Membranous glomerulonephritis pathophysiology
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Membranous glomerulonephritis from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Membranous glomerulonephritis pathophysiology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Membranous glomerulonephritis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Membranous glomerulonephritis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
It is thought that [disease name] is the result of / is mediated by / is produced by / is caused by either [hypothesis 1], [hypothesis 2], or [hypothesis 3].
Pathophysiology
Phospholipase A2 receptor
- The M-type PLA2R is the major antigen in human idiopathic MN. It is expressed in glomerular podocytes.
- There was no colocalization of PLA2R in secondary MN biopsies.
- PLA2R antigen detected within immune deposits by immunofluorescence of the biopsy specimen. [26]
- Detection of the immune complex specificity is 100 percent.
Thrombospondin type-1
- THSD7A has been found in patients with idiopathic MN who are negative for anti-PLA2R antibodies.
Neutral endopeptidase
- Anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies caused MN in the neonates.
- It resolves months after birth.
- The T helper-2 predominates in MN and minimal change disease.
Genetics
Associated Conditions
Gross Pathology
Microscopic Pathology
- Early biopsies may be normal
- Later: uniform diffuse capillary wall thickening without hypercellularity, without mesangial sclerosis and without inflammatory cells
- Proximal convoluted tubules contain hyaline droplets, reflecting protein reabsorption
- With progression, get membrane thickening, narrow capillary lumina, mesangial sclerosis and glomerulosclerosis
Immunofluorescence
- Granular diffuse peripheral deposits, usually IgG and C3, also C5b-C9 and occasionally IgM or IgA
- C4d immunostaining may be diagnostic (Histol Histopathol 2011;26:1391)
Stages
- Stage I: LM - normal for slightly thickened BM, slight GMB vacuolization; IF - fine granular IgG, C3; EM - scattered small subepithelial electron dense deposits, no foot process effacement or spikes
- Stage II: LM - moderately thickened BM with spikes and vacuolization; IF - moderate sized, granular IgG, C3; EM - diffuse spikes due to subepithelial deposits, diffuse foot process effacement
- Stage III: LM - markedly thickened GBM, residual spikes and vacuoles, chain like appearance; IF - coarsely granular IgG, C3; EM - intramembranous deposits, spikes, neomembrane formation and diffuse foot process effacement
- Stage IV: LM - markedly thickened GBM, few spikes, vacuoles and glomerulosclerosis; IF - focal IgG, C3; EM - sclerotic GBM, few deposits and lacunae
References
-
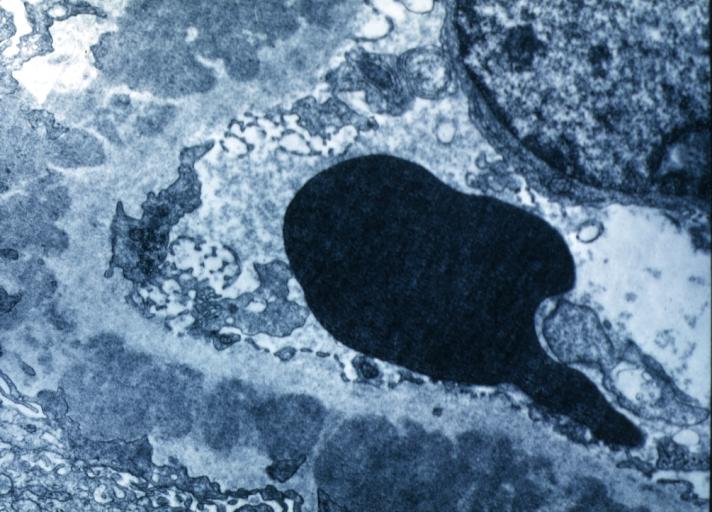
Membranous Glomerulonephritis: Electron micrography. An excellent example to show thickened basement membrane and immune complexes.
