C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) is a plasma-derived concentrate of C1 Esterase Inhibitor (Human) (C1-INH) that is FDA approved for the prevention of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) attacks. Common adverse reactions include injection site reaction, hypersensitivity, nasopharyngitis and dizziness.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
- HAEGARDA is contraindicated in individuals who have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to C1-INH preparations or its excipients.
Warnings
Hypersensitivity
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur. The signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions may include hives (local and generalized), tightness of the chest, difficulty breathing, wheezing, hypotension, and/or anaphylaxis during or after injection of HAEGARDA. In case of severe hypersensitivity, discontinue HAEGARDA administration and institute appropriate treatment. Epinephrine should be immediately available for treatment of severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Thromboembolic Events
- At the recommended subcutaneous dose, a causal relationship between thromboembolic events (TEEs) and the use of HAEGARDA has not been established. Thrombosis has occurred in treatment attempts with high doses of C1-INH intravenous (I.V.) for prevention or therapy of capillary leak syndrome before, during or after cardiac surgery (unapproved indication and dose).
Transmissible Infectious Agents
- Because HAEGARDA is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. The risk that such products will transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing for the presence of certain current virus infections, and by processes demonstrated to inactivate and/or remove certain viruses during manufacturing. Despite these measures, such products may still contain human pathogenic agents, including those not yet known or identified. Thus, the risk of transmission of infectious agents cannot be totally eliminated.
- All infections thought by a physician possibly to have been transmitted by HAEGARDA should be reported by lot number, by the physician or other healthcare provider, to the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Of the 90 subjects randomized in the double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study, 86 subjects received at least one dose of HAEGARDA and 86 subjects received at least one dose of placebo (Table 2). A total of 5081 injections of HAEGARDA and placebo were administered over a range of 3 to 19 weeks (median of 16.6 weeks for HAEGARDA; median of 16.3 weeks for placebo).
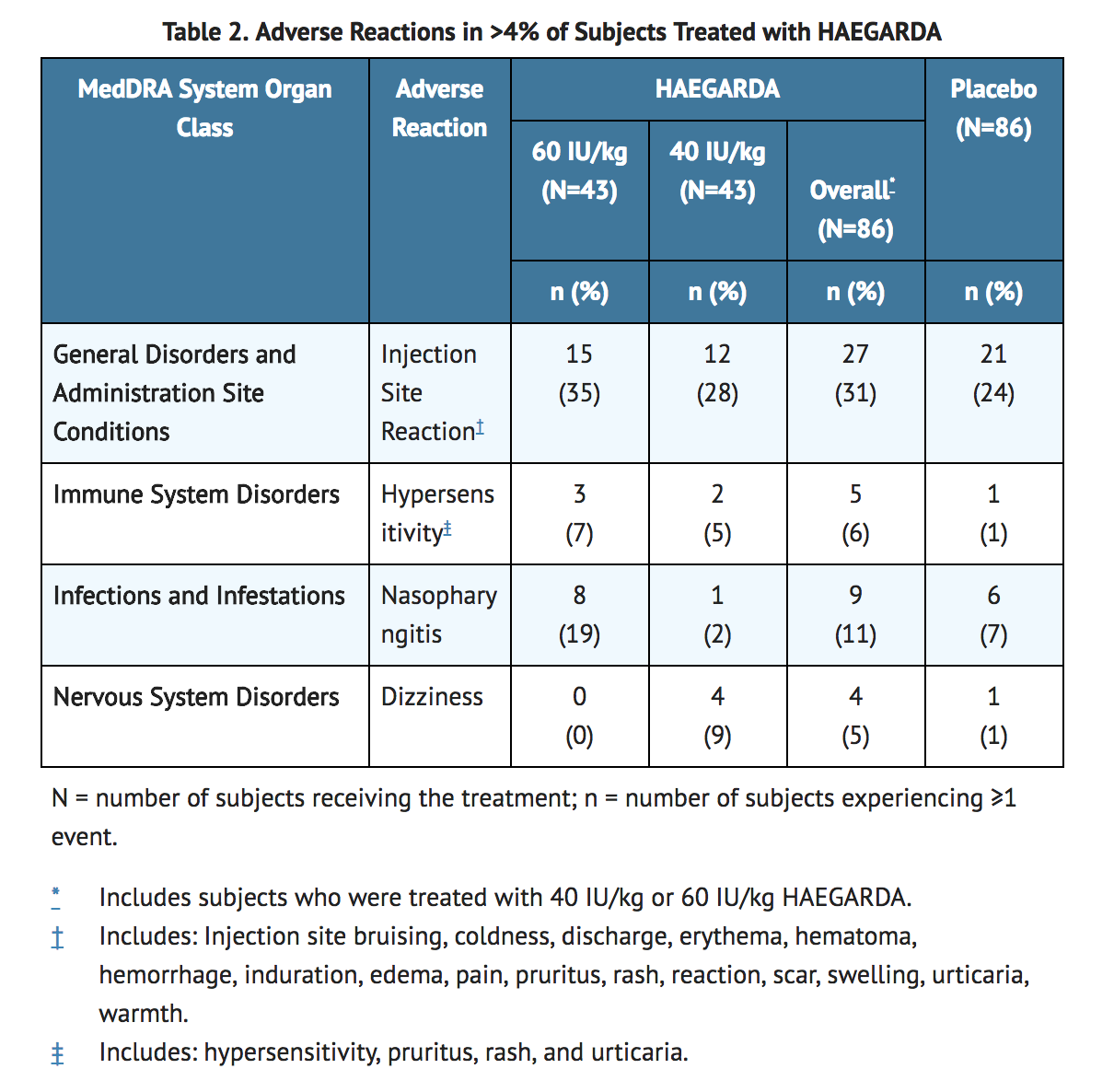
