Cirrhosis CT: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Cirrhosis}} | {{Cirrhosis}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{ | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Cherry}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Although CT scans are not routinely used in evaluation and diagnosis of cirrhosis, it | Although CT scans are not routinely used in evaluation and diagnosis of [[cirrhosis]], it may show the presence of [[Hepatic lobule|lobar]] [[Atrophy|atrophic]] and [[Hypertrophy (medical)|hypertrophic]] changes in the [[liver]], [[ascites]] and [[varices]]. CT scans also visualize the presence of [[tumors]], blocked [[Bile duct|bile ducts]] and help evaluate the size of the [[liver]]. | ||
==CT== | ==CT== | ||
* [[Computed tomography]] is not routinely used in the [[diagnosis]] and evaluation of [[cirrhosis]]. | |||
* [[Computed tomography|Computed tomography (CT) scanning]] complements [[ultrasound]] imaging. | |||
* CT scan is poor at detecting morphologic changes associated with early [[cirrhosis]], but may accurately demonstrate [[Nodule (medicine)|nodularity]] and [[Hepatic lobule|lobar]] atrophic and hypertrophic changes, [[ascites]] and [[varices]] in advanced disease. | |||
* CT findings may suggest the presence of [[cirrhosis]], but is not diagnostic. | |||
* CT portal phase imaging may be used in the assesment of patency of the [[portal vein]].<ref name="urlCirrhosis and Chronic Liver Failure: Part I. Diagnosis and Evaluation - September 1, 2006 - American Family Physician">{{cite web |url=http://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/0901/p756.html#afp20060901p756-b20 |title=Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Failure: Part I. Diagnosis and Evaluation - September 1, 2006 - American Family Physician |format= |work= |accessdate=2012-09-07}}</ref> | |||
