474176 |doi=10.1053/apmr.2002.36068 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Botulinum toxin delays the need for a surgery and decreases the magnitude of intervention.<ref name="pmid8959459">{{cite journal |vauthors=Albright AL |title=Intrathecal baclofen in cerebral palsy movement disorders |journal=J. Child Neurol. |volume=11 Suppl 1 |issue= |pages=S29–35 |year=1996 |pmid=8959459 |doi=10.1177/0883073896011001S05 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*The effect is temporary and the injection has to be repeated every three to six months. | |||
*Generalized [[weakness]] due to the global effect of the drug was reported. | |||
*The dose of [[botulinum]] toxin A is 20-30 unit/kg divided between the injected limbs. The dose should not exceed 1000 units. | |||
The | |||
{{#ev:youtube|l7l0csoCQkM}} | |||
===Intrathecal baclofen=== | |||
*[[Baclofen]] is administered through a pump into the [[subarachnoid]] space.<ref name="pmid21480874">{{cite journal |vauthors=Motta F, Antonello CE, Stignani C |title=Intrathecal baclofen and motor function in cerebral palsy |journal=Dev Med Child Neurol |volume=53 |issue=5 |pages=443–8 |year=2011 |pmid=21480874 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03904.x |url=}}</ref> | |||
*It can achieve higher [[CSF]] levels of the drug with less side effects. | |||
*It acts by blocking the I-a sensory afferents. | |||
*It is indicated in the patients with the highest of [[spasticity]] that is causing dysfunction and pain not responding to the more conventional methods of treatment. | |||
*It carries more risk of complications than other non interventional lines of treatment.<ref name="pmid15840761">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mathew A, Mathew MC, Thomas M, Antonisamy B |title=The efficacy of diazepam in enhancing motor function in children with spastic cerebral palsy |journal=J. Trop. Pediatr. |volume=51 |issue=2 |pages=109–13 |year=2005 |pmid=15840761 |doi=10.1093/tropej/fmh095 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*The pump must refilled every month together with assessment for the occurrence of complications. | |||
*Complications such as [[hypotonia]] and [[confusion]] occur in about half of the patients. | |||
*The dose is adjusted by the physician according to the response and the development of side effects. | |||
[[Image:Intrathecal-baclofen-pump.jpeg|center|thumb|400px|Intrathecal baclofen pump - Case courtesy of Dr Yair Glick, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 55762]] | |||
{{#ev:youtube|IeS-Wr4izo4}} | |||
===Oral muscle relaxants=== | |||
====Benzodiazepines==== | |||
*Binds to [[GABA]] receptors and causes [[presynaptic]] inhibition of the neurotransmission.<ref name="pmid15799138">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mathew A, Mathew MC |title=Bedtime diazepam enhances well-being in children with spastic cerebral palsy |journal=Pediatr Rehabil |volume=8 |issue=1 |pages=63–6 |year=2005 |pmid=15799138 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Most useful for acute cases of severe [[spasticity]].<ref name="pmid5339679">{{cite journal |vauthors=Engle HA |title=The effect of diazepam (Valium) in children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind study |journal=Dev Med Child Neurol |volume=8 |issue=6 |pages=661–7 |year=1966 |pmid=5339679 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Due to its muscle relaxing effect, it can aggravate the [[swallowing]] difficulties and cause [[aspiration]]. | |||
====Baclofen==== | |||
*[[GABA]] analogue and causes presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmission.<ref name="pmid26321489">{{cite journal |vauthors=Navarrete-Opazo AA, Gonzalez W, Nahuelhual P |title=Effectiveness of Oral Baclofen in the Treatment of Spasticity in Children and Adolescents With Cerebral Palsy |journal=Arch Phys Med Rehabil |volume=97 |issue=4 |pages=604–618 |year=2016 |pmid=26321489 |doi=10.1016/j.apmr.2015.08.417 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Much less effective than [[intrathecal]] baclofen. | |||
== | ====Dantrolene==== | ||
*Direct muscle relaxant by inhibiting the release of Ca+2 from the [[sarcoplasmic reticulum]].<ref name="pmid7004956">{{cite journal |vauthors=Joynt RL, Leonard JA |title=Dantrolene sodium suspension in treatment of spastic cerebral palsy |journal=Dev Med Child Neurol |volume=22 |issue=6 |pages=755–67 |year=1980 |pmid=7004956 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Used only in the short term for treatment of acute cases of severe hypertonicity. | |||
=== | |||
* | |||
* | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:32, 9 October 2017
|
Cerebral palsy Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cerebral palsy medical therapy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cerebral palsy medical therapy |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cerebral palsy medical therapy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Younes M.B.B.CH [2]
Overview
Pharmacologic medical therapies for cerebral palsy include botulinum toxin, intrathecal baclofen, and oral antispastics. The management of cerebral palsy should be individualized according to the patient's need and status of the disease. The disease itself is not progressive but the presentations might change with the maturation of the brain and the development of the skeletal system. Medical therapy aims at improvement of the motor function through relieving the spasticity of the limbs and preventing the occurrence of convulsions.
