Focal nodular hyperplasia
| Focal nodular hyperplasia | |
 | |
|---|---|
| Focal nodular hyperplasia. Image courtesy of RadsWiki | |
| DiseasesDB | 33467 |
| eMedicine | radio/286 |
| MeSH | D020518 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Contributors: Cafer Zorkun M.D., PhD.
Overview
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is a benign tumor of the liver (hepatic tumor), which is the second most prevalent tumor of the liver (the first is hepatic hemangioma). It is usually asymptomatic, rarely grows or bleeds, and has no malignant potential. This tumor is often resected because it is difficult to distinguish from hepatic adenoma. [1]
- Focal nodular hyperplasia is believed to occur as a result of a localized hepatocyte response to an underlying congenital arteriovenous malformation.
- Focal nodular hyperplasia is a hyperplastic process in which all the normal constituents of the liver are present but in an abnormally organized pattern.
- Malignant transformation of Focal nodular hyperplasia has not been reported.
- Focal nodular hyperplasia must be differentiated from fibrolamellar carcinoma, with which it shares imaging and gross features.
- Male-to-female ratio is 1:2-4.
Clinical Presentation
Focal nodular hyperplasia's most recognizable gross feature is a central stellate scar seen in 60-70% of cases. Microscopically, a lobular proliferation of bland-appearing hepatocytes with a bile ductular proliferation and malformed vessels within the fibrous scar is the most common pattern. Other patterns include telangiectatic, hyperplastic-adenomatous, and lesions with focal large-cell dysplasia.[2] Rarely, these lesions may be multiple or can occur as part of a syndrome with hemangiomas, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, hepatic adenomas, fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma, vascular malformations of the brain, meningiomas, and/or astrocytomas.[2]
Diagnosis
Computed Tomography
- Lobulated contours at CT.
- At unenhanced CT, the lesions are either hypoattenuating or isoattenuating to the surrounding liver.
- In the arterial phase, the lesions become hyperattenuating due to the homogeneous intense enhancement of the entire lesion, except the central scar.
- In the portal and later phases, the lesions become more isoattenuating with the surrounding liver and the central scar may show some enhancement.
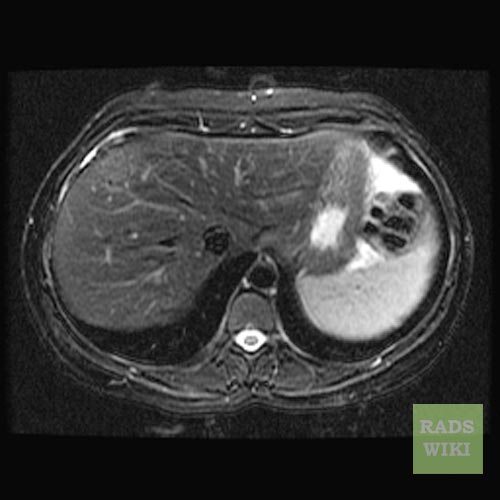
MRI
- Often isointense on T1-weighted images.
- Often isointense on T2-weighted images.
- Central scar
- Hypointense on T1-weighted images
- Variable signal-intensity pattern on T2-weighted images.
- Contrast
- Dense enhancement is seen in the arterial phase,
- Isointense during the portal venous phase
- Isointense on delayed images.
- Late and prolonged enhancement of the central stellate scar occasionally occurs.
Scintigraphy
- Will display uptake on sulfur colloid scan as Focal nodular hyperplasias contain Kupffer cells.
- Other hepatic lesions will be cold defects on sulfur colloid scans.
Diagnostic Findings
-
Axial T1 pre
-
Axial T1 post
-
Axial T1 post delayed
-
Axial T2
-
Coronal T2
References
- ↑ Shahid M. Hussain, Türkan Terkivatan, Pieter E. Zondervan, Esmée Lanjouw, Sjoerd de Rave, Jan N. M. IJzermans, and Rob A. de Man. Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: Findings at State-of-the-Art MR Imaging, US, CT, and Pathologic Analysis. RadioGraphics 2004 24: 3-17.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nguyen et al. Focal Nodular Hyperplasia of the Liver: A Comprehensive Pathologic Study of 305 Lesions and Recognition of New Histologic Forms. Am J Surg Path 1999: 23 (12); 1441-4.