Esophagitis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
=== Symptoms === | === Symptoms === | ||
The symptoms of esophagitis include: | The symptoms of esophagitis include: | ||
*[[Chest pain]], in the middle of the chest, often radiating to the back, usually associated with swallowing or soon after a meal | |||
*[[Nausea]] | |||
*[[Vomiting]] | |||
Sore throat or hoarseness | |||
*[[Mouth sores]] | |||
*[[Difficulty swallowing]] and/or [[painful swallowing]], especially if there is a feeling of food getting stuck on the way down | |||
*[[Bad breath]] ([[halitosis]]) | |||
Symptoms of underlying diseases include: | |||
*[[Indigestion]] | |||
*[[Heartburn]], [[acid reflux]], or [[unpleasant taste in the mouth]] | |||
*[[Excessive belching]] | |||
== Complete Differential Diagnosis == | == Complete Differential Diagnosis == | ||
Revision as of 13:57, 29 July 2012
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
WikiDoc Resources for Esophagitis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Esophagitis Most cited articles on Esophagitis |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Esophagitis |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Esophagitis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Esophagitis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Esophagitis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Esophagitis Discussion groups on Esophagitis Patient Handouts on Esophagitis Directions to Hospitals Treating Esophagitis Risk calculators and risk factors for Esophagitis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Esophagitis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1],Assistant Editor-in-Chief: Soumya Sachdeva
Synonyms and keywords: Oesophagitis
