|
|
| (396 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| In patients with pancreatic cancer, surgery is the primary modality of treatment.
| | ==Physical examination== |
| Extrapancreatic disease requires palliative therapy and curative resection is not performed in such patients.Patients with unresectable disease are treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy as a part of adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy.
| | ==References== |
| Curative resection is not contraindicated in all patients with vascular invasion.<ref name="pmid17632763">{{cite journal |vauthors=Al-Haddad M, Martin JK, Nguyen J, Pungpapong S, Raimondo M, Woodward T, Kim G, Noh K, Wallace MB |title=Vascular resection and reconstruction for pancreatic malignancy: a single center survival study |journal=J. Gastrointest. Surg. |volume=11 |issue=9 |pages=1168–74 |year=2007 |pmid=17632763 |doi=10.1007/s11605-007-0216-x |url=}}</ref>
| | {{reflist|2}} |
| Involvement of the portal or superior mesenteric vein can be resected and reconstructed with the help of splenic, saphenous or internal jugular veins. However, the involvement of arteries such as the hepatic, celiac or superior mesenteric are contraindications to resection.
| |
| Various methods of surgical resection may be employed and each of these has its own sets of risks and perioperative complications. The facts are discussed by the patient and surgical team before arriving at a well-informed decision.
| |
| The method of surgical resection depends on the following features:
| |
| *Locally invasive characteristics of the neoplasm
| |
| *Size
| |
| *Location
| |
| Methods of curative resection options include:
| |
| **Distal Pancreatectomy
| |
| *Total pancreatectomy
| |
| *Pancreaticoduodenectomy, where pylorus may or may not be spared on an individual basis
| |
|
| |
|
| The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has recommended certain guidelines on resectability of pancreatic neoplasms:<ref name="pmid28948329">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fonseca AL, Fleming JB |title=Surgery for pancreatic cancer: critical radiologic findings for clinical decision making |journal=Abdom Radiol (NY) |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2017 |pmid=28948329 |doi=10.1007/s00261-017-1332-z |url=}}</ref>
| | {{WH}} |
| *Patient selection is based on:
| | {{WS}} |
| **Resection margins
| |
| **High probability of cure
| |
| **Patient's age
| |
| **Comorbidities
| |
|
| |
| European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) has certain guidelines on the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer:<ref name="pmid26314780">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ducreux M, Cuhna AS, Caramella C, Hollebecque A, Burtin P, Goéré D, Seufferlein T, Haustermans K, Van Laethem JL, Conroy T, Arnold D |title=Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up |journal=Ann. Oncol. |volume=26 Suppl 5 |issue= |pages=v56–68 |year=2015 |pmid=26314780 |doi=10.1093/annonc/mdv295 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *Chemotherapy not preferred
| |
| *Gemcitabine is preferred over 5 FU
| |
| *Treatment is symptomatic with bypass surgery or stent placement for gastric outlet obstruction or obstructive jaundice
| |
|
| |
| In case of locally advanced disease which is unresectable, the following methods of treatment are preferred:<ref name="pmid25524417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rombouts SJ, Vogel JA, van Santvoort HC, van Lienden KP, van Hillegersberg R, Busch OR, Besselink MG, Molenaar IQ |title=Systematic review of innovative ablative therapies for the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer |journal=Br J Surg |volume=102 |issue=3 |pages=182–93 |year=2015 |pmid=25524417 |doi=10.1002/bjs.9716 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25524417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rombouts SJ, Vogel JA, van Santvoort HC, van Lienden KP, van Hillegersberg R, Busch OR, Besselink MG, Molenaar IQ |title=Systematic review of innovative ablative therapies for the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer |journal=Br J Surg |volume=102 |issue=3 |pages=182–93 |year=2015 |pmid=25524417 |doi=10.1002/bjs.9716 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| Microwave ablation
| |
| Photodynamic therapy
| |
| Irreversible electroporation
| |
| Photodynamic therapy
| |
