Argatroban
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alejandro Lemor, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and prophylaxis in PCI. Common adverse reactions include dyspnea, hypotension, fever, diarrhea, chest pain, back pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, sepsis, and cardiac arrest.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
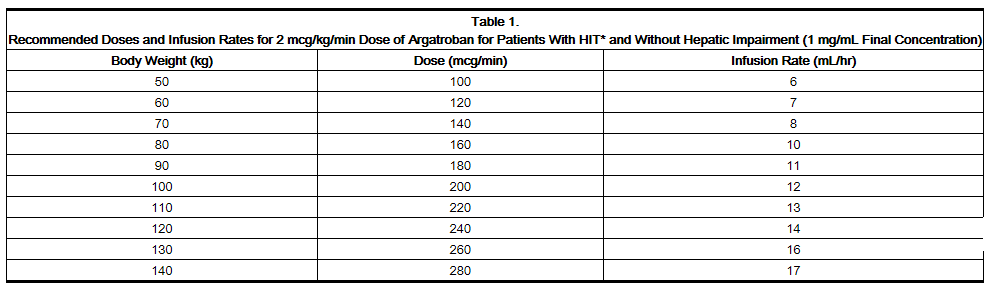
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
- Before administering argatroban, discontinue heparin therapy and obtain a baseline aPTT.
- Dosing Information
- Initial dose: 2 mcg/kg/min (continuous infusion)
- After the initiation of argatroban injection, adjust the dose (not to exceed 10 mcg/kg/min) as necessary to obtain a steady-state aPTT in the target range
Prophylaxis in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Initial dose: 25 mcg/kg/min , administer a bolus of 350 mcg/kg via a large bore IV line over 3 to 5 minutes.
- Check an activated clotting time (ACT) 5 to 10 minutes after the bolus dose is completed.
- The PCI procedure may proceed if the ACT is greater than 300 seconds.
- If the ACT is less than 300 seconds, an additional intravenous bolus dose of 150 mcg/kg should be administered, the infusion dose increased to 30 mcg/kg/min, and the ACT checked 5 to 10 minutes later
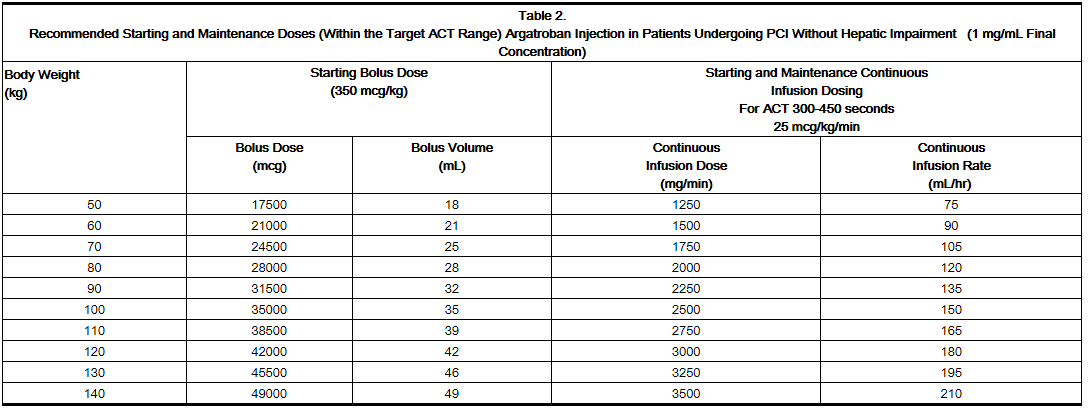
- If the ACT is greater than 450 seconds, decrease the infusion rate to 15 mcg/kg/min, and check the ACT 5 to 10 minutes later.

* No bolus dose is given if ACT greater than 450 seconds
- Continue titrating the dose until a therapeutic ACT (between 300 and 450 seconds) has been achieved; continue the same infusion rate for the duration of the PCI procedure.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
- Dosing Information
- Initial dose: 0.75 mcg/kg/min
- Check the aPTT two hours after the initiation of the argatroban infusion and adjust the dose to achieve the target aPTT.
- Increments of 0.1 to 0.25 mcg/kg/min for pediatric patients with normal hepatic function may be considered.
- Increments of 0.05 mcg/kg/min or lower for pediatric patients with impaired hepatic function may be considered.
- Initiate the infusion at a dose of 0.2 mcg/kg/min among seriously ill pediatric patients with impaired hepatic function
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Argatroban in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Argatroban in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Patients with major bleeding.