Medical Therapy
Botulinum toxin
- Botulinum toxin acts on the neuromuscular junction preventing the release of acetylcholine.[1]
- It has a relaxant effect on the muscles undergoing contractures.
- Primarily used if there are contractures causing deformity or jeopardizing the nearby joints.[1]
- The injections cause temporary improvement in the function of the affected limbs.
- Botulinum toxin injections may decrease the joint and bone deformities resulting from the contractures especially if combined with casting.[2]
- Children under four years in the early stages of contractures are the most category of patients to benefit from botulinum toxin.[3]
- Botulinum toxin delays the need for a surgery and decreases the magnitude of intervention.[4]
- The effect is temporary and the injection has to be repeated every three to six months.
- Generalized weakness due to the global effect of the drug was reported.
- The dose of botulinum toxin A is 20-30 unit/kg divided between the injected limbs. The dose should not exceed 1000 units.
{{#ev:youtube|l7l0csoCQkM}}
Intrathecal baclofen
- Baclofen is administered through a pump into the subarachnoid space.[5]
- It can achieve higher CSF levels of the drug with less side effects.
- It acts by blocking the I-a sensory afferents.
- It is indicated in the patients with the highest of spasticity that is causing dysfunction and pain not responding to the more conventional methods of treatment.
- It carries more risk of complications than other non interventional lines of treatment.[6]
- The pump must refilled every month together with assessment for the occurrence of complications.
- Complications such as hypotonia and confusion occur in about half of the patients.
- The dose is adjusted by the physician according to the response and the development of side effects.
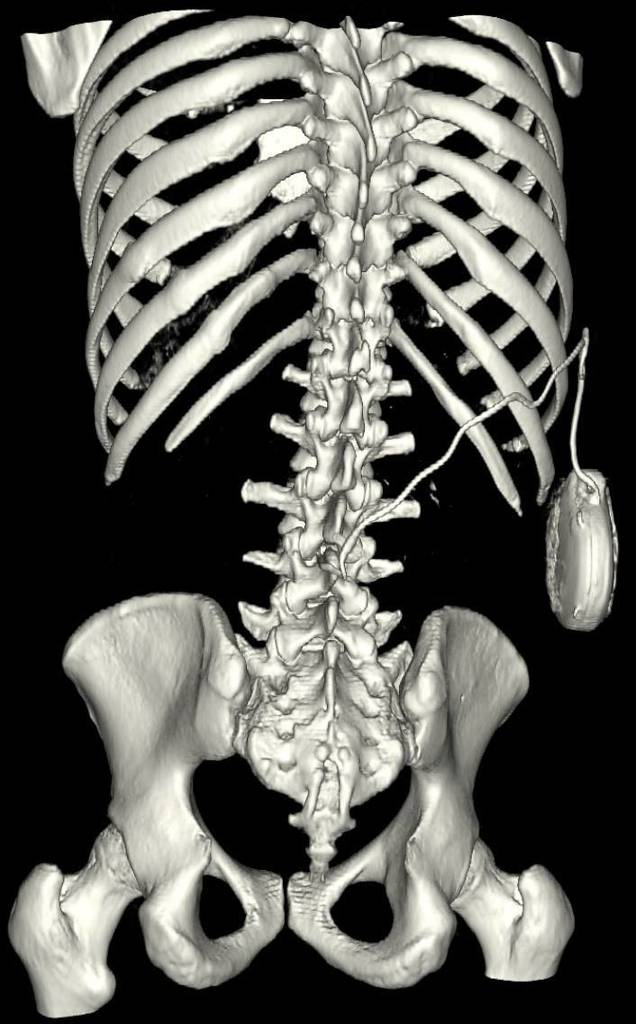
{{#ev:youtube|IeS-Wr4izo4}}
Oral muscle relaxants
Benzodiazepines
- Binds to GABA receptors and causes presynaptic inhibition of the neurotransmission.[7]
- Most useful for acute cases of severe spasticity.[8]
- Due to its muscle relaxing effect, it can aggravate the swallowing difficulties and cause aspiration.
Baclofen
- GABA analogue and causes presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmission.[9]
- Much less effective than intrathecal baclofen.
Dantrolene
- Direct muscle relaxant by inhibiting the release of Ca+2 from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.[10]