Overview
Esophagitis is defined as inflammation of the esophagus. The inflammation can be due to a variety of causes such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, viruses, or chemical injuries.
Pathophysiology
Causes
Common Causes
- The most common cause is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). If caused by GERD, the diseases is also called reflux esophagitis.
- Other causes of esophagitis include infections (most commonly candida, herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus). These infections are typically seen in immunocompromised people, such as those with HIV.
- Food allergies have also been known to cause esophagitis
- Chemical injury by alkaline or acid solutions may also cause esophagitis, and is usually seen in children or in adults who attempt suicide.
- Physical injury resulting from radiation therapy or by nasogastric tubes may also be responsible.
Diagnosis
Symptoms
The symptoms of esophagitis include:
- Chest pain, in the middle of the chest, often radiating to the back, usually associated with swallowing or soon after a meal
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Sore throat or hoarseness
- Mouth sores
- Difficulty swallowing and/or painful swallowing, especially if there is a feeling of food getting stuck on the way down
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Symptoms of underlying diseases include:
Complete Differential Diagnosis
In alphabetical order. [1] [2]
- Bacterial infection
- Candida
- Caustic burn
- Crohn's Disease
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Drugs, toxins
- Fungal infection
- Gastric tube
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Gastroscopy
- Hernias
- Herpes
- Metastasis