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to argatroban. (Airway, skin, and generalized hypersensitivity reactions have been reported)
Warnings
Risk of Hemorrhage
- Hemorrhage can occur at any site in the body in patients receiving argatroban.
- Unexplained fall in hematocrit or blood pressure may indicate hemorrhage.
- Intracranial and retroperitoneal hemorrahage have been reported.
- The risk of hemorrahage with argatroban may be increased in severe hypertension; immediately following lumbar puncture, spinal anesthesia, major surgery (especially involving the brain, spinal cord, or eye), hematologic conditions associated with increased bleeding tendencies such as congenital or acquired bleeding disorders, and gastrointestinal lesions such as ulcerations.
- Concomitant use of argatroban with antiplatelet agents, thrombolytics, and other anticoagulants may increase the risk of bleeding.
Use in Hepatic Impairment
- When administering argatroban to patients with hepatic impairment, start with a lower dose and carefully titrate until the desired level of anticoagulation is achieved.
- Achievement of steady state aPTT levels may take longer and require more argatroban dose adjustments in patients with hepatic impairment compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
- Also, upon cessation of argatroban infusion in the hepatically impaired patient, full reversal of anticoagulant effects may require longer than 4 hours due to decreased clearance and increased elimination half-life of argatroban.
- Avoid the use of high doses of argatroban in patients undergoing PCI who have clinically significant hepatic disease or AST/ALT levels ≥3 times the upper limit of normal.
Laboratory Tests
- Anticoagulation effects associated with argatroban infusion at doses up to 40 mcg/kg/min correlate with increases of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT).
- Although other global clot-based tests including prothrombin time (PT), the International Normalized Ratio (INR), and thrombin time (TT) are affected by argatroban, the therapeutic ranges for these tests have not been identified for argatroban therapy.
- In clinical trials in PCI, the activated clotting time (ACT) was used for monitoring argatroban anticoagulant activity during the procedure.
- The concomitant use of argatroban and warfarin results in prolongation of the PT and INR beyond that produced by warfarin alone.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse event rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Events in Patients with HIT (With or Without Thrombosis)
The following safety information is based on all 568 patients treated with argatroban in Study 1 and Study 2. The safety profile of the patients from these studies is compared with that of 193 historical controls in which the adverse events were collected retrospectively. Adverse events are separated into hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic events.
Major bleeding was defined as bleeding that was overt and associated with a hemoglobin decrease ≥2 g/dL, that led to a transfusion of ≥2 units, or that was intracranial, retroperitoneal, or into a major prosthetic joint. Minor bleeding was overt bleeding that did not meet the criteria for major bleeding.
Table 4 gives an overview of the most frequently observed hemorrhagic events, presented separately by major and minor bleeding, sorted by decreasing occurrence among argatroban-treated patients with HIT (with or without thrombosis).
Table 5 gives an overview of the most frequently observed non-hemorrhagic events sorted by decreasing frequency of occurrence (=2%) among argatroban-treated HIT/HITTS patients.
Adverse Events in Patients with or at Risk for HIT Patients Undergoing PCI
The following safety information is based on 91 patients initially treated with argatroban and 21 patients subsequently re-exposed to argatroban for a total of 112 PCIs with argatroban anticoagulation. Adverse events are separated into hemorrhagic (Table 6) and non-hemorrhagic (Table 7) events.
Major bleeding was defined as bleeding that was overt and associated with a hemoglobin decrease ≥5 g/dL, that led to transfusion of ≥2 units, or that was intracranial, retroperitoneal, or into a major prosthetic joint.
The rate of major bleeding events in patients treated with argatroban in the PCI trials was 1.8%.
Table 7 gives an overview of the most frequently observed non-hemorrhagic events (>2%), sorted by decreasing frequency of occurrence among argatroban-treated PCI patients.
There were 22 serious adverse events in 17 PCI patients (19.6% in 112 interventions). Table 8 lists the serious adverse events occurring in argatroban-treated-patients with or at risk for HIT undergoing PCI.
Intracranial Bleeding In Other Populations
Increased risks for intracranial bleeding have been observed in investigational studies of argatroban for other uses. In a study of patients with acute myocardial infarction receiving both argatroban and thrombolytic therapy (streptokinase or tissue plasminogen activator), the overall frequency of intracranial bleeding was 1% (8 out of 810 patients). Intracranial bleeding was not observed in 317 subjects or patients who did not receive concomitant thrombolysis.