- Of the injection site reactions occurring after treatment with HAEGARDA, 95% were of mild intensity and 83% resolved within 1 day after onset.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- No case of overdose has been reported. Doses corresponding to up to 117 IU/kg S.C. have been administered twice weekly in a fixed-dose clinical study.
Pharmacology
C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda)
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- C1-INH is a normal constituent of human plasma and belongs to the group of serine protease inhibitors (serpins) that includes antithrombin III, alpha1-protease inhibitor, alpha2-antiplasmin, and heparin cofactor II. As with the other inhibitors in this group, C1-INH has an important inhibiting potential on several of the major human cascade systems, including the complement, fibrinolytic and coagulation systems. Regulation of these systems is performed through the formation of complexes between the protease and the inhibitor, resulting in inactivation of both and consumption of the C1-INH.
- C1-INH, which is usually activated during the inflammatory process, inactivates its substrate by covalently binding to the reactive site. C1-INH is the only known inhibitor for the C1r and C1s subcomponents of complement component 1 (C1), coagulation factor XIIa, and plasma kallikrein. Additionally, C1-INH is the main inhibitor for coagulation factor XIa of the intrinsic coagulation cascade.
- HAE patients have absence or low levels of endogenous or functional C1-INH. Although the events that cause attacks of angioedema in HAE patients are not well defined, it has been postulated that increased vascular permeability and the clinical manifestation of HAE attacks may be primarily mediated through contact system activation. Suppression of contact system activation by C1-INH through the inactivation of plasma kallikrein and factor XIIa is thought to modulate this vascular permeability by preventing the generation of bradykinin. Administration of HAEGARDA replaces the missing or malfunctioning C1-INH protein in patients with HAE.
Structure
There is limited information regarding C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
- In untreated patients, insufficient levels of functional C1-INH lead to increased activation of C1, which results in decreased levels of complement component 4 (C4). The administration of HAEGARDA increases plasma levels of C1-INH in a dose-dependent manner and subsequently increases plasma concentrations of C4. The C4 plasma concentrations after S.C. administration of 60 IU/kg HAEGARDA were in the normal range (16 to 38 mg/dL).
Pharmacokinetics
- The pharmacokinetics (PK) of C1-INH were described using population PK analysis.
- The PK parameters of C1-INH following twice weekly subcutaneous 60 IU/kg dosing are shown in Table 4.