* [[Computed tomography|CT]] may be indicative of underlying [[etiology]] due to its classical appearances in some diseases: | |||
**[[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]: hypertrophied [[Caudate lobe of liver|caudate lobe]] | |||
**[[Hemochromatosis|Haemochromatosis]]: excess iron deposition leads to a dramatic increase in [[Liver|hepatic]] density | |||
* CT scan in patients with cirrhosis may be used to detect: | |||
** [[Liver|Hepatic]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodularity]] | |||
* | ** [[Atrophy]] of the right [[Lobe (anatomy)|lobe]] | ||
** [[Hypertrophy (medical)|Hypertrophy]] of the [[Caudate lobe of liver|caudate]] or left lobes | |||
* | ** [[Ascites]] | ||
** [[Varices]] | |||
** | ** [[Liver]] size | ||
** Blocked [[bile ducts]] | |||
** Blood flow through the [[liver]] | |||
** [[Tumor|Tumors]] | |||
* Side effects of CT scans: | |||
** Exposure to contrast and [[Radiation (medicine)|radiation]] | |||
===CT Images=== | |||
* CT of a [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic]] patient shows a [[liver]] with a shrunken, [[Nodule (medicine)|nodular]] appearance. | |||
[[File:Output qzgZxt.gif|500px|center|thumb|Liver Cirrhosis <br> Source: Wikimedia commons <ref name="urlFile:Morbus-Osler-CT-Leber-ax-012.jpg - Wikimedia Commons">{{cite web |url=https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Morbus-Osler-CT-Leber-ax-012.jpg |title=File:Morbus-Osler-CT-Leber-ax-012.jpg - Wikimedia Commons |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | |||