| High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU)
| |
| Iodine-125–cryosurgery
| |
| Iodine-125
| |
| Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)
| |
| Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
| |
|
| |
|
| CHEMOTHERAPY
| | ==References== |
| | {{Reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| Metastatic disease/ Advanced pancreatic cancer which is unresectable:<ref name="pmid28222309">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irigoyen A, Gallego J, Guillén Ponce C, Vera R, Iranzo V, Ales I, Arévalo S, Pisa A, Martín M, Salud A, Falcó E, Sáenz A, Manzano Mozo JL, Pulido G, Martínez Galán J, Pazo-Cid R, Rivera F, García García T, Serra O, Fernández Parra EM, Hurtado A, Gómez Reina MJ, López Gomez LJ, Martínez Ortega E, Benavides M, Aranda E |title=Gemcitabine-erlotinib versus gemcitabine-erlotinib-capecitabine in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: Efficacy and safety results of a phase IIb randomised study from the Spanish TTD Collaborative Group |journal=Eur. J. Cancer |volume=75 |issue= |pages=73–82 |year=2017 |pmid=28222309 |doi=10.1016/j.ejca.2016.12.032 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid28259610">{{cite journal |vauthors=Middleton G, Palmer DH, Greenhalf W, Ghaneh P, Jackson R, Cox T, Evans A, Shaw VE, Wadsley J, Valle JW, Propper D, Wasan H, Falk S, Cunningham D, Coxon F, Ross P, Madhusudan S, Wadd N, Corrie P, Hickish T, Costello E, Campbell F, Rawcliffe C, Neoptolemos JP |title=Vandetanib plus gemcitabine versus placebo plus gemcitabine in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic carcinoma (ViP): a prospective, randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase 2 trial |journal=Lancet Oncol. |volume=18 |issue=4 |pages=486–499 |year=2017 |pmid=28259610 |doi=10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30084-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid28105634">{{cite journal |vauthors=Xia BT, Fu B, Wang J, Kim Y, Ahmad SA, Dhar VK, Levinsky NC, Hanseman DJ, Habib DA, Wilson GC, Smith M, Olowokure OO, Kharofa J, Al Humaidi AH, Choe KA, Abbott DE, Ahmad SA |title=Does radiologic response correlate to pathologic response in patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy for borderline resectable pancreatic malignancy? |journal=J Surg Oncol |volume=115 |issue=4 |pages=376–383 |year=2017 |pmid=28105634 |doi=10.1002/jso.24538 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27484349">{{cite journal |vauthors=Choi SJ, Kim HJ, Kim JS, Bak YT, Kim JS |title=Radiation recall gastritis secondary to combination of gemcitabine and erlotinib in pancreatic cancer and response to PPI - a case report |journal=BMC Cancer |volume=16 |issue= |pages=588 |year=2016 |pmid=27484349 |pmc=4971692 |doi=10.1186/s12885-016-2616-3 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27358556">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wang Y, Hu GF, Zhang QQ, Tang N, Guo J, Liu LY, Han X, Wang X, Wang ZH |title=Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus erlotinib for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis |journal=Drug Des Devel Ther |volume=10 |issue= |pages=1961–72 |year=2016 |pmid=27358556 |pmc=4912328 |doi=10.2147/DDDT.S105442 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27139057">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hammel P, Huguet F, van Laethem JL, Goldstein D, Glimelius B, Artru P, Borbath I, Bouché O, Shannon J, André T, Mineur L, Chibaudel B, Bonnetain F, Louvet C |title=Effect of Chemoradiotherapy vs Chemotherapy on Survival in Patients With Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Controlled After 4 Months of Gemcitabine With or Without Erlotinib: The LAP07 Randomized Clinical Trial |journal=JAMA |volume=315 |issue=17 |pages=1844–53 |year=2016 |pmid=27139057 |doi=10.1001/jama.2016.4324 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26929778">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chen J, Kaley K, Garcon MC, Rodriguez T, Saif MW |title=A novel schedule of erlotinib/capecitabine (7/7) as salvage therapy in previously treated advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a case series |journal=Therap Adv Gastroenterol |volume=9 |issue=2 |pages=162–8 |year=2016 |pmid=26929778 |pmc=4749861 |doi=10.1177/1756283X15622779 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has recommended guidelines for treatment in patients based on their performance status.