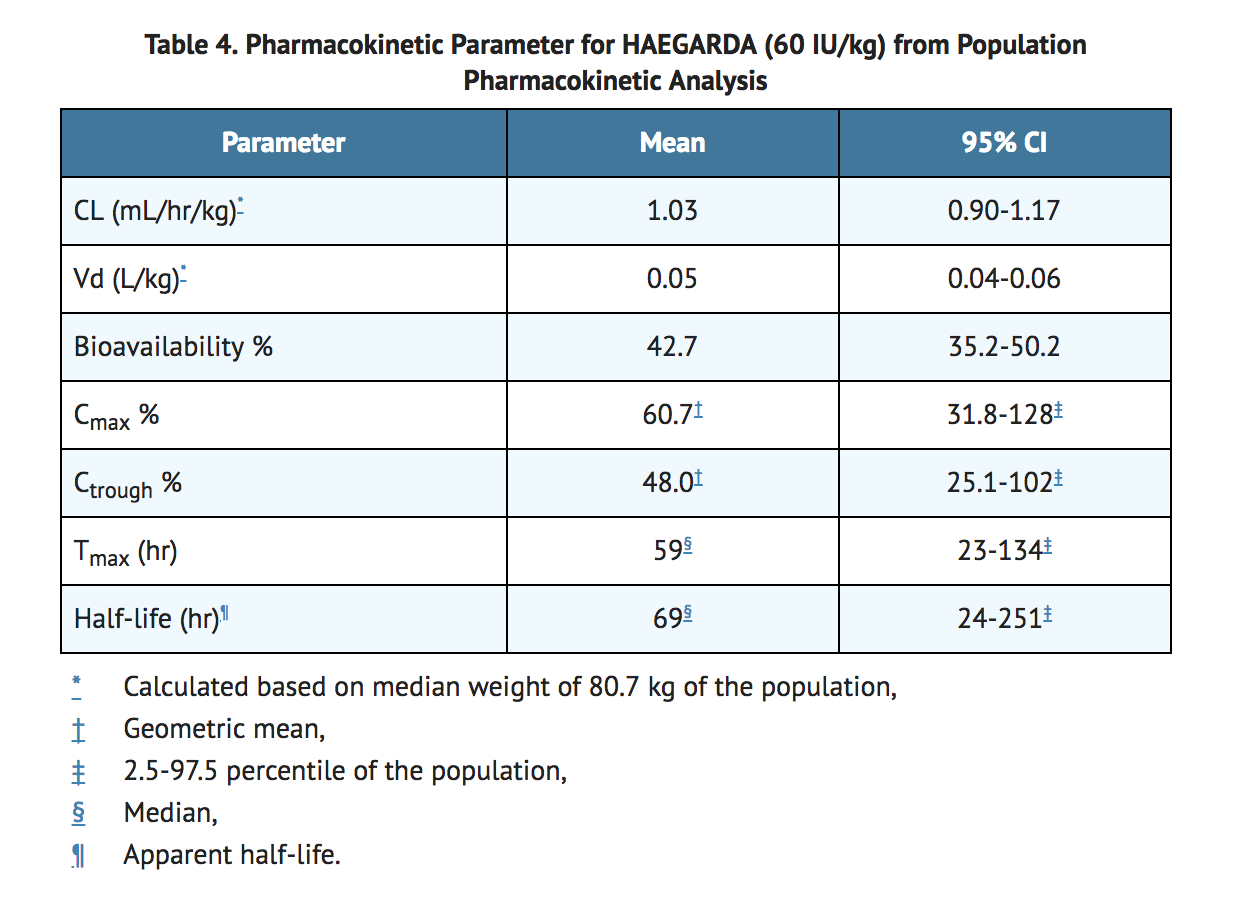
- The steady state PK of S.C. C1-INH is independent of dose between 20-80 IU/kg in HAE subjects.
- Studies have not been conducted to evaluate the PK of C1-INH in specific patient populations stratified by gender, race, age, or the presence of renal or hepatic impairment. The PK of C1-INH was not influenced at the age range of 12-72 years.
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
- The efficacy and safety of HAEGARDA for routine prophylaxis to prevent HAE attacks were demonstrated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. The study assessed 90 adult and adolescent subjects with symptomatic HAE type I or II. The median (range) age of subjects was 40 (12 to 72) years; 60 subjects were female and 30 subjects were male. Subjects were randomized to receive either 60 IU/kg or 40 IU/kg HAEGARDA in one 16-week treatment period and placebo in the other 16-week treatment period. Patients self-administered HAEGARDA or placebo subcutaneously 2 times per week. Efficacy was evaluated for the last 14 weeks of each treatment period.
- Twice per week S.C. doses of 60 IU/kg or 40 IU/kg HAEGARDA resulted in a significant difference in the time-normalized number of HAE attacks (the rate of attacks) relative to placebo (Table 5). The time normalized number of HAE attacks in subjects dosed with 60 IU/kg was 0.52 attacks per month compared to 4.03 attacks per month while receiving placebo (p <0.001). The time normalized number of HAE attacks in subjects dosed with 40 IU/kg was 1.19 attacks per month compared to 3.61 attacks per month while receiving placebo (p <0.001).
