Atelectasis
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
Atelectasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Atelectasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Atelectasis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Assistant Editor-in-Chief: Somal Khan, M.D.
Overview
Atelectasis is defined as a state in which the lung, in whole or in part, is collapsed or without air.[1] It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation. Infant respiratory distress syndrome includes another type of atelectasis, and is described and discussed in its own article.
Classification
Atelectasis may be an acute or chronic condition. In acute atelectasis, the lung has recently collapsed and is primarily notable only for airlessness. In chronic atelectasis, the affected area is often characterized by a complex mixture of airlessness, infection, widening of the bronchi (bronchiectasis), destruction, and scarring (fibrosis).
Acute Atelectasis
Acute atelectasis is a common postoperative complication, especially after chest or abdominal surgery. Acute atelectasis may also occur with an injury, usually to the chest (such as that caused by a car accident, a fall, or a stabbing). Atelectasis following surgery or injury, sometimes described as massive, involves most alveoli in one or more regions of the lungs. In these circumstances, the degree of collapse among alveoli tends to be quite consistent and complete. Large doses of opioids or sedatives, tight bandages, chest or abdominal pain, abdominal swelling (distention), and immobility of the body increase the risk of acute atelectasis following surgery or injury, or even spontaneously.
In acute atelectasis that occurs because of a deficiency in the amount or effectiveness of surfactant, many but not all alveoli collapse, and the degree of collapse is not uniform. Atelectasis in these circumstances may be limited to only a portion of one lung, or it may be present throughout both lungs. When premature babies are born with surfactant deficiency, they always develop acute atelectasis that progresses to neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.Adults can also develop acute atelectasis from excessive oxygen therapy and from mechanical ventilation, because of decreased effectiveness of surfactant.
Chronic Atelectasis
Chronic atelectasis may take one of two forms—middle lobe syndrome or rounded atelectasis. In middle lobe syndrome, the middle lobe of the right lung contracts, usually because of pressure on the bronchus from enlarged lymph glands and occasionally a tumor. The blocked, contracted lung may develop pneumonia that fails to resolve completely and leads to chronic inflammation, scarring, and bronchiectasis.
In rounded atelectasis (folded lung syndrome), an outer portion of the lung slowly collapses as a result of scarring and shrinkage of the membrane layers covering the lungs (pleura). This produces a rounded appearance on x-ray that doctors may mistake for a tumor. Rounded atelectasis is usually a complication of asbestos-induced disease of the pleura, but it may also result from other types of chronic scarring and thickening of the pleura.
Pathophysiology
There are several types of atelectasis according to their underlying mechanisms or the distribution of alveolar collapse; resorption, compression, microatelectasis and contraction atelectasis.
Causes
The most common cause is post-surgical atelectasis, characterized by splinting, restricted breathing after abdominal surgery. Outside of this context, atelectasis implies some blockage of a bronchiole or bronchus, which can be within the airway (foreign body, mucus plug), from the wall (tumor, usually squamous cell carcinoma) or compressing from the outside (tumor, lymph node, tubercle). Another cause is poor surfactant spreading during inspiration, causing an increase in surface tension which tends to collapse smaller alveoli.
Risk Factors
Smokers and the elderly are at an increased risk.