* Abdominal [[CT scan]] may be helpful in the diagnosis of portal hypertension. Findings on [[CT scan]] suggestive of portal hypertension include:<ref name="ProcopetBerzigotti2017">{{cite journal|last1=Procopet|first1=Bogdan|last2=Berzigotti|first2=Annalisa|title=Diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension: imaging, non-invasive markers of fibrosis and liver biopsy|journal=Gastroenterology Report|volume=5|issue=2|year=2017|pages=79–89|issn=2052-0034|doi=10.1093/gastro/gox012}}</ref><ref name="AagaardJensen1982">{{cite journal|last1=Aagaard|first1=J|last2=Jensen|first2=LI|last3=Sorensen|first3=TI|last4=Christensen|first4=U|last5=Burcharth|first5=F|title=Recanalized umbilical vein in portal hypertension|journal=American Journal of Roentgenology|volume=139|issue=6|year=1982|pages=1107–1110|issn=0361-803X|doi=10.2214/ajr.139.6.1107}}</ref><ref name="ChoPatel1995">{{cite journal|last1=Cho|first1=K C|last2=Patel|first2=Y D|last3=Wachsberg|first3=R H|last4=Seeff|first4=J|title=Varices in portal hypertension: evaluation with CT.|journal=RadioGraphics|volume=15|issue=3|year=1995|pages=609–622|issn=0271-5333|doi=10.1148/radiographics.15.3.7624566}}</ref><ref name="BandaliMirakhur2017">{{cite journal|last1=Bandali|first1=Murad Feroz|last2=Mirakhur|first2=Anirudh|last3=Lee|first3=Edward Wolfgang|last4=Ferris|first4=Mollie Clarke|last5=Sadler|first5=David James|last6=Gray|first6=Robin Ritchie|last7=Wong|first7=Jason Kam|title=Portal hypertension: Imaging of portosystemic collateral pathways and associated image-guided therapy|journal=World Journal of Gastroenterology|volume=23|issue=10|year=2017|pages=1735|issn=1007-9327|doi=10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735}}</ref> | |||