- Radiation
- Surgery
- Tumor
- Vomiting
Diagnostic Findings
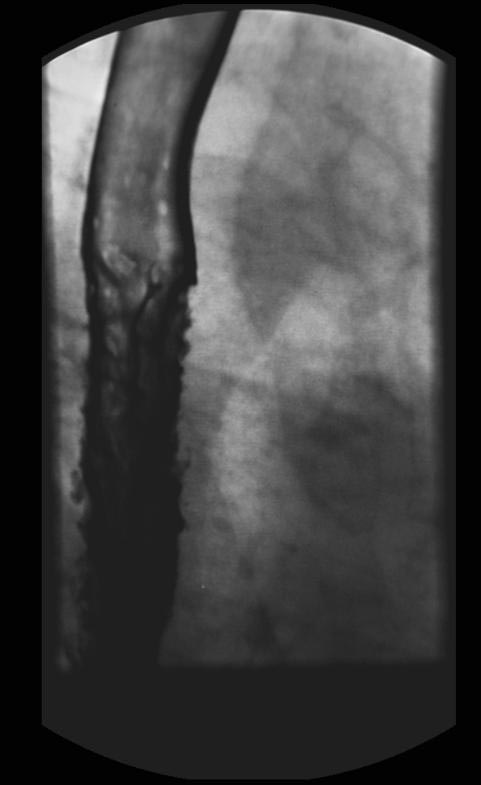
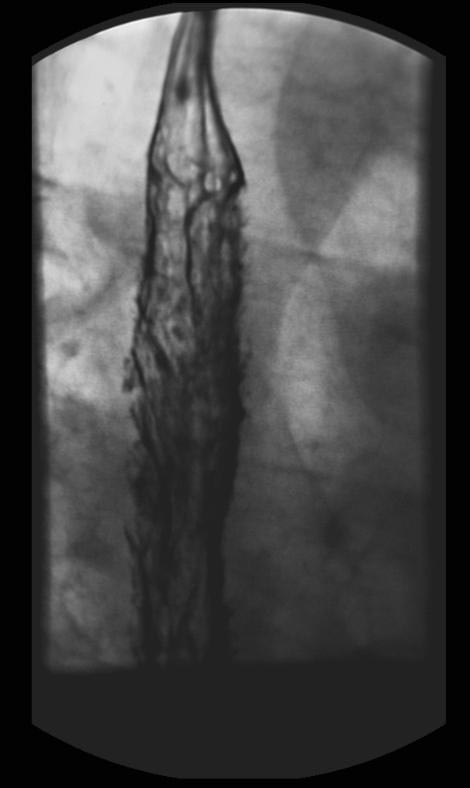
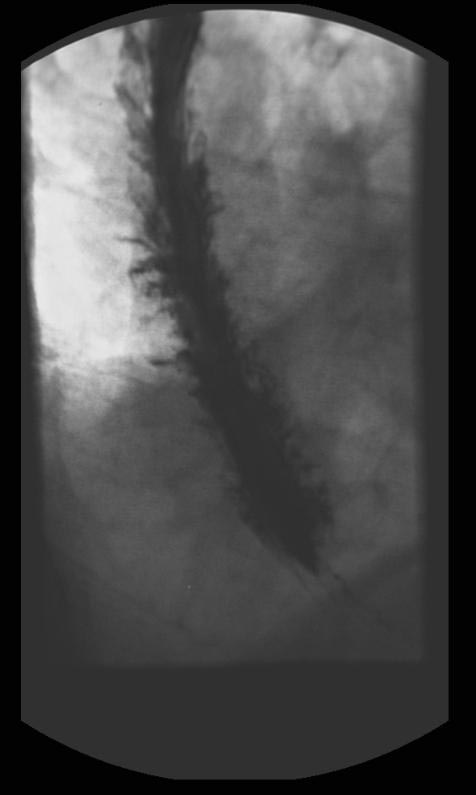
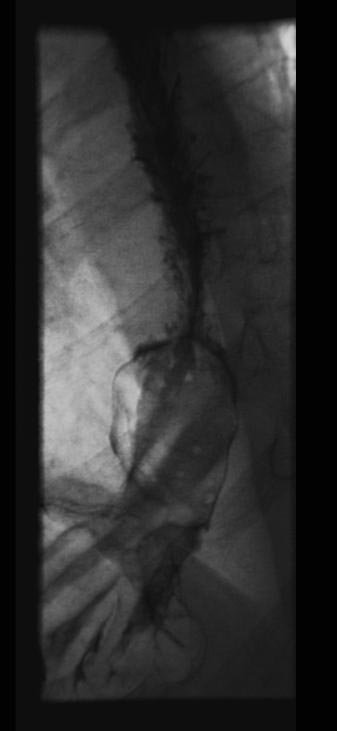
X-ray Findings
(Images shown below are courtesy of RadsWiki)
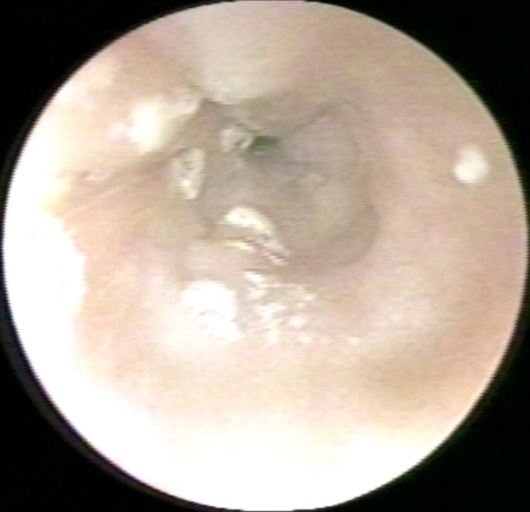
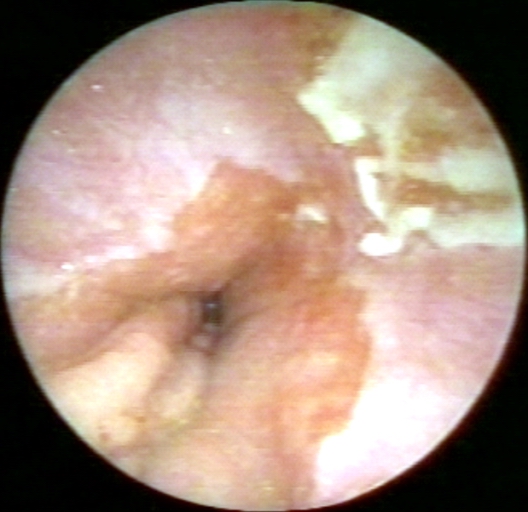
Endoscopic Findings
-
Candida esophagitis
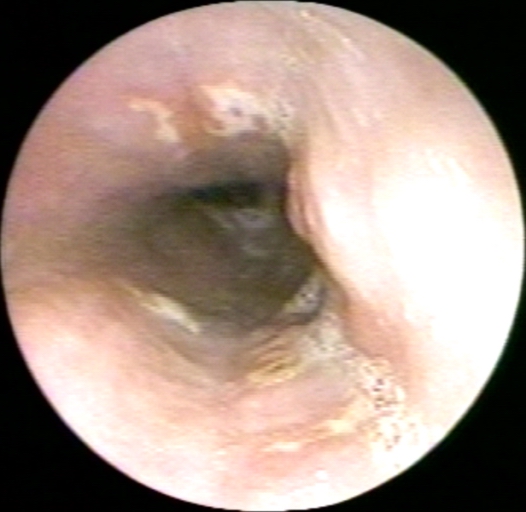
-
NSAID esophagitis
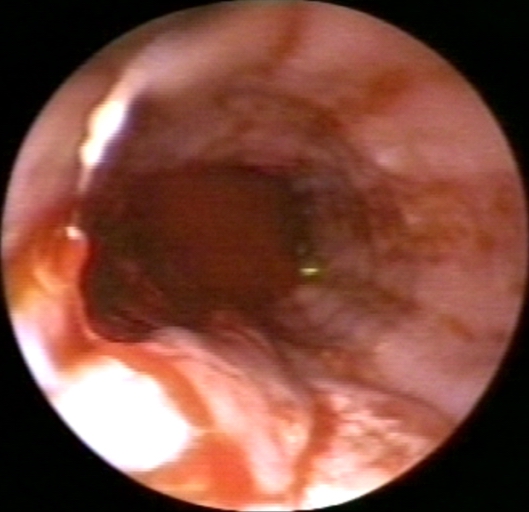
-
Peptic esophagitis
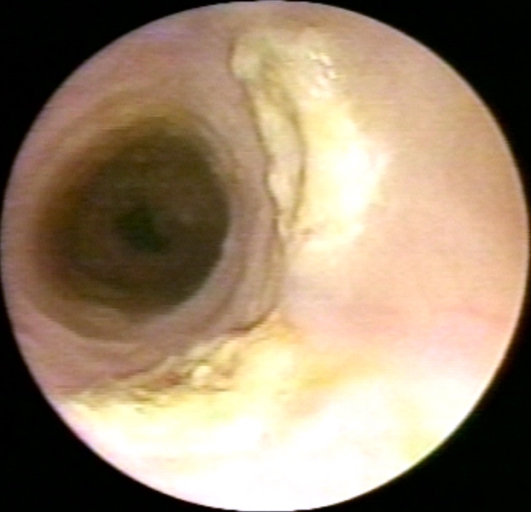
-
Herpetic esophagitis
-
Caustic lye esophagitis
Pathological Findings
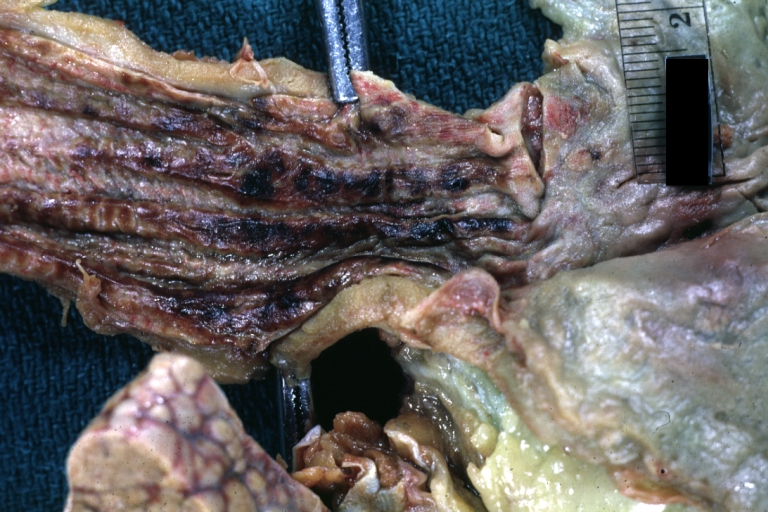
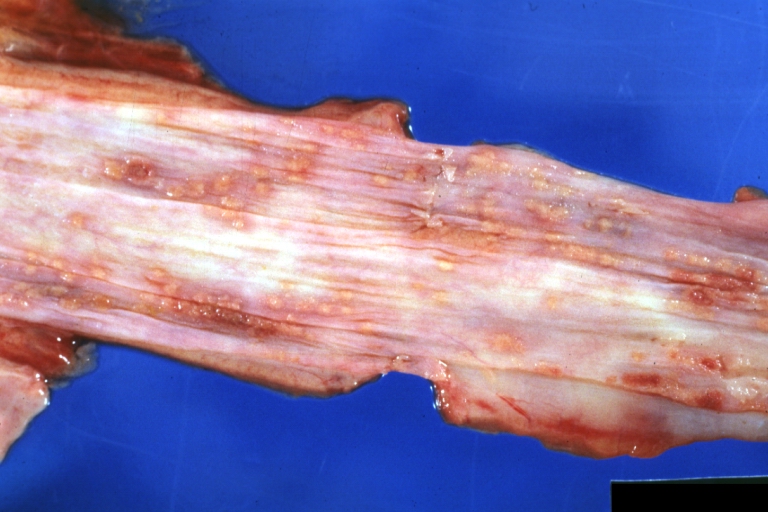
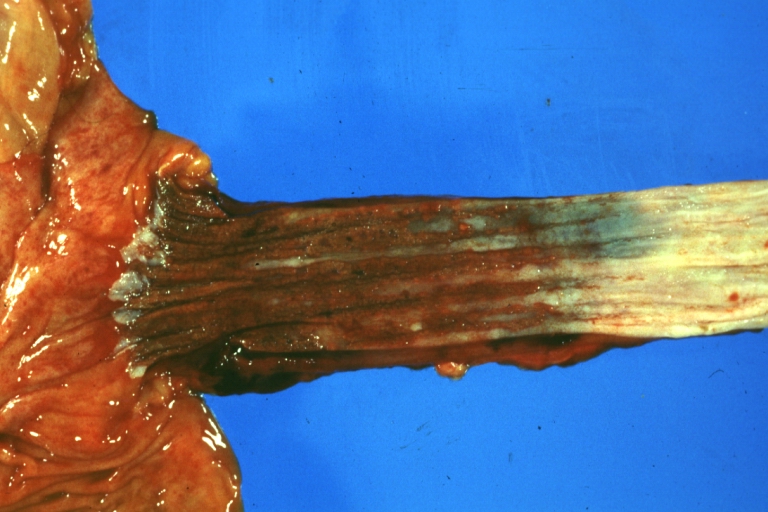
Gross Images
-
Esophagus: Candida: Gross natural color close up of distal esophagus mucosa, an excellent example of candida esophagitis