Diagnosis
Symptoms
- Cough, but not prominent
- Chest pain (rare)
- Dyspnea
Physical Examination
Vital Signs
- Low oxygen saturation,
- Fever
- Tachycardia or increased heart rate
Lung
- Pleural effusion (transudate type)
Extremities
Cyanosis (late sign)
Diagnosis
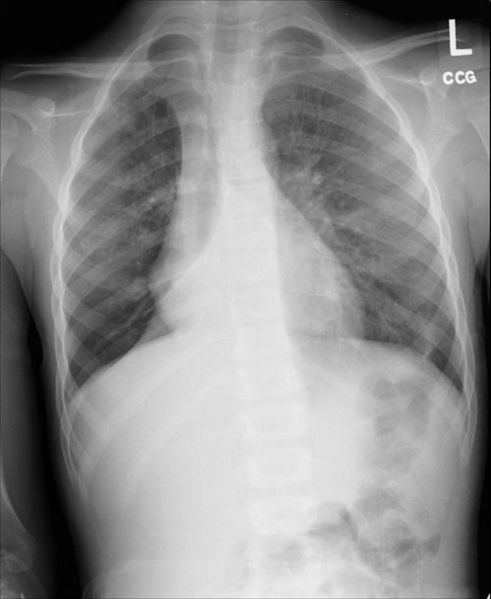
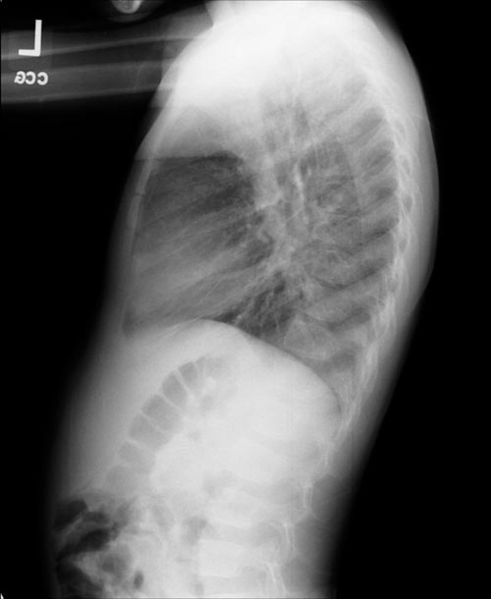