- Used only in the short term for treatment of acute cases of severe hypertonicity.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bjornson K, Hays R, Graubert C, Price R, Won F, McLaughlin JF, Cohen M (2007). "Botulinum toxin for spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: a comprehensive evaluation". Pediatrics. 120 (1): 49–58. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-0016. PMC 1920182. PMID 17606561.
- ↑ Molenaers G, Van Campenhout A, Fagard K, De Cat J, Desloovere K (2010). "The use of botulinum toxin A in children with cerebral palsy, with a focus on the lower limb". J Child Orthop. 4 (3): 183–95. doi:10.1007/s11832-010-0246-x. PMC 2866843. PMID 21629371.
- ↑ Murphy NA, Irwin MC, Hoff C (2002). "Intrathecal baclofen therapy in children with cerebral palsy: efficacy and complications". Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 83 (12): 1721–5. doi:10.1053/apmr.2002.36068. PMID 12474176.
- ↑ Albright AL (1996). "Intrathecal baclofen in cerebral palsy movement disorders". J. Child Neurol. 11 Suppl 1: S29–35. doi:10.1177/0883073896011001S05. PMID 8959459.
- ↑ Motta F, Antonello CE, Stignani C (2011). "Intrathecal baclofen and motor function in cerebral palsy". Dev Med Child Neurol. 53 (5): 443–8. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03904.x. PMID 21480874.
- ↑ Mathew A, Mathew MC, Thomas M, Antonisamy B (2005). "The efficacy of diazepam in enhancing motor function in children with spastic cerebral palsy". J. Trop. Pediatr. 51 (2): 109–13. doi:10.1093/tropej/fmh095. PMID 15840761.
- ↑ Mathew A, Mathew MC (2005). "Bedtime diazepam enhances well-being in children with spastic cerebral palsy". Pediatr Rehabil. 8 (1): 63–6. PMID 15799138.
- ↑ Engle HA (1966). "The effect of diazepam (Valium) in children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind study". Dev Med Child Neurol. 8 (6): 661–7. PMID 5339679.
- ↑ Navarrete-Opazo AA, Gonzalez W, Nahuelhual P (2016). "Effectiveness of Oral Baclofen in the Treatment of Spasticity in Children and Adolescents With Cerebral Palsy". Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 97 (4): 604–618. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2015.08.417. PMID 26321489.
- ↑ Joynt RL, Leonard JA (1980). "Dantrolene sodium suspension in treatment of spastic cerebral palsy". Dev Med Child Neurol. 22 (6): 755–67. PMID 7004956.