Lung abscess chest x ray
|
Lung abscess Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Lung abscess chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Lung abscess chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Lung abscess chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ;Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [2]
Overview
Diagnosis of lung abscess is often based on radiologic results showing a cavitary lesion with air fluid level, though blood cultures are normally required to identify the specific pathogen.
Chest X Ray
- An irregularly shaped thick walled cavity with an air-fluid level is typically seen in lung abscess on chest x ray. [1]
- Abscess is often unilateral and single involving posterior segments of the upper lobes and the apical segments of the lower lobes as these areas are gravity dependent when lying down. [2]
- The presence of air-fluid levels implies rupture into the bronchial tree or rarely growth of gas forming organism.The extent of the air-fluid level within a lung abscess is often the same in posteroanterior or lateral views.
- Anaerobic infection may be suggested by cavitation within a dense segmental consolidation in the dependent lung zones.
- Lung infection with a virulent organism results in more widespread tissue necrosis.
- Up to one-third of lung abscesses may be accompanied by an empyema.[3]
- Repeat chest radiographs must be obtained to determine the response of antimicrobial therapy.
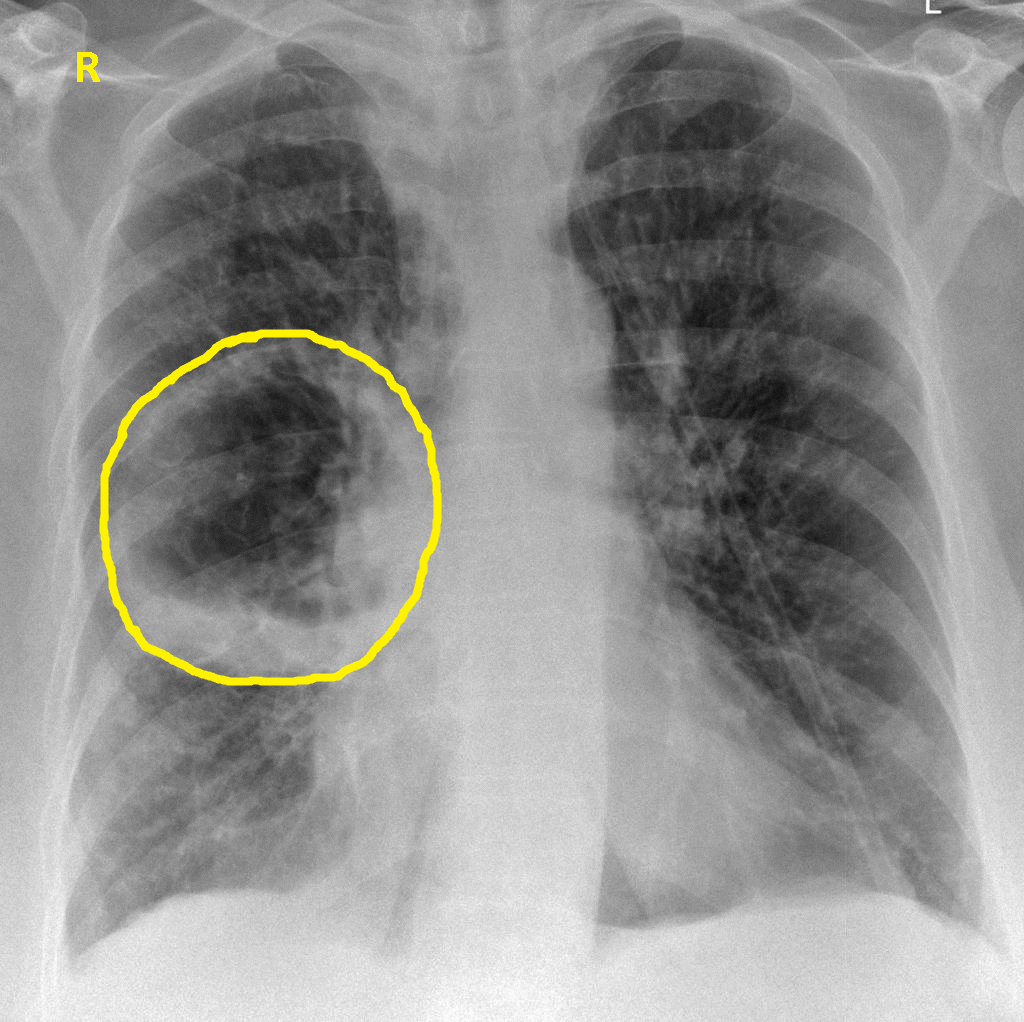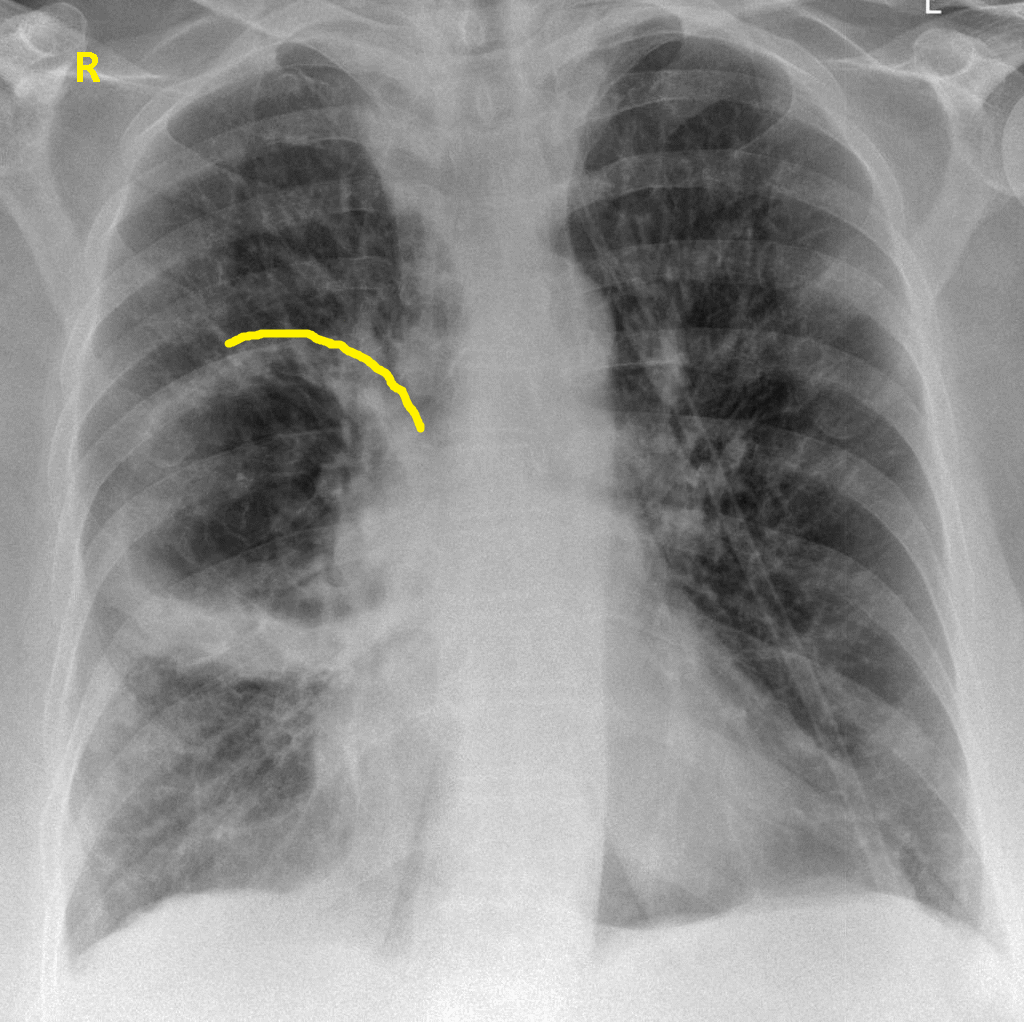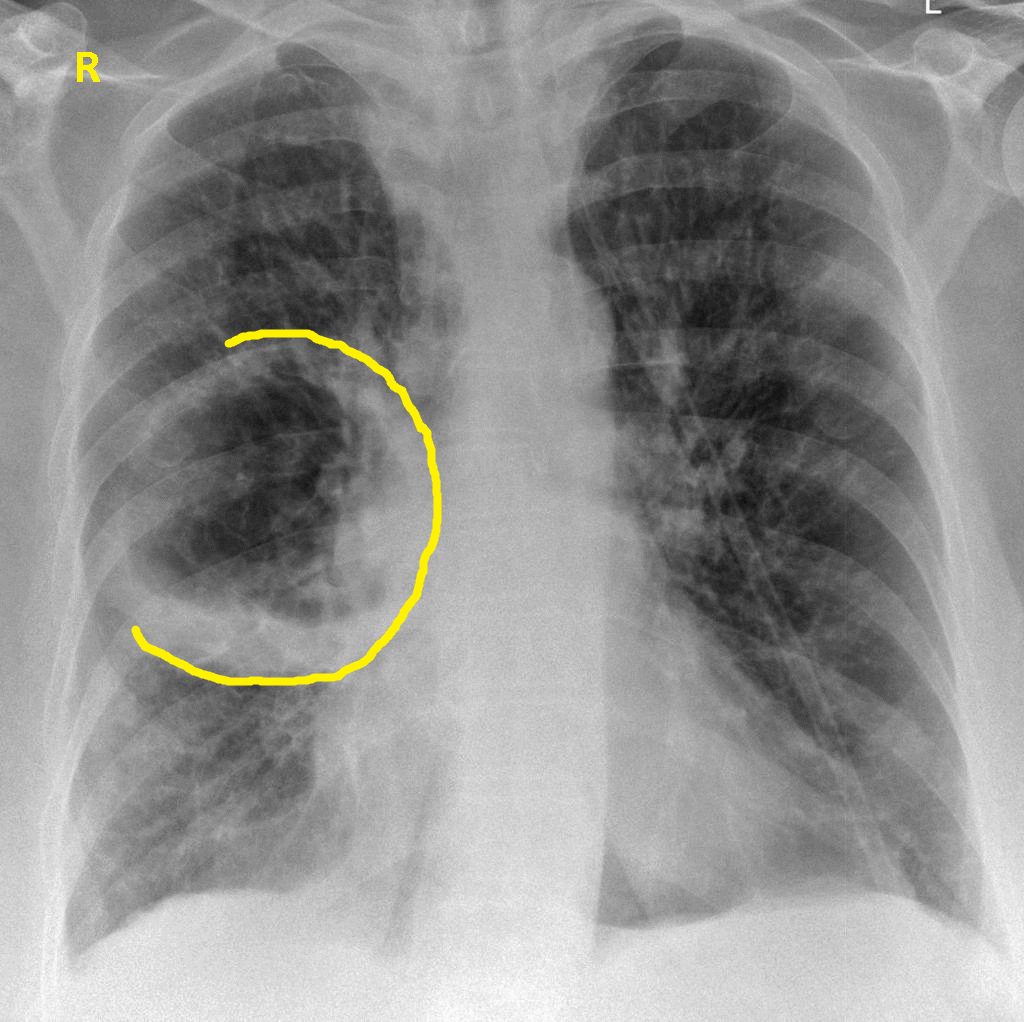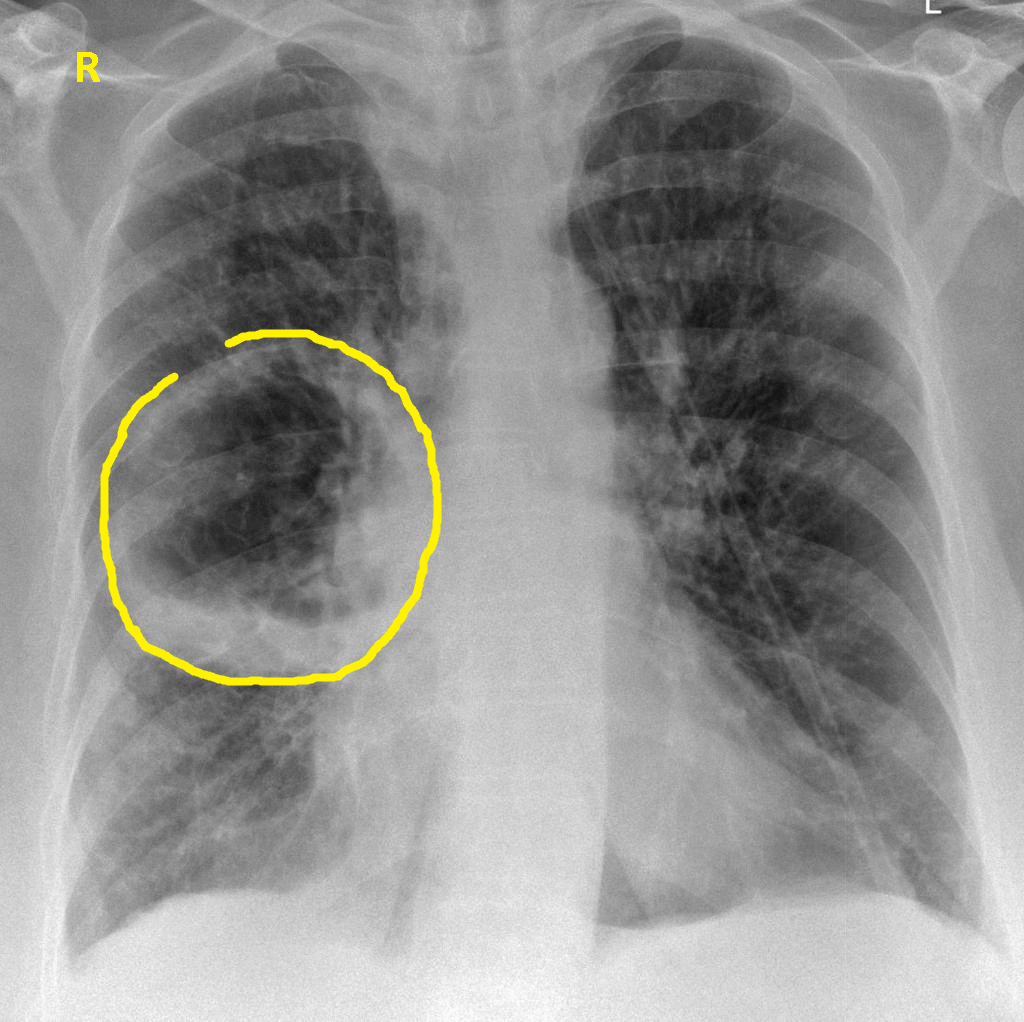
Chest X-ray AP-veiw :demonstarting a large right side pulmonary cavity.
Reference
- ↑ Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/15517">rID: 15517</a>
- ↑ Groff DB, Marquis J (1973). "Treatment of lung abscess by transbronchial catheter drainage". Radiology. 107 (1): 61–2. doi:10.1148/107.1.61. PMID 4689444.
- ↑ Stark DD, Federle MP, Goodman PC, Podrasky AE, Webb WR (1983). "Differentiating lung abscess and empyema: radiography and computed tomography". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 141 (1): 163–7. doi:10.2214/ajr.141.1.163. PMID 6602513.