-
Esophagitis Candida: Gross natural color close-up, an excellent example
-
Esophagitis Candida: Gross natural color excellent close-up photo case of acute myelomonocytic leukemia
-
Necrotizing esophagitis and gastritis, sulfuric acid ingested as suicide attempt
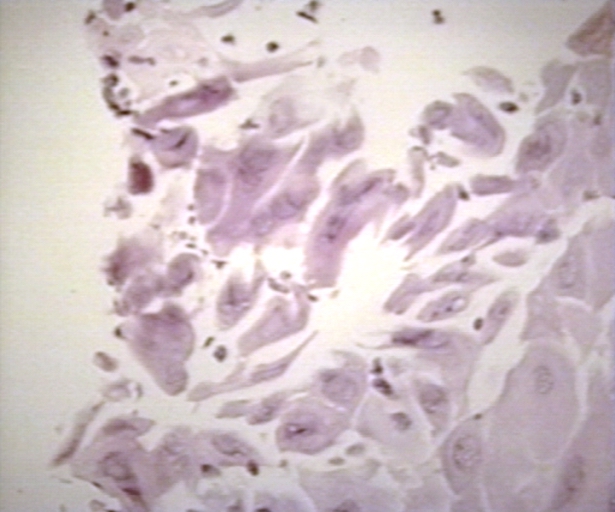
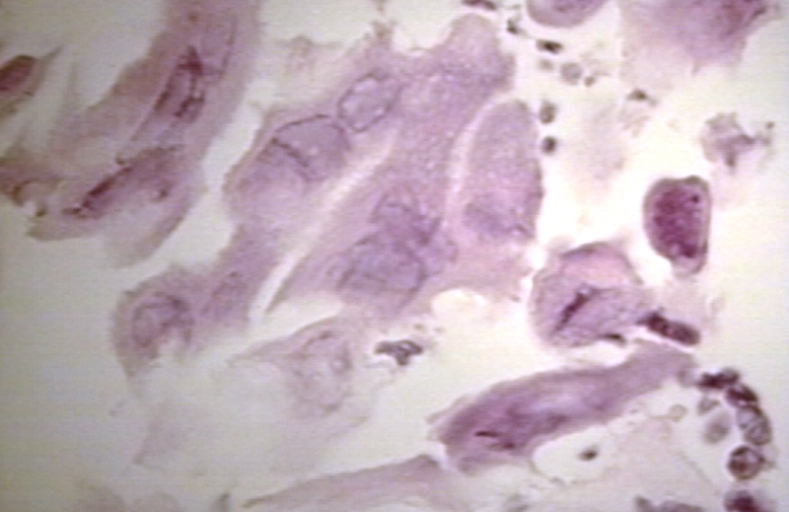
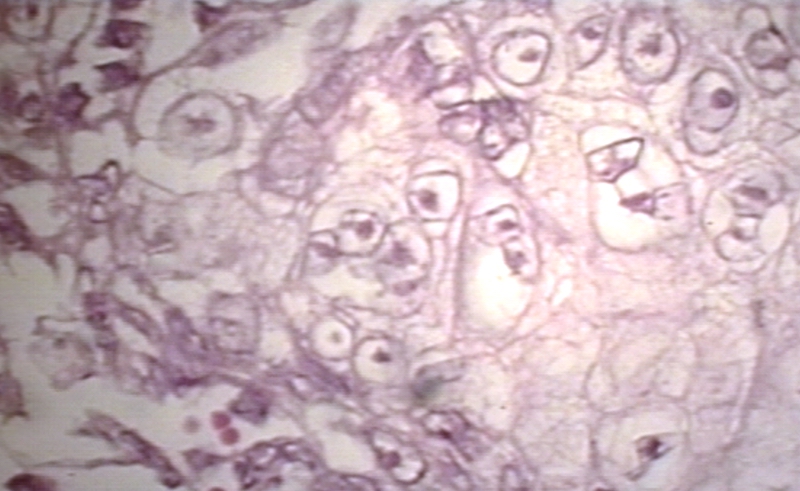
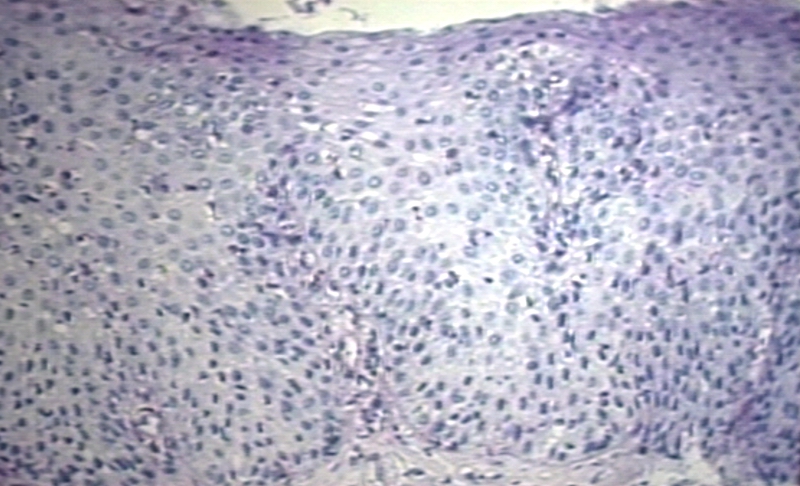
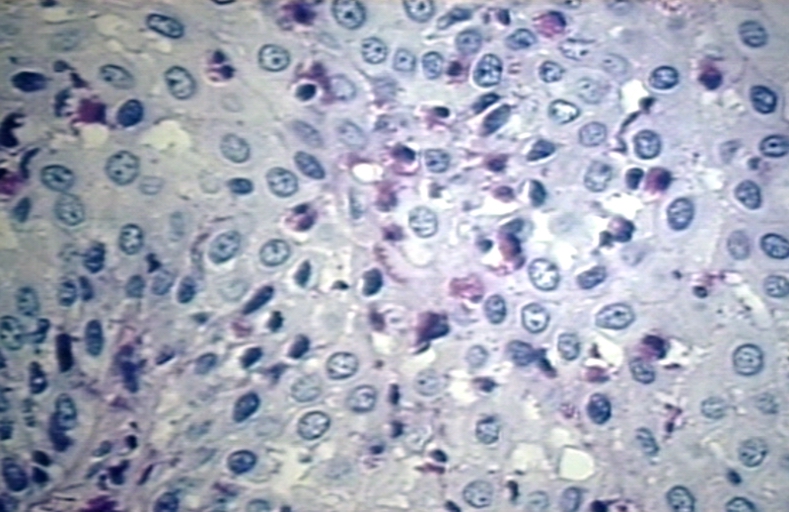
Microscopic Images
-
Herpes esophagitis 100 x
-
Herpes esophagitis 400 x
-
Herpes esophagitis 600 x
-
Reflux esophagitis 100 x
-
Reflux esophagitis 400 x
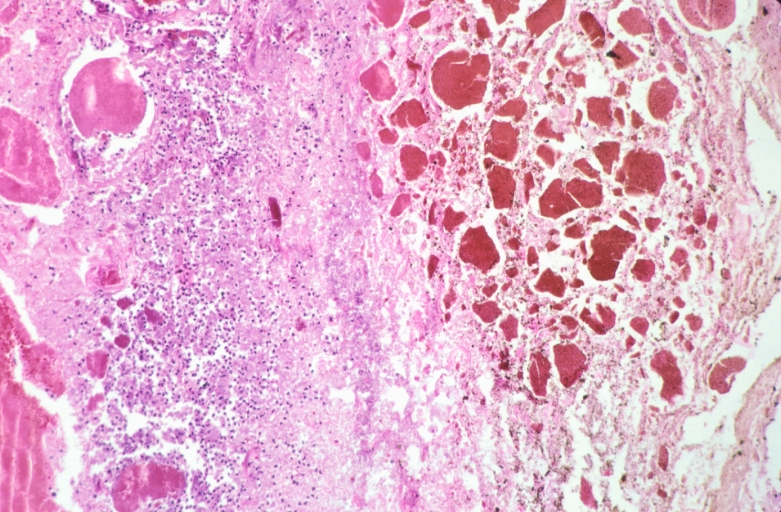
-
Necrotizing esophagitis and gastritis, sulfuric acid ingested as suicide attempt
Histopathological Findings: Herpes esophagitis
<youtube v=bJME-CJvHfs/>
References
{{Gastroenterology}