| |
| In order to predict survival of patients in various stages of pancreatic cancer, the performance status of a patient is a major prognostic factor. Patients with poor prognostic factors have poor performance status. This includes-<ref name="pmid22996141">{{cite journal |vauthors=Tas F, Sen F, Odabas H, Kılıc L, Keskın S, Yıldız I |title=Performance status of patients is the major prognostic factor at all stages of pancreatic cancer |journal=Int. J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=18 |issue=5 |pages=839–46 |year=2013 |pmid=22996141 |doi=10.1007/s10147-012-0474-9 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| Metastatic disease
| |
| Large tumor
| |
| Severe weight loss
| |
| In patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic disease with good performance status
| |
| Preferred treatment: FOLFIRINOX<ref name="pmid21561347">{{cite journal |vauthors=Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Péré-Vergé D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M |title=FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=364 |issue=19 |pages=1817–25 |year=2011 |pmid=21561347 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1011923 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| In patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic disease with good performance status with intolerance to FOLFIRINOX
| |
| Preferred treatment:Paclitaxel protein bound+ Gemcitabine
| |
| In patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic disease with poor performance status
| |
| Preferred treatment: Gemcitabine monotherapy
| |
| In patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic disease with poor performance status refractory to Gemcitabine:
| |
| Preferred treatment: Capecitabine or capecitabine+erlotinib<ref name="pmid17947726">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kulke MH, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Meyerhardt JA, Zhu AX, Enzinger PC, Kwak EL, Muzikansky A, Lawrence C, Fuchs CS |title=Capecitabine plus erlotinib in gemcitabine-refractory advanced pancreatic cancer |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=25 |issue=30 |pages=4787–92 |year=2007 |pmid=17947726 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2007.11.8521 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| One year survival of FOLFIRINOX (leucovorin+5-lfuorouracil [LV5-FU]+oxaliplatin+irinotecan)>Gemcitabine
| |
| One year survival of Gemcitabine+ Erlotinib> Gemcitabine<ref name="pmid28541474">{{cite journal |vauthors=Furuse J, Gemma A, Ichikawa W, Okusaka T, Seki A, Ishii T |title=Postmarketing surveillance study of erlotinib plus gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer in Japan: POLARIS final analysis |journal=Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=47 |issue=9 |pages=832–839 |year=2017 |pmid=28541474 |doi=10.1093/jjco/hyx075 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid28702772">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fountzilas C, Chhatrala R, Khushalani N, Tan W, LeVea C, Hutson A, Tucker C, Ma WW, Warren G, Boland P, Iyer R |title=A phase II trial of erlotinib monotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer as a first- or second-line agent |journal=Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2017 |pmid=28702772 |doi=10.1007/s00280-017-3375-9 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| One year survival of Gemcitabine+ Capecitabine≥Gemcitabine <ref name="pmid18669454">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bernhard J, Dietrich D, Scheithauer W, Gerber D, Bodoky G, Ruhstaller T, Glimelius B, Bajetta E, Schüller J, Saletti P, Bauer J, Figer A, Pestalozzi BC, Köhne CH, Mingrone W, Stemmer SM, Tàmas K, Kornek GV, Koeberle D, Herrmann R |title=Clinical benefit and quality of life in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine plus capecitabine versus gemcitabine alone: a randomized multicenter phase III clinical trial--SAKK 44/00-CECOG/PAN.1.3.001 |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=26 |issue=22 |pages=3695–701 |year=2008 |pmid=18669454 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2007.15.6240 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19858379">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cunningham D, Chau I, Stocken DD, Valle JW, Smith D, Steward W, Harper PG, Dunn J, Tudur-Smith C, West J, Falk S, Crellin A, Adab F, Thompson J, Leonard P, Ostrowski J, Eatock M, Scheithauer W, Herrmann R, Neoptolemos JP |title=Phase III randomized comparison of gemcitabine versus gemcitabine plus capecitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=27 |issue=33 |pages=5513–8 |year=2009 |pmid=19858379 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2009.24.2446 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| One year survival of Gemcitabine+ nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel> Gemcitabine<ref name="pmid28820270">{{cite journal |vauthors=Passero FC, Saif MW |title=Second line treatment options for pancreatic cancer |journal=Expert Opin Pharmacother |volume=18 |issue=15 |pages=1607–1617 |year=2017 |pmid=28820270 |doi=10.1080/14656566.2017.1369955 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24939470">{{cite journal |vauthors=Saif MW |title=Advanced stage pancreatic cancer: novel therapeutic options |journal=Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol |volume=7 |issue=4 |pages=487–98 |year=2014 |pmid=24939470 |doi=10.1586/17512433.2014.910451 |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| | |- |
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| NEW TREATMENTS
| |