CT | ** [[Cirrhosis|Cirrhotic liver]], as shrinkage and atrophy in liver | ||
** Re-canalized [[umbilical vein]]--[[pathognomonic]] | |||
** Dilated [[portal vein]] and/or [[splanchnic]] veins | |||
** [[Esophageal varices]] | |||
** [[Collaterals]] in any [[Abdominal organs|abdominal organ]] | |||
** [[Splenomegaly]] | |||
** [[Ascites]] | |||
'''Portal hypertension''' | |||
{| | |||
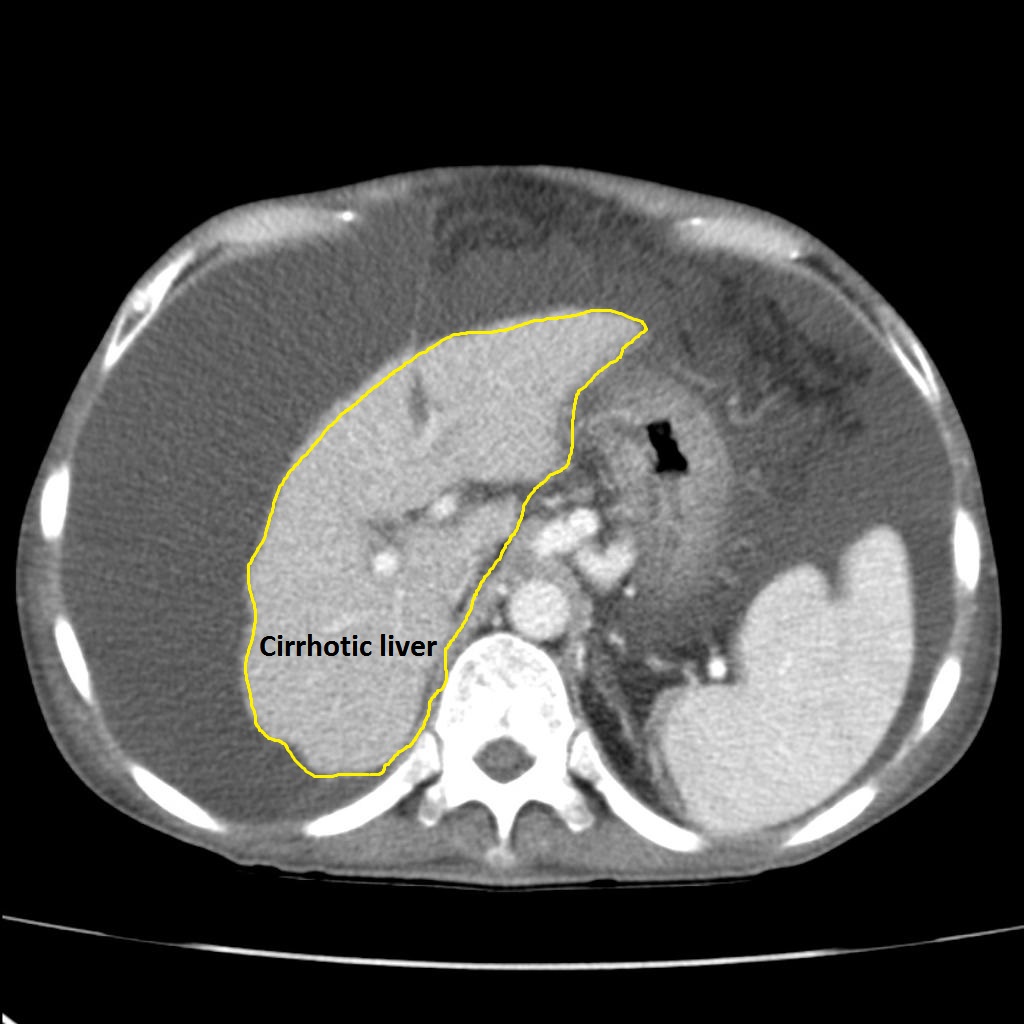
|[[Image:Cirrhosis-secondary-to-chronic-hepatitis-c.jpg|thumb|250px|Cirrhosis-Case courtesy of Dr David Cuete, via Radiopaedia.org<ref>From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/23057">rID: 23057</ref>]] | |||
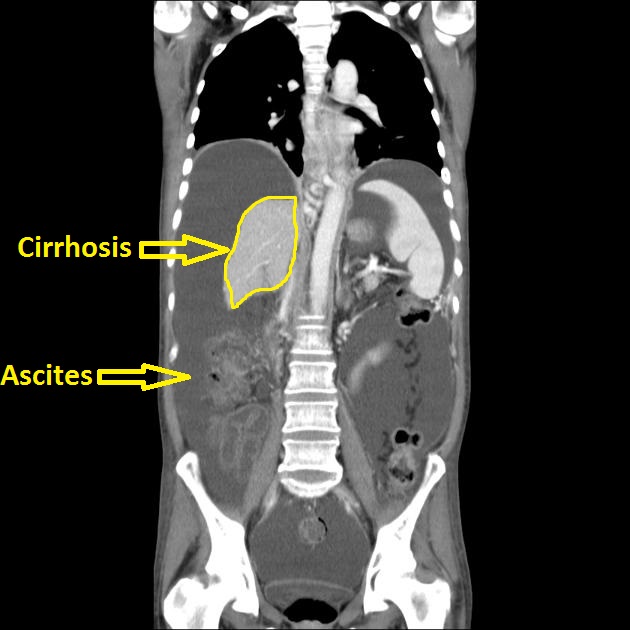
|[[Image:Cirrhosis111.jpg|thumb|250px|Cirrhosis-Case courtesy of Dr David Cuete, via Radiopaedia.org<ref>From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/23057">rID: 23057</ref>]] | |||
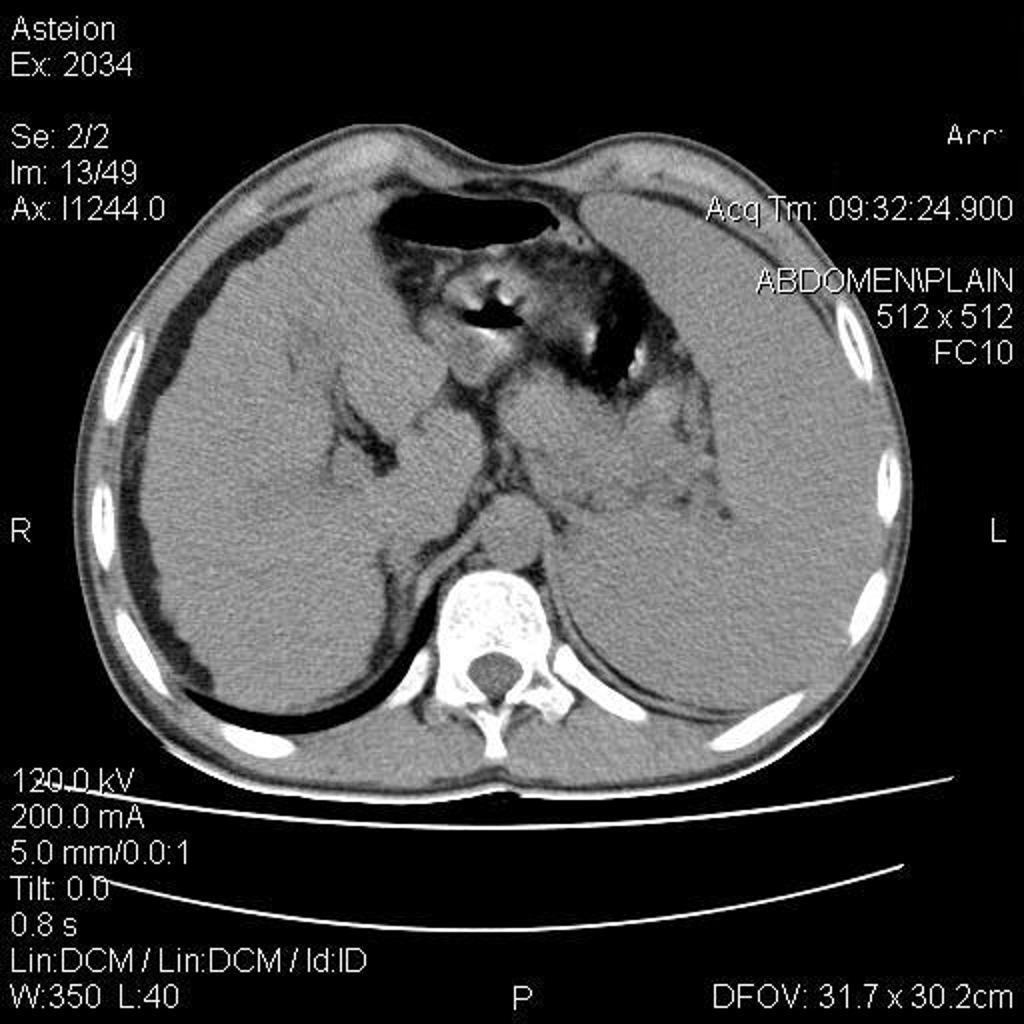
|[[Image:Cirrhotic-liver-in-wilson-disease.jpg|thumb|230px|Cirrhotic liver in wilson disease-Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, via Radiopaedia.org<ref>From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/5379">rID: 5379</ref>]] | |||
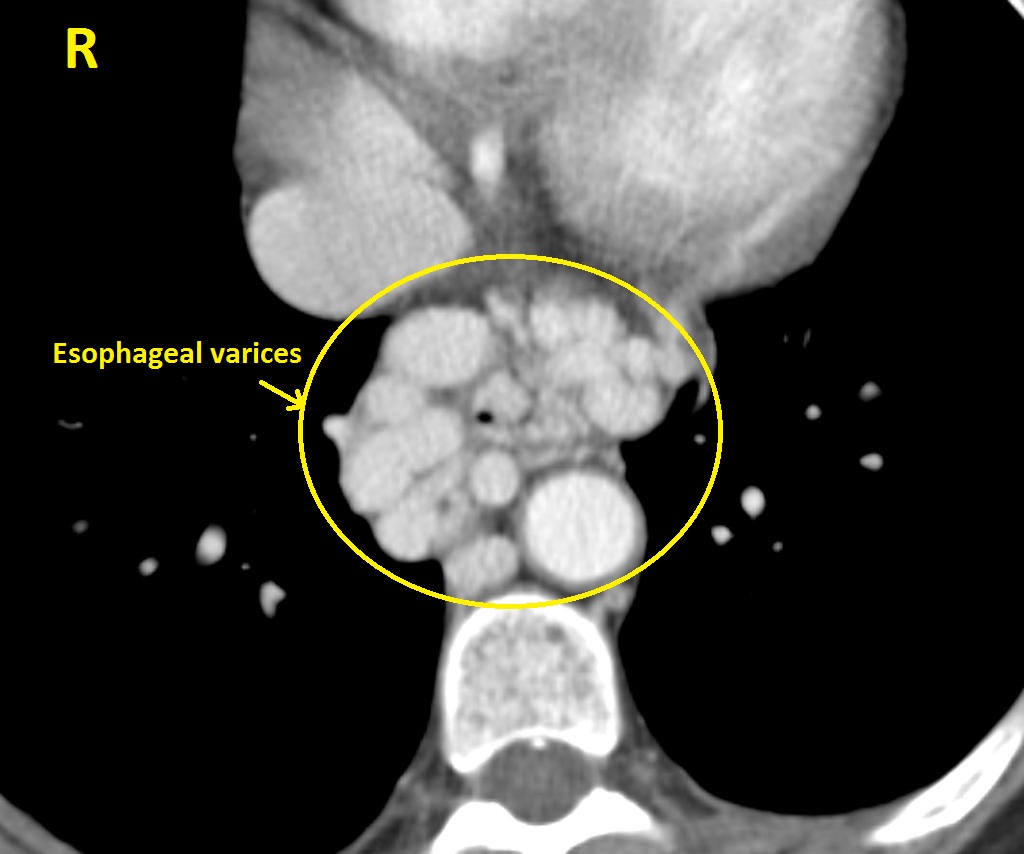
|[[Image:Oesophageal-varices.jpg|thumb|300px|Esophageal varices-Case courtesy of Dr Roberto Schubert, via Radiopaedia.org<ref>From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/15852">rID: 15852</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