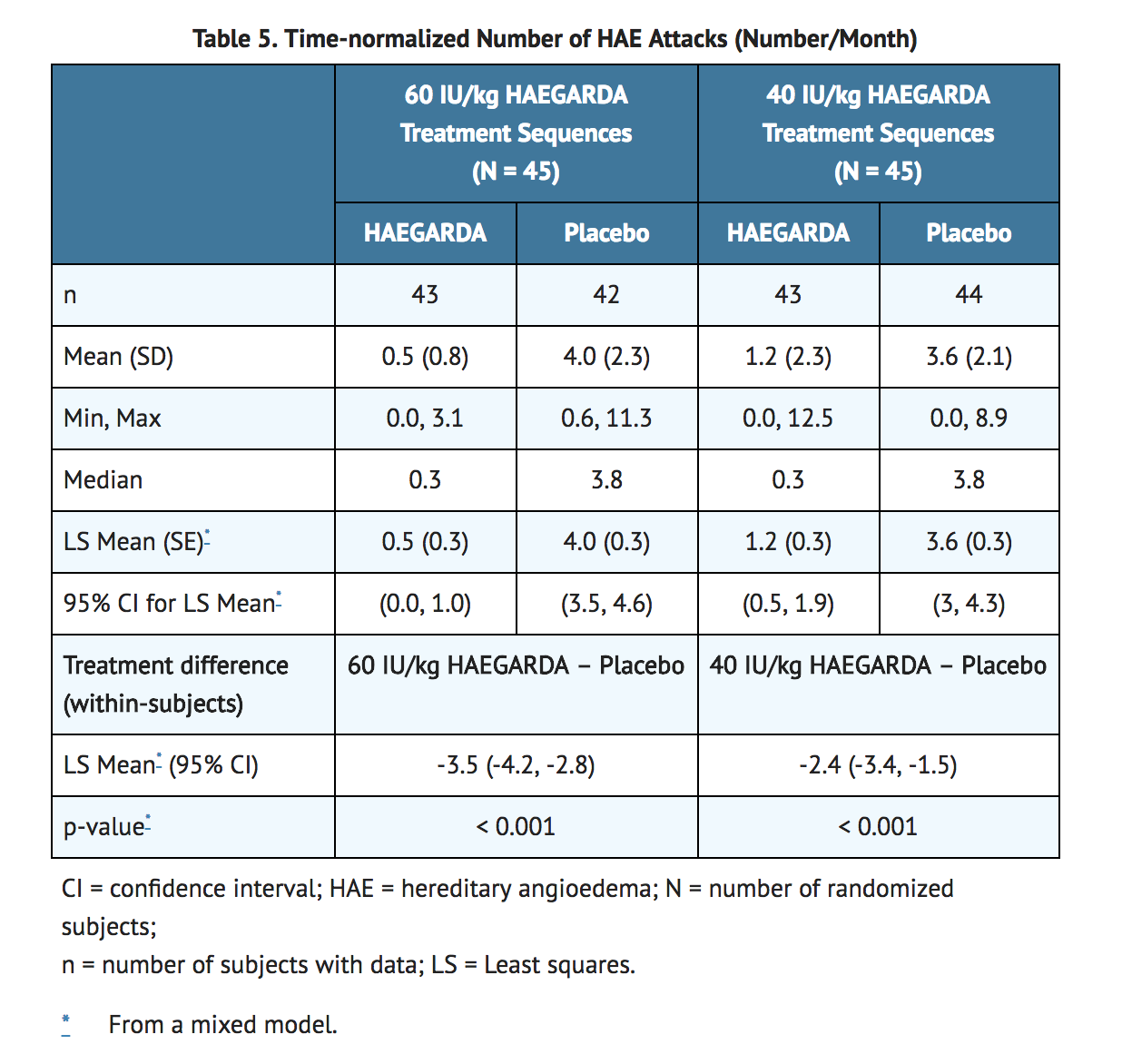
- The median (25th, 75th percentile) percentage reduction in the time-normalized number of HAE attacks relative to placebo was 95% (79, 100) on 60 IU/kg HAEGARDA and 89% (70, 100) on 40 IU/kg HAEGARDA among subjects with evaluable data in both treatment periods.