| Irinotecan in an encapsulated form inside a nanoliposome is being used in advanced pancreatic cancer patients who have been earlier been treated using gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. <ref name="pmid27140876">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chiang NJ, Chang JY, Shan YS, Chen LT |title=Development of nanoliposomal irinotecan (nal-IRI, MM-398, PEP02) in the management of metastatic pancreatic cancer |journal=Expert Opin Pharmacother |volume=17 |issue=10 |pages=1413–20 |year=2016 |pmid=27140876 |doi=10.1080/14656566.2016.1183646 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| Liposomal Irinotecan is used along with leucovorin and fluorouracil.<ref name="pmid26615328">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wang-Gillam A, Li CP, Bodoky G, Dean A, Shan YS, Jameson G, Macarulla T, Lee KH, Cunningham D, Blanc JF, Hubner RA, Chiu CF, Schwartsmann G, Siveke JT, Braiteh F, Moyo V, Belanger B, Dhindsa N, Bayever E, Von Hoff DD, Chen LT |title=Nanoliposomal irinotecan with fluorouracil and folinic acid in metastatic pancreatic cancer after previous gemcitabine-based therapy (NAPOLI-1): a global, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial |journal=Lancet |volume=387 |issue=10018 |pages=545–57 |year=2016 |pmid=26615328 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00986-1 |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| | |- |
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| ADJUVANT THERAPY
| | == History and Symptoms == |
| The use of gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy is considered a standard form of therapy following surgical resection in pancreatic cancer patients.<ref name="pmid4015380">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kalser MH, Ellenberg SS |title=Pancreatic cancer. Adjuvant combined radiation and chemotherapy following curative resection |journal=Arch Surg |volume=120 |issue=8 |pages=899–903 |year=1985 |pmid=4015380 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15028824">{{cite journal |vauthors=Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Friess H, Bassi C, Dunn JA, Hickey H, Beger H, Fernandez-Cruz L, Dervenis C, Lacaine F, Falconi M, Pederzoli P, Pap A, Spooner D, Kerr DJ, Büchler MW |title=A randomized trial of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy after resection of pancreatic cancer |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=350 |issue=12 |pages=1200–10 |year=2004 |pmid=15028824 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa032295 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20083754">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yang R, Cheung MC, Byrne MM, Jin X, Montero AJ, Jones C, Koniaris LG |title=Survival effects of adjuvant chemoradiotherapy after resection for pancreatic carcinoma |journal=Arch Surg |volume=145 |issue=1 |pages=49–56 |year=2010 |pmid=20083754 |doi=10.1001/archsurg.2009.244 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17227978">{{cite journal |vauthors=Oettle H, Post S, Neuhaus P, Gellert K, Langrehr J, Ridwelski K, Schramm H, Fahlke J, Zuelke C, Burkart C, Gutberlet K, Kettner E, Schmalenberg H, Weigang-Koehler K, Bechstein WO, Niedergethmann M, Schmidt-Wolf I, Roll L, Doerken B, Riess H |title=Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine vs observation in patients undergoing curative-intent resection of pancreatic cancer: a randomized controlled trial |journal=JAMA |volume=297 |issue=3 |pages=267–77 |year=2007 |pmid=17227978 |doi=10.1001/jama.297.3.267 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| NEOADJUVANT THERAPY
| |
| Neoadjuvant therapy may be used as a form of therapy due to the following reasons:<ref name="pmid9850029">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pisters PW, Abbruzzese JL, Janjan NA, Cleary KR, Charnsangavej C, Goswitz MS, Rich TA, Raijman I, Wolff RA, Lenzi R, Lee JE, Evans DB |title=Rapid-fractionation preoperative chemoradiation, pancreaticoduodenectomy, and intraoperative radiation therapy for resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=16 |issue=12 |pages=3843–50 |year=1998 |pmid=9850029 |doi=10.1200/JCO.1998.16.12.3843 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid12011133">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pisters PW, Wolff RA, Janjan NA, Cleary KR, Charnsangavej C, Crane CN, Lenzi R, Vauthey JN, Lee JE, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB |title=Preoperative paclitaxel and concurrent rapid-fractionation radiation for resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: toxicities, histologic response rates, and event-free outcome |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=20 |issue=10 |pages=2537–44 |year=2002 |pmid=12011133 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2002.11.064 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24306217">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kadera BE, Sunjaya DB, Isacoff WH, Li L, Hines OJ, Tomlinson JS, Dawson DW, Rochefort MM, Donald GW, Clerkin BM, Reber HA, Donahue TR |title=Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: association between prolonged preoperative treatment and lymph-node negativity and overall survival |journal=JAMA Surg |volume=149 |issue=2 |pages=145–53 |year=2014 |pmid=24306217 |doi=10.1001/jamasurg.2013.2690 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21969502">{{cite journal |vauthors=Loehrer PJ, Feng Y, Cardenes H, Wagner L, Brell JM, Cella D, Flynn P, Ramanathan RK, Crane CH, Alberts SR, Benson AB |title=Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=29 |issue=31 |pages=4105–12 |year=2011 |pmid=21969502 |pmc=3525836 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8904 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| Toxic effects of chemotherapy can be tolerated more easily before surgery as compared to after resection
| |
| Shrinkage of tumor with neoadjuvant therapy makes resection easier and improves patient prognosis
| |
| Systemic treatment for cancer involving various systems improves prognosis
| |
| No therapy is considered as first line therapy under this category.Decisions for treatment are made on an individual basis.