'''Recanalized Umbilical Vein''' | |||
< | {| | ||
Image: | |[[Image:Uv1.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | ||
</ | |[[Image:Uv2.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | ||
|[[Image:Uv3.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | |||
|- | | |||
|[[Image:Uv4.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | |||
|[[Image:Uv5.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | |||
|[[Image:Uv6.jpg|thumb|380px|Recanalized Umbilical Vein- Case courtesy of Radswiki, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:24, 13 December 2017
|
Cirrhosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Cirrhosis CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cirrhosis CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sudarshana Datta, MD [2]
Overview
Although CT scans are not routinely used in evaluation and diagnosis of cirrhosis, it may show the presence of lobar atrophic and hypertrophic changes in the liver, ascites and varices. CT scans also visualize the presence of tumors, blocked bile ducts and help evaluate the size of the liver.
CT
- Computed tomography is not routinely used in the diagnosis and evaluation of cirrhosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) scanning complements ultrasound imaging.
- CT scan is poor at detecting morphologic changes associated with early cirrhosis, but may accurately demonstrate nodularity and lobar atrophic and hypertrophic changes, ascites and varices in advanced disease.
- CT findings may suggest the presence of cirrhosis, but is not diagnostic.
- CT portal phase imaging may be used in the assesment of patency of the portal vein.[1]