The safety and effectiveness of argatroban for cardiac indications other than PCI in patients with HIT have not been established. Intracranial bleeding was also observed in a prospective, placebo-controlled study of argatroban in patients who had onset of acute stroke within 12 hours of study entry. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage was reported in 5 of 117 patients (4.3%) who received argatroban at 1 to 3 mcg/kg/min and in none of the 54 patients who received placebo. Asymptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 5 (4.3%) and 2 (3.7%) of the patients, respectively.
Allergic Reactions
One hundred fifty-six allergic reactions or suspected allergic reactions were observed in 1,127 individuals who were treated with argatroban in clinical pharmacology studies or for various clinical indications. About 95% (148/156) of these reactions occurred in patients who concomitantly received thrombolytic therapy (e.g., streptokinase) or contrast media.
Allergic reactions or suspected allergic reactions in populations other than patients with HIT (with or without thrombosis) include (in descending order or frequency):
- Airway reactions (coughing, dyspnea): 10% or more
- Skin reactions (rash, bullous eruption): 1 to <10%
- General reactions (vasodilation): 1 to 10%
Limited data are available on the potential formation of drug-related antibodies. Plasma from 12 healthy volunteers treated with argatroban over 6 days showed no evidence of neutralizing antibodies. No loss of anticoagulant activity was noted with repeated administration of argatroban to more than 40 patients.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Argatroban Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
(Description)
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
Solution
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Y-Site
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Admixture
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Syringe
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
TPN/TNA
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Argatroban
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
Argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor that reversibly binds to the thrombin active site. Argatroban does not require the co-factor antithrombin III for antithrombotic activity. Argatroban exerts its anticoagulant effects by inhibiting thrombin-catalyzed or -induced reactions, including fibrin formation; activation of coagulation factors V, VIII, and XIII; activation of protein C; and platelet aggregation.
Argatroban inhibits thrombin with an inhibition constant (Ki) of 0.04 μM. At therapeutic concentrations, argatroban has little or no effect on related serine proteases (trypsin, factor Xa, plasmin, and kallikrein).
Argatroban is capable of inhibiting the action of both free and clot-associated thrombin.
Structure
Argatroban is a synthetic direct thrombin inhibitor and the chemical name is 1-[5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-1-oxo-2-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8- quinolinyl)sulfonyl]amino]pentyl]-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid, monohydrate. Argatroban has 4 asymmetric carbons. One of the asymmetric carbons has an R configuration (stereoisomer Type I) and an S configuration (stereoisomer Type II). Argatroban consists of a mixture of R and S stereoisomers at a ratio of approximately 65:35. The molecular formula of Argatroban is C23H36N6O5S•H2O. Its molecular weight is 526.66 g/mol. The structural formula is shown below:

Argatroban is a white, odorless crystalline powder that is freely soluble in glacial acetic acid, slightly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, and ether. Argatroban Injection is a sterile clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous solution. Argatroban is available in 250-mg (in 2.5-mL) single-use amber vials, with white flip-top caps. Each mL of sterile, nonpyrogenic solution contains 100 mg Argatroban. Inert ingredients: 1300 mg Propylene glycol, 800 mg Dehydrated alcohol.
Pharmacodynamics
When argatroban is administered by continuous infusion, anticoagulant effects and plasma concentrations of argatroban follow similar, predictable temporal response profiles, with low intersubject variability. Immediately upon initiation of argatroban infusion, anticoagulant effects are produced as plasma argatroban concentrations begin to rise. Steady-state levels of both drug and anticoagulant effect are typically attained within 1 to 3 hours and are maintained until the infusion is discontinued or the dosage adjusted. Steady-state plasma argatroban concentrations increase proportionally with dose (for infusion doses up to 40 mcg/kg/min in healthy subjects) and are well correlated with steady-state anticoagulant effects. For infusion doses up to 40 mcg/kg/min, argatroban increases in a dose-dependent fashion, the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), the activated clotting time (ACT), the prothrombin time (PT), the International Normalized Ratio (INR), and the thrombin time (TT) in healthy volunteers and cardiac patients. Representative steady-state plasma argatroban concentrations and anticoagulant effects are shown below for argatroban infusion doses up to 10 mcg/kg/min.

Effect on International Normalized Ratio (INR): Because argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor, co-administration of argatroban and warfarin produces a combined effect on the laboratory measurement of the INR. However, concurrent therapy, compared to warfarin monotherapy, exerts no additional effect on vitamin K–dependent factor Xa activity.