| |
|
| |
|
| SURGERY
| | * History should include: |
| | ** Appearance of bowel movements |
| | ** Travel history |
| | ** Associated symptoms |
| | ** Immune status |
| | ** Woodland exposure |
| | ==References== |
| | {{reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple Procedure)<ref name="pmid26314780">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ducreux M, Cuhna AS, Caramella C, Hollebecque A, Burtin P, Goéré D, Seufferlein T, Haustermans K, Van Laethem JL, Conroy T, Arnold D |title=Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up |journal=Ann. Oncol. |volume=26 Suppl 5 |issue= |pages=v56–68 |year=2015 |pmid=26314780 |doi=10.1093/annonc/mdv295 |url=}}</ref>
| | {{WH}} |
| It is mainly performed for tumors located in:
| | {{WS}} |
| Periampullary region
| |
| Duodenum
| |
| Bile duct (Cholangiocarcinoma)
| |
| Pancreatic duct
| |
| Head of pancreas
| |
| Whipple procedure involves removal of the following components due to common blood supply:
| |
| Stomach antrum
| |
| Gallbladder
| |
| Duodenum
| |
| Head of pancreas
| |
| After removal of the above structures, the biliary and distal pancreatic ducts are anastomosed to the jejunum to facilitate surgical drainage. Biliary drainage may also be performed preoperatively.<ref name="pmid20071702">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Gaag NA, Rauws EA, van Eijck CH, Bruno MJ, van der Harst E, Kubben FJ, Gerritsen JJ, Greve JW, Gerhards MF, de Hingh IH, Klinkenbijl JH, Nio CY, de Castro SM, Busch OR, van Gulik TM, Bossuyt PM, Gouma DJ |title=Preoperative biliary drainage for cancer of the head of the pancreas |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=362 |issue=2 |pages=129–37 |year=2010 |pmid=20071702 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0903230 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20071702">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Gaag NA, Rauws EA, van Eijck CH, Bruno MJ, van der Harst E, Kubben FJ, Gerritsen JJ, Greve JW, Gerhards MF, de Hingh IH, Klinkenbijl JH, Nio CY, de Castro SM, Busch OR, van Gulik TM, Bossuyt PM, Gouma DJ |title=Preoperative biliary drainage for cancer of the head of the pancreas |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=362 |issue=2 |pages=129–37 |year=2010 |pmid=20071702 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0903230 |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| This procedure is associated with several morbidities:<ref name="pmid17667503">{{cite journal |vauthors=McPhee JT, Hill JS, Whalen GF, Zayaruzny M, Litwin DE, Sullivan ME, Anderson FA, Tseng JF |title=Perioperative mortality for pancreatectomy: a national perspective |journal=Ann. Surg. |volume=246 |issue=2 |pages=246–53 |year=2007 |pmid=17667503 |pmc=1933570 |doi=10.1097/01.sla.0000259993.17350.3a |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17462460">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pawlik TM, Gleisner AL, Cameron JL, Winter JM, Assumpcao L, Lillemoe KD, Wolfgang C, Hruban RH, Schulick RD, Yeo CJ, Choti MA |title=Prognostic relevance of lymph node ratio following pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer |journal=Surgery |volume=141 |issue=5 |pages=610–8 |year=2007 |pmid=17462460 |doi=10.1016/j.surg.2006.12.013 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17786531">{{cite journal |vauthors=House MG, Gönen M, Jarnagin WR, D'Angelica M, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Brennan MF, Allen PJ |title=Prognostic significance of pathologic nodal status in patients with resected pancreatic cancer |journal=J. Gastrointest. Surg. |volume=11 |issue=11 |pages=1549–55 |year=2007 |pmid=17786531 |doi=10.1007/s11605-007-0243-7 |url=}}</ref>