- CT may be indicative of underlying etiology due to its classical appearances in some diseases:
- Budd-Chiari syndrome: hypertrophied caudate lobe
- Haemochromatosis: excess iron deposition leads to a dramatic increase in hepatic density
- CT scan in patients with cirrhosis may be used to detect:
- Hepatic nodularity
- Atrophy of the right lobe
- Hypertrophy of the caudate or left lobes
- Ascites
- Varices
- Liver size
- Blocked bile ducts
- Blood flow through the liver
- Tumors
- Side effects of CT scans:
- Exposure to contrast and radiation
CT Images
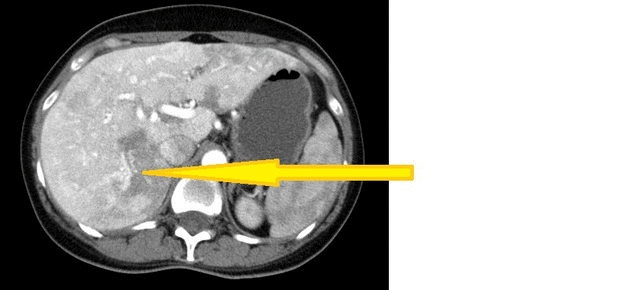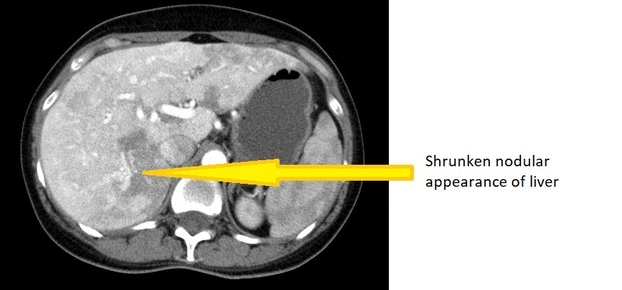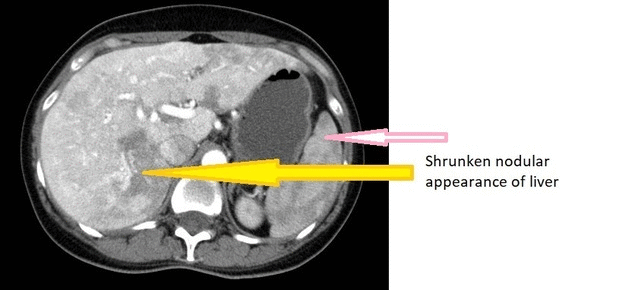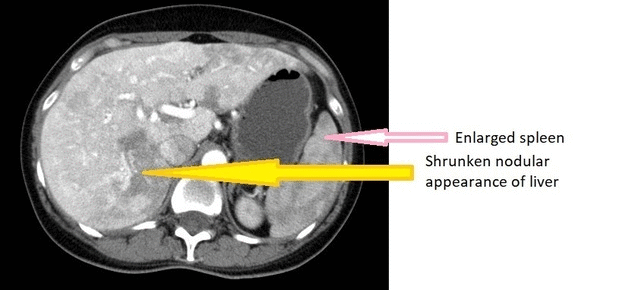
Source: Wikimedia commons [2]
- Abdominal CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of portal hypertension. Findings on CT scan suggestive of portal hypertension include:[3][4][5][6]
- Cirrhotic liver, as shrinkage and atrophy in liver
- Re-canalized umbilical vein--pathognomonic
- Dilated portal vein and/or splanchnic veins
- Esophageal varices
- Collaterals in any abdominal organ
- Splenomegaly
- Ascites
Portal hypertension
 |
 |
 |
 |
Recanalized Umbilical Vein
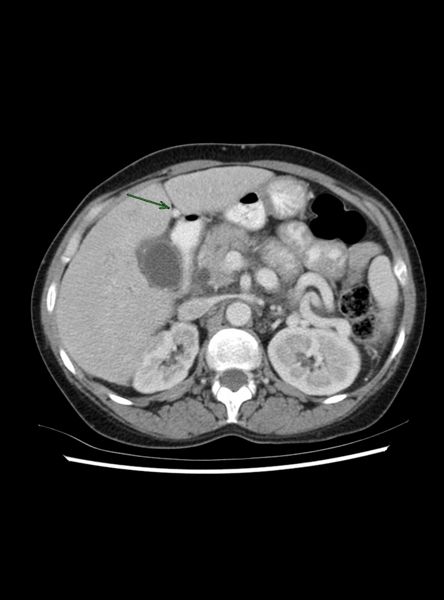 |
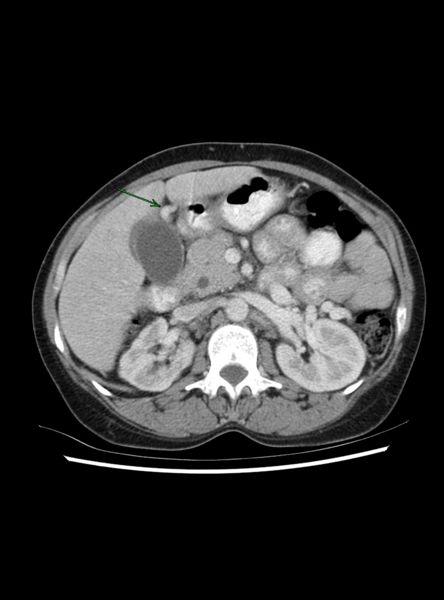 |
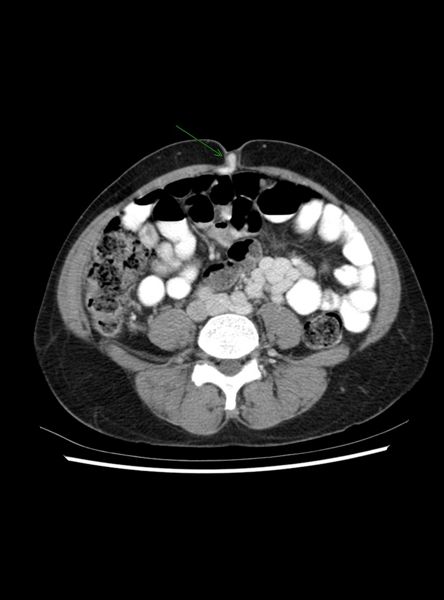 |
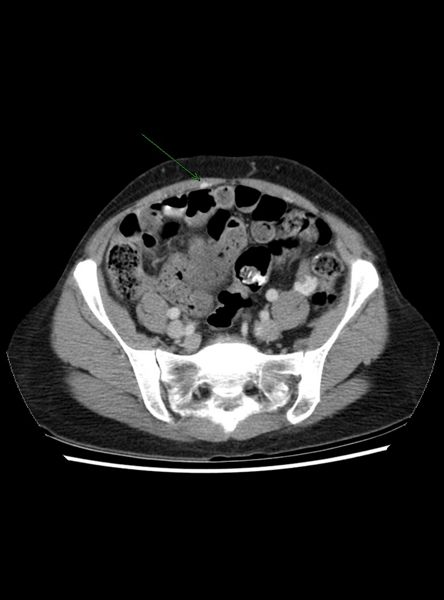 |
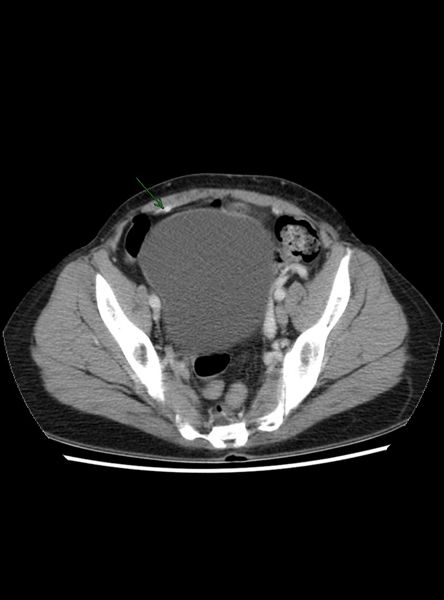 |
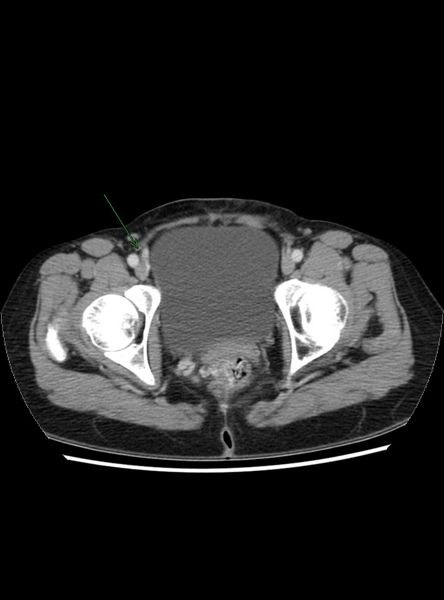 |
References
