Alvimopan
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=
Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [1]
|genericName=
|aOrAn=
an
|drugClass=
opioid antagonist
|indication=
upper and lower gastrointestinal recovery following surgeries that include partial bowel resection with primary anastomosis
|hasBlackBoxWarning=
Yes
|adverseReactions=
|blackBoxWarningTitle=
WARNING
|blackBoxWarningBody= POTENTIAL RISK OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION WITH LONG-TERM USE:
- Increased incidence of myocardial infarction was seen in a clinical trial of patients taking alvimopan for long-term use.
- ENTEREG is available only through a restricted program for short-term use (15 doses) called the ENTEREG Access Support and Education (E.A.S.E.®) Program.
|fdaLIADAdult=
Condition1
- ENTEREG is indicated to accelerate the time to upper and lower gastrointestinal recovery following surgeries that include partial bowel resection with primary anastomosis.
- For hospital use only. The recommended adult dosage of ENTEREG is 12 mg administered 30 minutes to 5 hours prior to surgery followed by 12 mg twice daily beginning the day after surgery until discharge for a maximum of 7 days. Patients should not receive more than 15 doses of ENTEREG.
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Alvimopan in adult patients.
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Alvimopan in adult patients.
|fdaLIADPed=
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Alvimopan in pediatric patients.
|offLabelPedGuideSupport=
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Alvimopan in pediatric patients.
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Alvimopan in pediatric patients.
|contraindications=
- ENTEREG is contraindicated in patients who have taken therapeutic doses of opioids for more than 7 consecutive days immediately prior to taking ENTEREG.
|warnings=
Precautions
- Potential Risk of Myocardial Infarction with Long-term Use
- There were more reports of myocardial infarctions in patients treated with alvimopan 0.5 mg twice daily compared with placebo-treated patients in a 12-month study of patients treated with opioids for chronic non-cancer pain (alvimopan 0.5 mg, n = 538; placebo, n = 267). In this study, the majority of myocardial infarctions occurred between 1 and 4 months after initiation of treatment. This imbalance has not been observed in other studies of ENTEREG in patients treated with opioids for chronic pain, nor in patients treated within the surgical setting, including patients undergoing surgeries that included bowel resection who received ENTEREG 12 mg twice daily for up to 7 days (the indicated dose and patient population; ENTEREG 12 mg, n = 1,142; placebo, n = 1,120). A causal relationship with alvimopan with long-term use has not been established.
- ENTEREG is available only through a program under a REMS that restricts use to enrolled hospitals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- E.A.S.E. ENTEREG REMS Program
- ENTEREG is available only through a program called the ENTEREG Access Support and Education (E.A.S.E.) ENTEREG REMS Program that restricts use to enrolled hospitals because of the potential risk of myocardial infarction with long-term use of ENTEREG.
- Notable requirements of the E.A.S.E. Program include the following:
- ENTEREG is available only for short-term (15 doses) use in hospitalized patients. Only hospitals that have enrolled in and met all of the requirements for the E.A.S.E. program may use ENTEREG.
- To enroll in the E.A.S.E. Program, an authorized hospital representative must acknowledge that:
- hospital staff who prescribe, dispense, or administer ENTEREG have been provided the educational materials on the need to limit use of ENTEREG to short-term, inpatient use;
- patients will not receive more than 15 doses of ENTEREG; and
- ENTEREG will not be dispensed to patients after they have been discharged from the hospital.
- To enroll in the E.A.S.E. Program, an authorized hospital representative must acknowledge that:
- Further information is available at www.ENTEREGREMS.com or 1-877-282-4786.
- Gastrointestinal-Related Adverse Reactions in Opioid-Tolerant Patients
- Patients recently exposed to opioids are expected to be more sensitive to the effects of μ-opioid receptor antagonists, such as ENTEREG. Since ENTEREG acts peripherally, clinical signs and symptoms of increased sensitivity would be related to the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea). Patients receiving more than 3 doses of an opioid within the week prior to surgery were not studied in the postoperative ileus clinical trials. Therefore, if ENTEREG is administered to these patients, they should be monitored for gastrointestinal adverse reactions. ENTEREG is contraindicated in patients who have taken therapeutic doses of opioids for more than 7 consecutive days immediately prior to taking ENTEREG.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
- Patients with severe hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of serious adverse reactions (including dose-related serious adverse reactions) because up to 10-fold higher plasma levels of drug have been observed in such patients compared with patients with normal hepatic function. Therefore, the use of ENTEREG is not recommended in this population.