| | ==Other Imaging Findings== |
| Postoperative abcess
| | * [[Endoscopy]] |
| Wound infection<ref name="pmid17723881">{{cite journal |vauthors=Limongelli P, Pai M, Bansi D, Thiallinagram A, Tait P, Jackson J, Habib NA, Williamson RC, Jiao LR |title=Correlation between preoperative biliary drainage, bile duct contamination, and postoperative outcomes for pancreatic surgery |journal=Surgery |volume=142 |issue=3 |pages=313–8 |year=2007 |pmid=17723881 |doi=10.1016/j.surg.2007.04.022 |url=}}</ref>
| | * [[Barium enema]] |
| Anastomotic leak
| | * [[Colonoscopy]] |
| Delay in gastric emptying<ref name="pmid17981197">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wente MN, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, Izbicki JR, Neoptolemos JP, Padbury RT, Sarr MG, Traverso LW, Yeo CJ, Büchler MW |title=Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) after pancreatic surgery: a suggested definition by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) |journal=Surgery |volume=142 |issue=5 |pages=761–8 |year=2007 |pmid=17981197 |doi=10.1016/j.surg.2007.05.005 |url=}}</ref>
| | * [[Sigmoidoscopy]] |
|
| |
| Pylorus sparing Whipple procedure:
| |
| The pylorus may be spared as a modification of Whipple procedure to decrease gastric emptying due to antrectomy. This significantly reduces the incidence of nutritional deficiencies arising from this surgery.
| |
|
| |
|
| | ==Other diagnostic studies== |
| | == Other Diagnostic Studies == |
|
| |
|
| The European Society for Medical Oncology states that the only curative therapy is surgical resection.
| | * Breath hydrogen test |
| Ten percent is the five year survival of patients with pancreatic cancer.
| |
| Patients with node-positive tumors have very poor long term survival.
| |
|
| |
|
| Distal Pancreatectomy
| | * [[HIV test]]ing for those patients suspected of having HIV |
| This procedure has a limited use in curative resection of pancreatic cancer.
| |
| It is mainly performed for tumors located in:
| |
| Body of pancreas
| |
| Tail of pancreas
| |
| This form of surgery has fewer morbidities than the Whipple procedure.
| |
|
| |
|
|
| | == |
| Distal Pancreatectomy involves the following components:
| |
| Separation of the distal pancreas bearing the tumor from the normal tissue
| |
| Resection of the affected portion
| |
| Oversewing of the distal pancreatic duct
| |
|
| |
|
| This procedure is associated with several morbidities:
| | ==Overview== |
| Pancreatic endocrine insufficiency
| |
| Bleeding
| |
| Leakage of pancreatic stump
| |
|
| |
|
| Total Pancreatectomy
| | ==References== |
| | {{reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{WH}} |
| | {{WS}} |
|
| |
|
| It is the least preferred due to high mortality rate.
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| It is mainly performed for tumors located in:
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| Neck of the pancreas.
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| Due to involvement of neck, patients develop insulin dependent DM.