The relationship between INR on co-therapy and warfarin alone is dependent on both the dose of argatroban and the thromboplastin reagent used. This relationship is influenced by the International Sensitivity Index (ISI) of the thromboplastin. Data for 2 commonly utilized thromboplastins with ISI values of 0.88 (Innovin, Dade) and 1.78 (Thromboplastin C Plus, Dade) are presented in Figure 2 for an argatroban dose of 2 mcg/kg/min. Thromboplastins with higher ISI values than shown result in higher INRs on combined therapy of warfarin and argatroban. These data are based on results obtained in normal individuals.
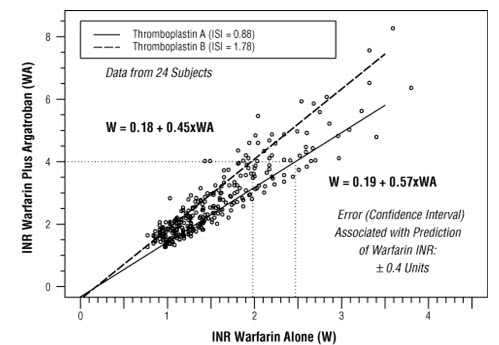
The graph above demonstrates the relationship between INR for warfarin alone and INR for warfarin co-administered with argatroban at a dose of 2 mcg/kg/min. To calculate INR for warfarin alone (INRW), based on INR for co-therapy of warfarin and argatroban (INRWA), when the argatroban dose is 2 mcg/kg/min, use the equation next to the appropriate curve. Example: At a dose of 2 mcg/kg/min and an INR performed with Thromboplastin A, the equation 0.19 + 0.57 (INRWA) = INRW would allow a prediction of the INR on warfarin alone (INRW). Thus, using an INRWA value of 4.0 obtained on combined therapy: INRW = 0.19 + 0.57 (4) = 2.47 as the value for INR on warfarin alone. The error (confidence interval) associated with a prediction is ± 0.4 units. Similar linear relationships and prediction errors exist for argatroban at a dose of 1 mcg/kg/min. Thus, for argatroban doses of 1 or 2 mcg/kg/min, INRW can be predicted from INRWA. For argatroban doses greater than 2 mcg/kg/min, the error associated with predicting INRW from INRWA is ± 1. Thus, INRW cannot be reliably predicted from INRWA at doses greater than 2 mcg/kg/min.
Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
Argatroban distributes mainly in the extracellular fluid as evidenced by an apparent steady-state volume of distribution of 174 mL/kg (12.18 L in a 70-kg adult). Argatroban is 54% bound to human serum proteins, with binding to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein being 20% and 34%, respectively.
Metabolism
The main route of argatroban metabolism is hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring in the liver. The formation of each of the 4 known metabolites is catalyzed in vitro by the human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/5. The primary metabolite (M1) exerts 3- to 5-fold weaker anticoagulant effects than argatroban. Unchanged argatroban is the major component in plasma. The plasma concentrations of M1 range between 0% and 20% of that of the parent drug. The other metabolites (M2 to M4) are found only in very low quantities in the urine and have not been detected in plasma or feces. These data, together with the lack of effect of erythromycin (a potent CYP3A4/5 inhibitor) on argatroban pharmacokinetics, suggest that CYP3A4/5-mediated metabolism is not an important elimination pathway in vivo.
Total body clearance is approximately 5.1 mL/kg/min (0.31 L/kg/hr) for infusion doses up to 40 mcg/kg/min. The terminal elimination half-life of argatroban ranges between 39 and 51 minutes.
There is no interconversion of the 21–(R):21–(S) diastereoisomers. The plasma ratio of these diastereoisomers is unchanged by metabolism or hepatic impairment, remaining constant at 65:35 (± 2%).
Excretion
Argatroban is excreted primarily in the feces, presumably through biliary secretion. In a study in which 14C-argatroban (5 mcg/kg/min) was infused for 4 hours into healthy subjects, approximately 65% of the radioactivity was recovered in the feces within 6 days of the start of infusion with little or no radioactivity subsequently detected. Approximately 22% of the radioactivity appeared in the urine within 12 hours of the start of infusion. Little or no additional urinary radioactivity was subsequently detected. Average percent recovery of unchanged drug, relative to total dose, was 16% in urine and at least 14% in feces.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Argatroban Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
Condition 1
(Description)
Condition 2
(Description)
Condition 3
(Description)
How Supplied
(Description)
Storage
There is limited information regarding Argatroban Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Argatroban |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Argatroban |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
(Patient Counseling Information)
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Argatroban interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Argatroban Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
- (Paired Confused Name 1a) — (Paired Confused Name 1b)
- (Paired Confused Name 2a) — (Paired Confused Name 2b)
- (Paired Confused Name 3a) — (Paired Confused Name 3b)
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.