- The percentage of responders (95% CI) with a ≥50% reduction in the time-normalized number of HAE attacks on HAEGARDA relative to placebo was 83% (73%, 90%). Ninety percent (90%) of subjects on 60 IU/kg responded to treatment and 76% of subjects on 40 IU/kg responded to treatment.
- The percentages of subjects (95% CI) with ≥70% and ≥90% reductions in the time-normalized number of HAE attacks on HAEGARDA relative to placebo were 74% (64%, 83%) and 50% (39%, 61%), respectively. The percentages of subjects with ≥70% and ≥90% reductions in comparison to placebo in the time-normalized number of HAE attacks were 83% and 58% on 60 IU/kg and 67% and 43% on 40 IU/kg. Seventy-one percent (71%) of subjects on 60 IU/kg and 53% of subjects on 40 IU/kg had ≥1 HAE attack per 4 week period on placebo and <1 HAE attack per 4 week period on HAEGARDA.
- A total of 40% of subjects on 60 IU/kg and 38% of subjects on 40 IU/kg were attack-free, and the median rate of HAE attacks per month was 0.3 on both doses.
- HAEGARDA resulted in a significant difference in the time-normalized number of uses of rescue medication (the rate of rescue medication use) relative to placebo. A dose of 60 IU/kg resulted in a mean rate of rescue medication of 0.3 uses per month, compared to 3.9 uses per month with placebo. A dose of 40 IU/kg resulted in a mean rate of rescue medication use of 1.1 uses per month, compared to 5.6 uses per month with placebo.
How Supplied
- HAEGARDA is supplied in a kit containing a lyophilized powder in a single-use vial.
- HAEGARDA is packaged with Sterile Water for Injection, USP (4 mL for reconstitution of 2000 IU or 6 mL for reconstitution of 3000 IU) and one Mix2Vial filter transfer set. Not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage
- When stored at temperatures up to 30°C (86°F), HAEGARDA is stable for the period indicated by the expiration date on the carton and vial label.
- Keep HAEGARDA in its original carton until ready to use.
- Do not freeze.
- Protect from light.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- All risks and benefits of HAEGARDA should be discussed with the patient/caregiver before prescribing or administering it to the patient.
Inform patients/caregivers to immediately report the following to their physician:
- Signs and symptoms of allergic hypersensitivity reactions, such as hives, tightness of the chest, difficulty breathing, wheezing, hypotension and/or anaphylaxis experienced during or after injection of HAEGARDA.
- Signs and symptoms of a thromboembolic event, including pain and/or swelling of an arm or leg with warmth over the affected area, discoloration of an arm or leg, unexplained shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort that worsens on deep breathing, unexplained rapid pulse, numbness or weakness on one side of the body.
Inform all patients/caregivers:
- HAEGARDA is indicated for HAE prophylaxis and should not be used for the treatment of acute HAE attacks. Patients/caregivers should be counselled regarding the appropriate course of action if breakthrough HAE attacks occur while on HAEGARDA, including:
- Individualized rescue treatment for acute HAE attacks.
- Situations in which to seek immediate medical attention, such as acute laryngeal HAE attacks.
- Patients/caregivers must ensure an adequate supply of HAEGARDA when traveling.
- Because HAEGARDA is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. Inform patients of the risks and benefits of HAEGARDA before prescribing or administering it to the patient.
- Patients with known risk factors for thromboembolic events are at an increased risk for these events.
- Ensure that the patient/caregiver has access to and has received training in the administration of subcutaneous epinephrine and/or other appropriate supportive therapy for the treatment of any acute anaphylactic or severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Advise female patients:
- Patients should notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant while taking HAEGARDA.
- Patients should notify their physician if they are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed while taking HAEGARDA.
- Self-administration - Ensure that the patient/caregiver receives clear instructions and training on S.C. administration in the home or other appropriate setting and has demonstrated the ability to perform S.C. injection.
- The patient (or caregiver) has the necessary dexterity and comprehension to be trained to self-administer.
- Instruct patients/caregivers to record the lot number from the HAEGARDA vial label every time they use HAEGARDA.
- The attached HAEGARDA "Patient Product Information (PPI)" contains more detailed instructions for patients/caregivers who will be self-administering HAEGARDA.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Haegarda
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding C1 esterase inhibitor subcutaneous (Haegarda) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.