| | |- |
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| PALLIATIVE THERAPY
| | ==Video codes== |
|
| |
|
| Pain
| | ===Normal video=== |
| There are various techniques for pain management as palliative therapy in patients:
| | {{#ev:youtube|x6e9Pk6inYI}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|4uSSvD1BAHg}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|PQXb5D-5UZw}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|UVJYQlUm2A8}} |
|
| |
|
| Narcotic analgesics
| | ===Video in table=== |
| Narcotic analgesics+ tricyclic antidepressants/ antiemetics
| | <div style="width:350px">{{#ev:youtube|5ucSlgqGAno}}</div> |
| Endoscopic decompression with stent placement in patients with biliary or pancreatic duct obstruction
| |
| Radiation therapy
| |
| Neurolysis of the celiac ganglia by many approaches
| |
| Intraoperative
| |
| transgastric
| |
| transthoracic
| |
| transabdominal
| |
|
| |
|
| Jaundice
| | ===Floating video=== |
| Obstructive jaundice can present with features of cholangitis:
| |
| Fever and chills
| |
| Nausea, vomitting
| |
| Clay coloured stools
| |
| Dark urine
| |
| yellowish discolration of skin
| |
| pruritus
| |
| right upper quadrant pain
| |
| Anorexia
| |
| Preferred treatment in patients: Endoscopic decompression with stent placement in patients with biliary obstruction
| |
| Techniques of biliary decompression:
| |
| Cholecystojejunostomy
| |
| Choledochojejunostomy
| |
|
| |
|
| Types of stents:
| | {| class="infobox mw-collapsible" id="floatvideo" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; width:361px; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| Metal- costly, longer lifespan
| | | Title |
| Plastic- cheaper, need replacement every three months
| | |- |
|
| | |- |
| Duodenal obstruction
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ypYI_lmLD7g|350}} |
| Preferred treatment:
| | |- |
| Endoscopic stenting of duodenal obstruction
| | |} |
| Gastrojejunostomy
| | |
| | ===Redirect=== |
| | #REDIRECT[[Esophageal web]] |
| | |
| | ===synonym website=== |
| | https://mq.b2i.sg/snow-owl/#!terminology/snomed/10743008 |
| | |
| | ===Image=== |
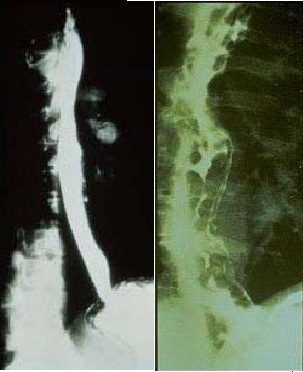
| | [[Image: Normal versus Abnormal Barium study of esophagus.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Normal versus Abnormal Barium study of esophagus with varices]] |
| | |
| | |
| | ===Image to the right=== |
| | {| style="float: right; width: 350px;" |
| | | [[Image:Coxiella burnetii.JPG|right|400px|C. burnetii, the Q fever causing agent]] |
| | |} |
| | |
| | ===Image and text to the right=== |
| | |
| | <figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline>[[File:Global distribution of leptospirosis.jpg|577x577px]]</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017. |
| | |
| | ===Gallery=== |
| | |
| | <gallery widths="250px"> |
| | |
| | Pancreatic insulinoma histology 2.JPG|Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). ''Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas''<ref name=aaa> Neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas. Libre Pathology. http://librepathology.org/wiki/index.php/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas</ref> |
| | |
| | Pancreatic insulinoma histopathology 3.JPG|Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Chromogranin A immunostain. ''Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas''<ref name=aaa> Neuroendocrine tumour of the pancreas. Libre Pathology. http://librepathology.org/wiki/index.php/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas</ref> |
| | |
| | Pancreatic insulinoma histology 4.JPG|Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Insulin immunostain. ''Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas''<ref name=aaa> Neuroendocrine tumour of the pancreas. Libre Pathology. http://librepathology.org/wiki/index.php/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas</ref> |
| | |
| | </gallery> |
| | ==References== |
| | {{Reflist|2}} |
| | {{WS}} |
| | {{WH}} |
| | |
| | |
| | REFERENCES |
| | <references /> |
| | |
| | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] |
| | [[Category:Needs overview]] |
| | [[Category:Hepatology]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |
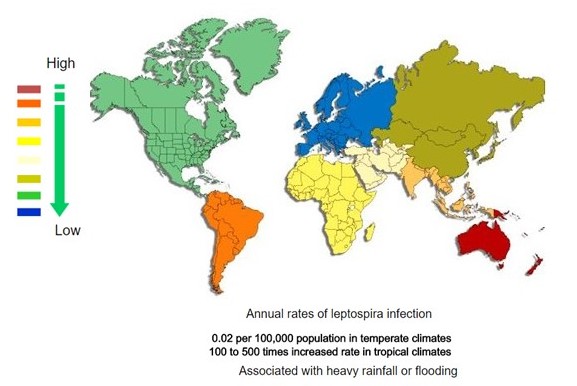 </figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/2/2f/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_2.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Chromogranin A immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/a/a3/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histopathology_3.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Insulin immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/d/d5/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_4.JPG)