- ↑ "Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Failure: Part I. Diagnosis and Evaluation - September 1, 2006 - American Family Physician". Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "File:Morbus-Osler-CT-Leber-ax-012.jpg - Wikimedia Commons". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Procopet, Bogdan; Berzigotti, Annalisa (2017). "Diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension: imaging, non-invasive markers of fibrosis and liver biopsy". Gastroenterology Report. 5 (2): 79–89. doi:10.1093/gastro/gox012. ISSN 2052-0034.
- ↑ Aagaard, J; Jensen, LI; Sorensen, TI; Christensen, U; Burcharth, F (1982). "Recanalized umbilical vein in portal hypertension". American Journal of Roentgenology. 139 (6): 1107–1110. doi:10.2214/ajr.139.6.1107. ISSN 0361-803X.
- ↑ Cho, K C; Patel, Y D; Wachsberg, R H; Seeff, J (1995). "Varices in portal hypertension: evaluation with CT". RadioGraphics. 15 (3): 609–622. doi:10.1148/radiographics.15.3.7624566. ISSN 0271-5333.
- ↑ Bandali, Murad Feroz; Mirakhur, Anirudh; Lee, Edward Wolfgang; Ferris, Mollie Clarke; Sadler, David James; Gray, Robin Ritchie; Wong, Jason Kam (2017). "Portal hypertension: Imaging of portosystemic collateral pathways and associated image-guided therapy". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 23 (10): 1735. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735. ISSN 1007-9327.
- ↑ From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/23057">rID: 23057
- ↑ From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/23057">rID: 23057
- ↑ From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/5379">rID: 5379
- ↑ From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/15852">rID: 15852
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11810">rID: 11810