Benzocaine (injection): Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) m (Changed protection level for "Benzocaine" ([Edit=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 12:03, 9 July 2014 (UTC)) [Move=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 12:03, 9 July 2014 (UTC)))) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 12:03, 25 June 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]
Overview
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
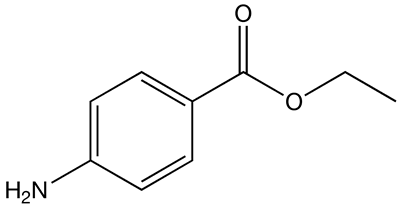
| Formula | C9H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 165.189 g/mol |
Benzocaine is a local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments, including oral pain relievers such as Orajel and topical pain relievers such as Lanacane.
Chemical properties
Benzocaine is an ester, and can be prepared from the organic acid PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid) and ethanol by Fischer esterification. The melting point of Benzocaine is 88-90 degrees Celsius, and the boiling point is 172 degrees Celsius. The density of Benzocaine is 1.17g/cm3
History
Benzocaine was first synthesised by a German chemical firm named Ritsert, in the town of Eberbach, in Baden-Württemberg in 1902.
How it relieves pain
Pain is caused by the stimulation of free nerve endings. When the nerve endings are stimulated, sodium enters the neuron, which causes an electrical potential to build up in the nerve. Once the electrical potential becomes big enough the signal is propagated down the nerve toward the central nervous system, which interprets this as pain.
Esters of PABA work as a chemical barrier, stopping the sodium from being able to enter the nerve ending.
Side effects
Allergic reactions occur with ester local anaesthetics (like benzocaine) because of the PABA structure.
Benzocaine also is a well-known cause of methemoglobinemia. Because it may be used in topical creams with a concentration as much as 20%, it is not difficult to administer a dose sufficient to cause this problem.
Other uses
Benzocaine can also be used as a fish tranquilizer. Due to its low solubility in water, stock solution can be made with ethanol (95%). 25 g of benzocaine per 200 ml ethanol will make a solution strong enough to knock saltwater fish out in 2-4 minutes. They will regain equilibrium after 10-15 minutes. Use 5 ml stock solution per 1 L of saltwater. Some benzocaine will precipitate out of solution when added to the saltwater, so it is recommended to add the volume of stock solution you will be using to a separate container and mix it with some saltwater before adding it to the tank.
Benzocaine is also used as a key ingredient in Phenazone, an anti-inflammatory, and is also used in some glycerol-based ear medications for use in removing excess wax as well as ear conditions such as Otitis Media and swimmers ear.
It is also used in certain condoms to prolong sex by numbing the penis.[1]
Benzocaine is an ingredient in some anal sex lubricants.[2]
References
External links
- FDA investigation of the possible adverse effects of benzocaine mouth and throat sprays.
- http://www.endonurse.com
Template:Vasoprotectives
Template:Antipruritics
Template:Throat preparations
de:Benzocain
it:Benzocaina
he:בנזוקאין
hu:Benzokain
nl:Benzocaïne
- Pages with script errors
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Local anesthetics