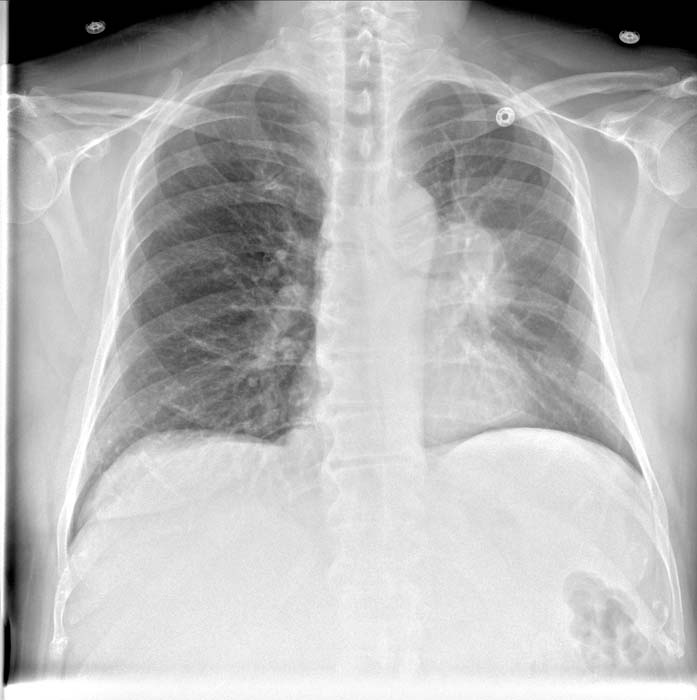
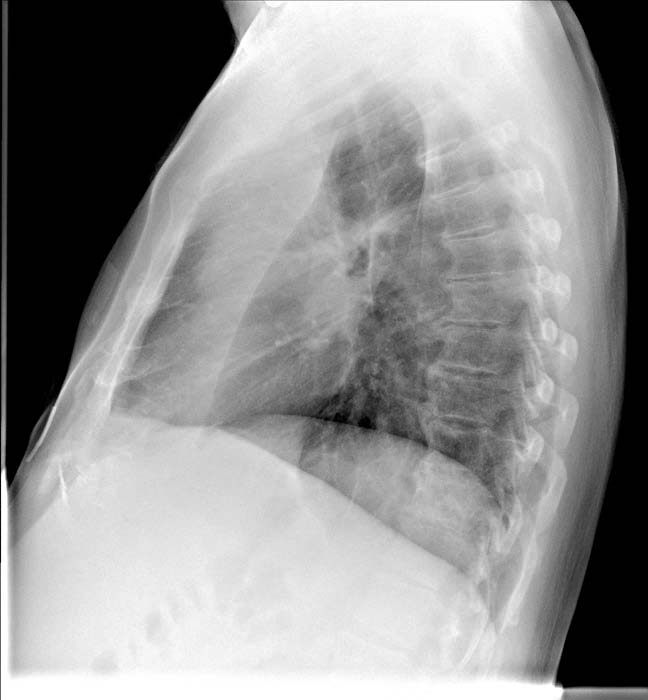
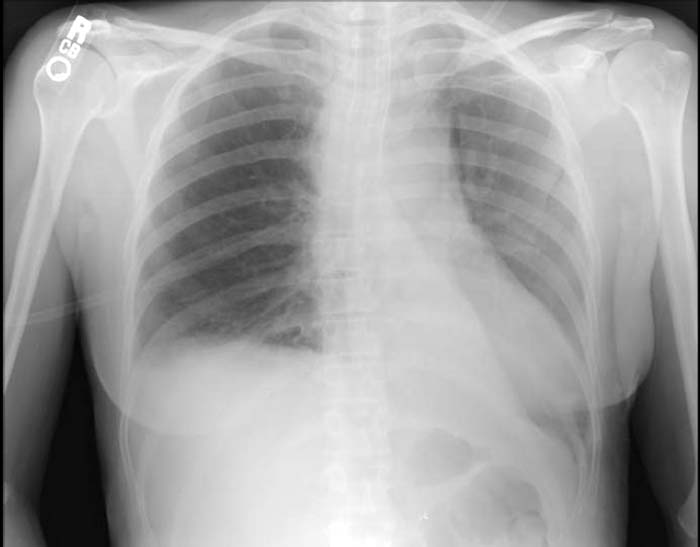
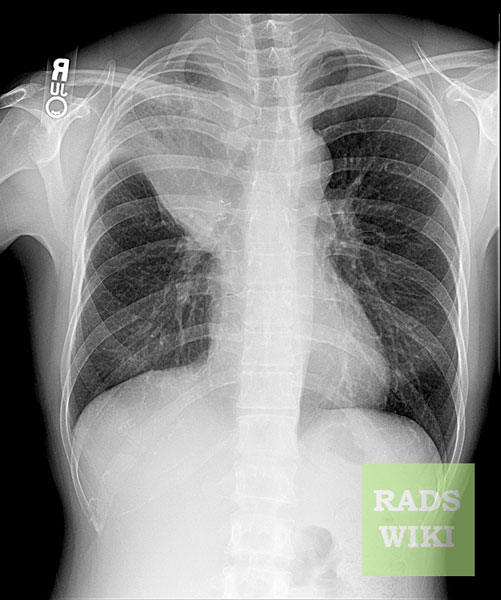
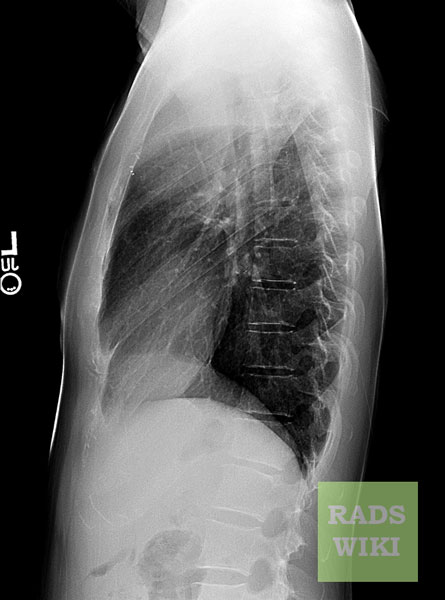
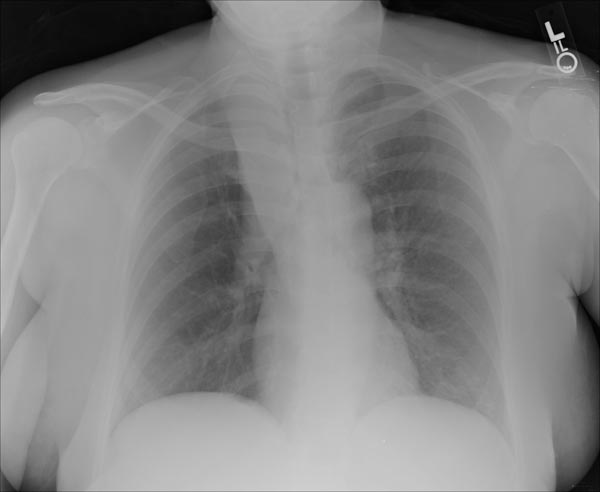
Chest X-ray
Post-surgical atelectasis will be bibasal in pattern.