-
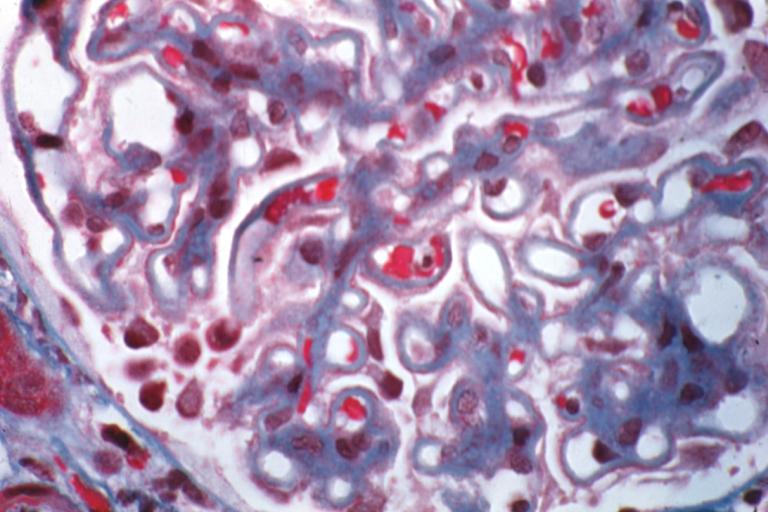
Membranous Glomerulonephritis: Micro trichrome high mag excellent to show thickened capillary basement membranes
-
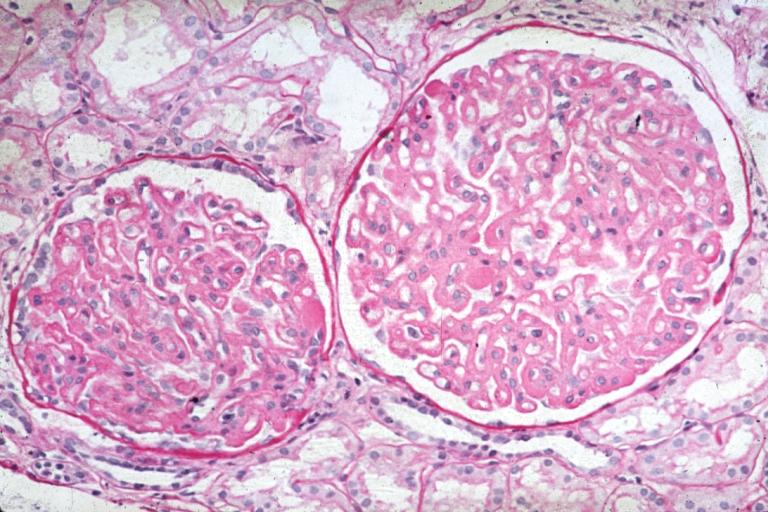
Membranous Glomerulonephritis: Micro PAS high mag excellent example of this lesion
-
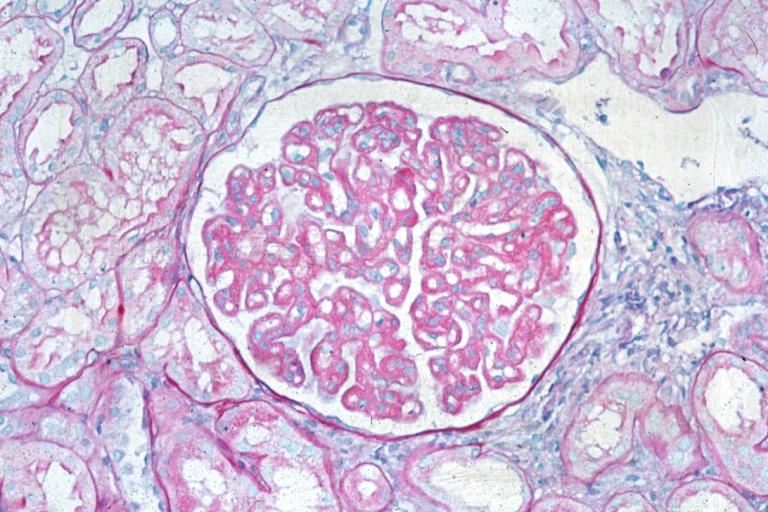
Membranous Glomerulonephritis: Micro PAS med mag