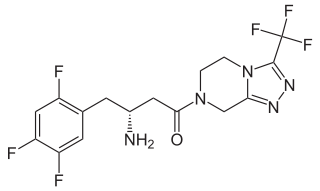
Sitagliptin
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [1] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 87% |
| Protein binding | 38% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4- and CYP2C8-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 8 to 14 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Renal (80%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H15F6N5O |
| Molar mass | 407.314 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Sitagliptin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Sitagliptin Most cited articles on Sitagliptin |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Sitagliptin |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Sitagliptin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Sitagliptin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Sitagliptin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Sitagliptin Discussion groups on Sitagliptin Patient Handouts on Sitagliptin Directions to Hospitals Treating Sitagliptin Risk calculators and risk factors for Sitagliptin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Sitagliptin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Overview
Sitagliptin, previously identified as MK-0431, is a new oral hypoglycemic (anti-diabetic drug) of the new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. This enzyme-inhibiting drug is to be used either alone (monotherapy) or in combination with metformin or a thiazolidinedione for the control of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Potential benefits of this medicine include a lower incidence of side-effects (e.g., less hypoglycemia, less weight gain) in the control of blood glucose. Another potential advantages of sitagliptin is that it can be taken as a pill - it does not need to be injected.
Adverse effects
In clinical trials, adverse effects were as common with sitagliptin (whether used alone or with metformin or pioglitazone) as they were with placebo, except for nausea and common cold-like symptoms, which were more common with sitagliptin.[2] There is no significant difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between placebo and sitagliptin.[2]
History
Sitagliptin was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on October 17, 2006[3] and is marketed in the US as Januvia by Merck & Co. On April 2, 2007, the FDA approved an oral combination of sitagliptin and metformin marketed in the US as Janumet.
Mechanism
The drug works to competitively inhibit a protein/enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4), that results in an increased amount of active incretins (GLP-1 and GIP), reduced amount of release of glucagon (diminishes its release) and increased release of insulin (increases its synthesis and release) to restore blood glucose levels towards normal. As the blood glucose level approaches normal, the amounts of insulin released and glucagon suppressed diminishes thus tending to prevent an "overshoot" and subsequent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) which is seen with some other oral hypoglycemic agents.
Sitagliptin works by inhibiting the inactivation of the incretins GLP-1 and GIP by DPP-4.[4] By preventing GLP-1 and GIP inactivation, GLP-1 and GIP are able to potentiate the secretion of insulin and suppress the release of glucagon by the pancreas.
Sitagliptin incorporates a beta amino acid moiety that allows for a more favorable fit into the active site of DPP-4. The trifluorophenyl moiety also fits into a hydrophobic region of the active site.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Herman G, Stevens C, Van Dyck K, Bergman A, Yi B, De Smet M, Snyder K, Hilliard D, Tanen M, Tanaka W, Wang A, Zeng W, Musson D, Winchell G, Davies M, Ramael S, Gottesdiener K, Wagner J (2005). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sitagliptin, an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, in healthy subjects: results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with single oral doses". Clin Pharmacol Ther. 78 (6): 675–88. PMID 16338283.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Januvia Side Effects & Drug Interactions". RxList.com. 2007. Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ↑ "FDA Approves New Treatment for Diabetes" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. October 17, 2006. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ↑ Herman G, Bergman A, Liu F, Stevens C, Wang A, Zeng W, Chen L, Snyder K, Hilliard D, Tanen M, Tanaka W, Meehan A, Lasseter K, Dilzer S, Blum R, Wagner J (2006). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic effects of the oral DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin in middle-aged obese subjects". J Clin Pharmacol. 46 (8): 876–86. PMID 16855072.
External links
- Merck Announces FDA Acceptance of New Drug Application for JANUVIA™ - Merck press release.
- The race to get DPP-4 inhibitors to market - Forbes.com
- Merck's March Madness - Forbes.com
- Banting and Best Diabetes Centre at UT mk-0431 - Sitagliptin
- Banting and Best Diabetes Centre at UT dp_iv - About DPP-4
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
- Anti-diabetic drugs
- Endocrinology