Images shown in this section are courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted.
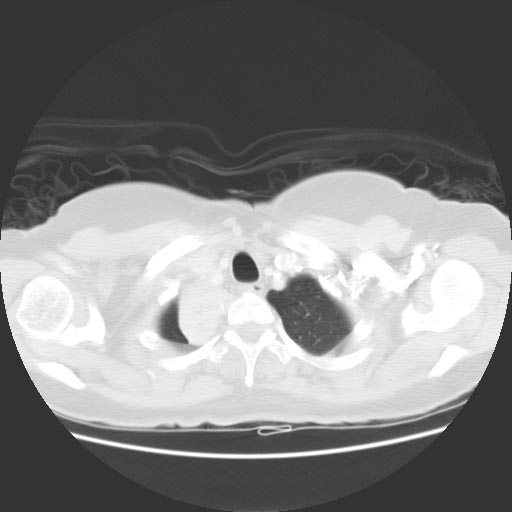
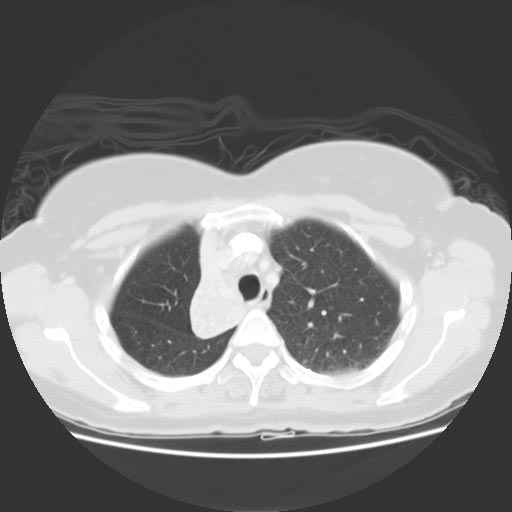
Computed tomography
Images shown in this section are courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted.
Bronchoscopy
Treatment
Treatment is directed at correcting the underlying cause. Post-surgical atelectasis is treated by physiotherapy, focusing on deep breathing and encouraging coughing. An incentive spirometer is often used as part of the breathing exercises. Ambulation is also highly encouraged to improve lung inflation. People with chest deformities or neurologic conditions that cause shallow breathing for long periods may benefit from mechanical devices that assist their breathing. One method is continuous positive airway pressure, which delivers pressurized air or oxygen through a nose or face mask to help ensure that the alveoli do not collapse, even at the end of a breath. This is helpful, as partially-inflated alveoli can be expanded more easily than collapsed alveoli. Sometimes additional respiratory support is needed with a mechanical ventilator.
The primary treatment for acute massive atelectasis is correction of the underlying cause. A blockage that cannot be removed by coughing or by suctioning the airways often can be removed by bronchoscopy. Antibiotics are given for an infection. Chronic atelectasis often is treated with antibiotics because infection is almost inevitable. In certain cases, the affected part of the lung may be surgically removed when recurring or chronic infections become disabling or bleeding is significant. If a tumor is blocking the airway, relieving the obstruction by surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or laser therapy may prevent atelectasis from progressing and recurrent obstructive pneumonia from developing.
References
- ↑ Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005