Ascariasis pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Ascariasis}} | {{Ascariasis}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}{{AE}}{{FB}} | ||
== | ==Overview== | ||
[[ | Ascariasis is the most common human [[helminth]] infection.<ref name="Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine">Kim, Kami; Weiss, Louis; Tanowitz, Herbert (2016). "Chapter 39:Parasitic Infections". Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine Sixth Edition. Elsevier. pp. 682–698. ISBN 978-1-4557-3383-5.</ref> The transmission of infection is usually from hand to mouth, and humans are the only known host.<ref name="Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine" /> | ||
= | |||
==Pathophysiology== | |||
Ascariasis is a soil-transmitted [[helminth]] infection with the round worm([[nematode]]) called [[Ascaris lumbricoides]], and humans are the only known host.<ref name="Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine">Kim, Kami; Weiss, Louis; Tanowitz, Herbert (2016). "Chapter 39:Parasitic Infections". Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine Sixth Edition. Elsevier. pp. 682–698. ISBN 978-1-4557-3383-5.</ref> The pathogenesis of ascariasis involves the following processes:<ref name="Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine" /><ref name="Ferri's Clinical Advisor">Ferri, Fred (2017). "Chapter:Ascariasis". Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2017. Elsevier. pp. 117–117. ISBN 978-0-3232-8048-8.</ref><ref name="Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics">Kliegman, Robert; Stanton, Bonita; St. Geme, Joseph; Schor, Nina (2016). "Chapter 291:Ascariasis (Ascaris lumbricoides)". Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics Twentieth Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1733–1734. ISBN 978-1-4557-7566-8.</ref> | |||
===Transmission=== | |||
* The eggs are primarily transmitted from hand to mouth, but they may also be ingested in raw fruits and vegetables grown in soil contaminated with the eggs of ascaris. | |||
* The eggs may also be ingested in water contaminated with the [[ova]] of ascaris or via inhalation of [[ova]] in regions with high worm burden. [[Ascaris infection]] occurs about 9-12 days after egg ingestion. | |||
===Dissemination=== | |||
* Following ingestion of the eggs, the fertilized [[ova]] hatch in the [[small intestine]] and the larvae penetrates the [[intestinal mucosa]]. | |||
* The larvae then proceeds to the lungs via the venous circulation and migrates through the [[alveoli]] and the [[bronchial tree]], resulting in pulmonary ascariasis. | |||
* The larvae ascend the bronchial tree to the throat, and are subsequently swallowed and returned to the intestines where maturation into adult worms occur. | |||
===Pathogenesis=== | |||
*The adult worms have a life span of 10-24 months within the human host. The adult male worms are 10-30cm long, while the adult female worms are larger and they measure up to 40cm long. | |||
*[[Intestinal obstruction]] associated with [[intestinal perforation]], [[volvulus]] and [[intussusception]] can occur in patients with large worm burdens. Worms can also migrate into the [[biliary tree]] resulting in [[biliary colic]] and [[pancreatitis]]. | |||
*Migration of worms to the appendix can result in [[acute appendicitis]]. | |||
* The fecund female worm produces a very high output of eggs (about 200,000 eggs/day), and eggs are passed out of the intestine with the feces where they can survive for years in warm, moist, shaded soil. | |||
*At temperatures of 5-10<sup>0</sup>C, the eggs of ascaris can remain viable for as long as two years. | |||
[[Image:Ascariasis LifeCycle - CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases.gif|thumb|1200px| | |||
(1) Adult worms live in the lumen of the small intestine. A female may produce approximately 200,000 eggs per day, which are passed with the feces. (2) Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but are not infective. (2) and (3) Fertile eggs embryonate and become infective in 5-10 days depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil). (4) Infective eggs are swallowed. (5) The larvae hatch, invade the intestinal mucosa, and are carried via the portal, then systemic circulation to the lungs. (6) The larvae mature further in the lungs (10 to 14 days), penetrate the alveolar walls, ascend the bronchial tree to the throat. (7) The larvae are then swallowed. Upon reaching the small intestine, they develop into adult worms. The female ascaris begin depositing eggs in 8-10 weeks. Adult worms can live 1 to 2 years. - Source: <nowiki>https://www.cdc.gov/</nowiki>|center|alt=The Life Cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{ | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:28, 29 July 2020
|
Ascariasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ascariasis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ascariasis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ascariasis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Fatimo Biobaku M.B.B.S [2]
Overview
Ascariasis is the most common human helminth infection.[1] The transmission of infection is usually from hand to mouth, and humans are the only known host.[1]
Pathophysiology
Ascariasis is a soil-transmitted helminth infection with the round worm(nematode) called Ascaris lumbricoides, and humans are the only known host.[1] The pathogenesis of ascariasis involves the following processes:[1][2][3]
Transmission
- The eggs are primarily transmitted from hand to mouth, but they may also be ingested in raw fruits and vegetables grown in soil contaminated with the eggs of ascaris.
- The eggs may also be ingested in water contaminated with the ova of ascaris or via inhalation of ova in regions with high worm burden. Ascaris infection occurs about 9-12 days after egg ingestion.
Dissemination
- Following ingestion of the eggs, the fertilized ova hatch in the small intestine and the larvae penetrates the intestinal mucosa.
- The larvae then proceeds to the lungs via the venous circulation and migrates through the alveoli and the bronchial tree, resulting in pulmonary ascariasis.
- The larvae ascend the bronchial tree to the throat, and are subsequently swallowed and returned to the intestines where maturation into adult worms occur.
Pathogenesis
- The adult worms have a life span of 10-24 months within the human host. The adult male worms are 10-30cm long, while the adult female worms are larger and they measure up to 40cm long.
- Intestinal obstruction associated with intestinal perforation, volvulus and intussusception can occur in patients with large worm burdens. Worms can also migrate into the biliary tree resulting in biliary colic and pancreatitis.
- Migration of worms to the appendix can result in acute appendicitis.
- The fecund female worm produces a very high output of eggs (about 200,000 eggs/day), and eggs are passed out of the intestine with the feces where they can survive for years in warm, moist, shaded soil.
- At temperatures of 5-100C, the eggs of ascaris can remain viable for as long as two years.
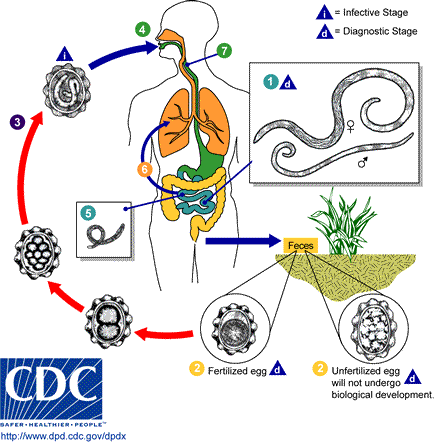
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Kim, Kami; Weiss, Louis; Tanowitz, Herbert (2016). "Chapter 39:Parasitic Infections". Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine Sixth Edition. Elsevier. pp. 682–698. ISBN 978-1-4557-3383-5.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred (2017). "Chapter:Ascariasis". Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2017. Elsevier. pp. 117–117. ISBN 978-0-3232-8048-8.
- ↑ Kliegman, Robert; Stanton, Bonita; St. Geme, Joseph; Schor, Nina (2016). "Chapter 291:Ascariasis (Ascaris lumbricoides)". Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics Twentieth Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1733–1734. ISBN 978-1-4557-7566-8.