- End-Stage Renal Disease
- No studies have been conducted in patients with end-stage renal disease. ENTEREG is not recommended for use in these patients.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Patients with Complete Gastrointestinal Obstruction
- No studies have been conducted in patients with complete gastrointestinal obstruction or in patients who have surgery for correction of complete bowel obstruction. ENTEREG is not recommended for use in these patients.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Pancreatic and Gastric Anastomoses
- ENTEREG has not been studied in patients having pancreatic or gastric anastomosis. Therefore, ENTEREG is not recommended for use in these patients.
|clinicalTrials=
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be compared directly with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. The adverse event information from clinical trials does, however, provide a basis for identifying the adverse events that appear to be related to drug use and for approximating rates.
- The data described below reflect exposure to ENTEREG 12 mg in 1,793 patients in 10 placebo-controlled studies. The population was 19 to 97 years old, 64% were female, and 84% were Caucasian; 64% were undergoing a surgery that included bowel resection. The first dose of ENTEREG was administered 30 minutes to 5 hours before the scheduled start of surgery and then twice daily until hospital discharge (or for a maximum of 7 days of postoperative treatment).
- Among ENTEREG-treated patients undergoing surgeries that included a bowel resection, the most common adverse reaction (incidence ≥1.5%) occurring with a higher frequency than placebo was dyspepsia (ENTEREG, 1.5%; placebo, 0.8%). Adverse reactions are events that occurred after the first dose of study medication treatment and within 7 days of the last dose of study medication or events present at baseline that increased in severity after the start of study medication treatment.
|postmarketing=
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|drugInteractions=
- Potential for Drugs to Affect Alvimopan Pharmacokinetics
- An in vitro study indicates that alvimopan is not a substrate of CYP enzymes. Therefore, concomitant administration of ENTEREG with inducers or inhibitors of CYP enzymes is unlikely to alter the metabolism of alvimopan.
- Potential for Alvimopan to Affect the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
- Based on in vitro data, ENTEREG is unlikely to alter the pharmacokinetics of coadministered drugs through inhibition of CYP isoforms such as 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 3A4, 2D6, and 2E1 or induction of CYP isoforms such as 1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4.
- In vitro, ENTEREG did not inhibit p-glycoprotein.
- Effects of Alvimopan on Intravenous Morphine
- Coadministration of alvimopan does not appear to alter the pharmacokinetics of morphine and its metabolite, morphine-6-glucuronide, to a clinically significant degree when morphine is administered intravenously. Dosage adjustment for intravenously administered morphine is not necessary when it is coadministered with alvimopan.
- Effects of Concomitant Acid Blockers or Antibiotics
- A population pharmacokinetic analysis suggests that the pharmacokinetics of alvimopan were not affected by concomitant administration of acid blockers or antibiotics. No dosage adjustments are necessary in patients taking acid blockers or antibiotics.
|useInPregnancyFDA=
- Pregnancy Category B
- Risk Summary: There are no adequate and/or well-controlled studies with ENTEREG in pregnant women. No fetal harm was observed in animal reproduction studies with oral administration of alvimopan to rats at doses 68 to 136 times the recommended human oral dose, or with intravenous administration to rats and rabbits at doses 3.4 to 6.8 times, and 5 to 10 times, respectively, the recommended human oral dose. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, ENTEREG should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Animal Data: Reproduction studies were performed in pregnant rats at oral doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (about 68 to 136 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area) and at intravenous doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 6.8 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area) and in pregnant rabbits at intravenous doses up to 15 mg/kg/day (about 5 to 10 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area), and revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to alvimopa
|useInPregnancyAUS=
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Alvimopan in women who are pregnant.
|useInLaborDelivery= There is no FDA guidance on use of Alvimopan during labor and delivery.
|useInNursing=
- It is not known whether ENTEREG is present in human milk. Alvimopan and its 'metabolite' are detected in the milk of lactating rats. Exercise caution when administering ENTEREG to a nursing woman.
|useInPed=
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
|useInGeri=
- Of the total number of patients in 6 clinical efficacy studies treated with ENTEREG 12 mg or placebo, 46% were 65 years of age and over, while 18% were 75 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. No dosage adjustment based on increased age is required.
|useInGender= There is no FDA guidance on the use of Alvimopan with respect to specific gender populations.
|useInRace=
- No dosage adjustment is necessary in Black, Hispanic, and Japanese patients. However, the exposure to ENTEREG in Japanese healthy male volunteers was approximately 2-fold greater than in Caucasian subjects. Japanese patients should be closely monitored for possible adverse effects (e.g., diarrhea, gastrointestinal pain, cramping) that could indicate high drug or 'metabolite' levels, and ENTEREG should be discontinued if adverse events occur.
|useInRenalImpair=
- ENTEREG is not recommended for use in patients with end-stage renal disease. Dosage adjustment is not required for patients with mild-to-severe renal impairment, but they should be monitored for adverse effects. Patients with severe renal impairment should be closely monitored for possible adverse effects (e.g., diarrhea, gastrointestinal pain, cramping) that could indicate high drug or 'metabolite' levels, and ENTEREG should be discontinued if adverse events occur.
|useInHepaticImpair=
- ENTEREG is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Dosage adjustment is not required for patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment should be closely monitored for possible adverse effects (e.g., diarrhea, gastrointestinal pain, cramping) that could indicate high drug or 'metabolite' levels, and ENTEREG should be discontinued if adverse events occur.
|useInReproPotential= There is no FDA guidance on the use of Alvimopan in women of reproductive potentials and males.
|useInImmunocomp= There is no FDA guidance one the use of Alvimopan in patients who are immunocompromised.
|administration=
- Oral
|monitoring=
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|IVCompat=
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|overdose=
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|drugBox=
|mechAction=
- Alvimopan is a selective antagonist of the cloned human μ-opioid receptor with a Ki of 0.4 nM (0.2 ng/mL) and no measurable opioid-agonist effects in standard pharmacologic assays. The dissociation of [3H]-alvimopan from the human μ-opioid receptor is slower than that of other opioid ligands, consistent with its higher affinity for the receptor. At concentrations of 1 to 10 µM, alvimopan demonstrated no activity at any of over 70 non-opioid receptors, enzymes, and ion channels.
- Postoperative ileus is the impairment of gastrointestinal motility after intra-abdominal surgery or other, non-abdominal surgeries. Postoperative ileus affects all segments of the gastrointestinal tract and may last from 5 to 6 days, or even longer. This may potentially delay gastrointestinal recovery and hospital discharge until its resolution. It is characterized by abdominal distention and bloating, nausea, vomiting, pain, accumulation of gas and fluids in the bowel, and delayed passage of flatus and defecation. Postoperative ileus is the result of a multifactorial process that includes inhibitory sympathetic input and release of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other mediators (e.g., endogenous opioids). A component of postoperative ileus also results from an inflammatory reaction and the effects of opioid analgesics. Morphine and other μ-opioid receptor agonists are universally used for the treatment of acute postsurgical pain; however, they are known to have an inhibitory effect on gastrointestinal motility and may prolong the duration of postoperative ileus.
- Following oral administration, alvimopan antagonizes the peripheral effects of opioids on gastrointestinal motility and secretion by competitively binding to gastrointestinal tract μ-opioid receptors. The antagonism produced by alvimopan at opioid receptors is evident in isolated guinea pig ileum preparations in which alvimopan competitively antagonizes the effects of morphine on contractility. Alvimopan achieves this selective gastrointestinal opioid antagonism without reversing the central analgesic effects of μ-opioid agonists.
|structure=
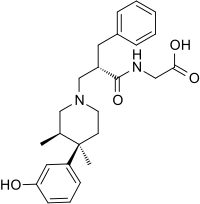
- ENTEREG capsules contain alvimopan, an opioid antagonist. Chemically, alvimopan is the single stereoisomer [[;<2(S)-[4(R)-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3(R),4-dimethyl-1-piperidinyl]methyl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl]amino]acetic acid dihydrate. It has the following structural formula:
- Alvimopan is a white to light beige powder with a molecular weight of 460.6, and the empirical formula is C25H32N2O4•2H2O. It has a solubility of <0.1 mg/mL in water or buffered solutions between pH 3.0 and 9.0, 1 to 5 mg/mL in buffered solutions at pH 1.2, and 10 to 25 mg/mL in aqueous 0.1 N sodium hydroxide. At physiological pH, alvimopan is zwitterionic, a property that contributes to its low solubility.
- ENTEREG capsules for oral administration contain 12 mg of alvimopan on an anhydrous basis suspended in the inactive ingredient polyethylene glycol.
|PD=
- In an exploratory study in healthy volunteers, alvimopan 12 mg administered twice a day reduced the delay in small and large bowel transit induced by codeine 30 mg administered 4 times a day, as measured by gastrointestinal scintigraphy. In the same study, concomitant alvimopan did not reduce the delay in gastric emptying induced by codeine.
- In a study designed to evaluate potential effects on cardiac conduction, alvimopan did not cause clinically significant QTc prolongation at doses up to 24 mg twice daily (twice the approved dosage regimen) for 7 days. The potential for QTc effects at higher doses has not been studied.
|PK=
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|nonClinToxic=
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|clinicalStudies=
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|howSupplied=
|fdaPatientInfo=
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Alvimopan in the drug label.
|alcohol=
- Alcohol-Alvimopan interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
|brandNames=
- ®[1]
|lookAlike=
- A® — B®[2]
|drugShortage=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Alvimopan |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Alvimopan |Label Name=Alvimopan11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Alvimopan |Label Name=Alvimopan11.png
}}
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)