Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Right ventricular myocardial infarction}} | {{Right ventricular myocardial infarction}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The diagnosis can be made using a right-sided electrocardiogram, on which ST-segment elevation in leads V3R and V4R will be seen. | A right ventricular MI is a heart attack or cessation of blood flow to the heart muscle that involves the right side of the heart. A right sided lead [[ECG]] should be ordered and clearly labeled among any patient with ST elevation in the inferior leads ([[Electrocardiogram#Limb Leads|II]], [[Electrocardiogram#Limb Leads|III]] and [[Electrocardiogram#Limb Leads|aVF]]). The diagnosis of right ventricular MI can be made using a right-sided electrocardiogram, on which [[ST-segment elevation]] in leads V3R and V4R will be seen. | ||
==Electrocardiogram== | ==Electrocardiogram== | ||
* In addition to evidence of an acute [[Acute myocardial infarction|inferior]] or [[Acute myocardial infarction|inferoposterior]] [[myocardial infarction]], the ECG may demonstrate ≥ 1 mm of doming ST elevation in the right sided precordial leads V4R to V6R. | * In addition to evidence of an acute [[Acute myocardial infarction|inferior]] or [[Acute myocardial infarction|inferoposterior]] [[myocardial infarction]], the ECG may demonstrate ≥ 1 mm of doming ST elevation in the right sided precordial leads V4R to V6R. | ||
* Right sided ST elevation, particularly in V4R, is indicative of acute right ventricular injury <ref>Isner, JM. Right ventricular myocardial infarction. JAMA 1988; 259:712. PMID 3275819</ref> <ref>Kinch, JW, Ryan, TJ. Right ventricular infarction. N Engl J Med 1994; 330:1211. PMID 8139631</ref> <ref>Zehender, M, Kasper, W, Kauder, E, et al. Right ventricular infarction as an independent predictor of prognosis after acute inferior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:981. PMID 8450875</ref> and correlates closely with [[occlusion]] of the proximal [[right coronary artery]]. | * Right sided ST elevation, particularly in V4R, is indicative of acute right ventricular injury <ref>Isner, JM. Right ventricular myocardial infarction. JAMA 1988; 259:712. PMID 3275819</ref> <ref>Kinch, JW, Ryan, TJ. Right ventricular infarction. N Engl J Med 1994; 330:1211. PMID 8139631</ref> <ref>Zehender, M, Kasper, W, Kauder, E, et al. Right ventricular infarction as an independent predictor of prognosis after acute inferior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:981. PMID 8450875</ref> and correlates closely with [[occlusion]] of the proximal [[right coronary artery]]. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
* [[Pulmonary embolism]], [[pericarditis]], and [[Acute myocardial infarction|anteroseptal myocardial infarction]] also cause elevation of the [[ST segment]] in the right-sided precordial leads. As a result, an electrocardiographic diagnosis of [[Right ventricular myocardial infarction|right ventricular infarction]] cannot be made when one of these conditions is present. <ref>Williams, JF. Right ventricular infarction. Clin Cardiol 1990; 13:309. PMID 2189611</ref> <ref>Kahn, JK, Bernstein, M, Bengston, JR. Isolated right ventricular myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118:708. PMID 8460858</ref> | * [[Pulmonary embolism]], [[pericarditis]], and [[Acute myocardial infarction|anteroseptal myocardial infarction]] also cause elevation of the [[ST segment]] in the right-sided precordial leads. As a result, an electrocardiographic diagnosis of [[Right ventricular myocardial infarction|right ventricular infarction]] cannot be made when one of these conditions is present. <ref>Williams, JF. Right ventricular infarction. Clin Cardiol 1990; 13:309. PMID 2189611</ref> <ref>Kahn, JK, Bernstein, M, Bengston, JR. Isolated right ventricular myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118:708. PMID 8460858</ref> | ||
==EKG Examples== | |||
Shown below is an EKG image featuring [[ST elevation]] at [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V4R]] depicting right ventricular myocardial infarction. | |||
[[File:Casus2_1.jpg|500px|center]] | |||
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead EKG image featuring [[ST elevation]] in [[Electrocardiogram#Limb|II]], [[Electrocardiogram#Limb|III]], [[Electrocardiogram#Augmented limb|aVF]], [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V2]], [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V3]], [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V4]] and [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V5]] depicting [[inferior myocardial infarction]] and right ventricular myocardial infarction | |||
[[File:Casus2_2.jpg|500px|center]] | |||
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is an EKG image featuring right ventricular myocardial infarction. Note the [[ST elevation]] in lead [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V1]] and high R/S ratio in V1. | |||
[[File:RightVentricularMyocardialInfarction.jpg|500px|center]] | |||
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/File:De-RV_MI.jpg | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is an EKG featuring ST elevation in lead [[Electrocardiogram#Precordial|V1]] depicting right ventricular myocardial infarction | |||
[[File:RV MI.jpg|500px|center]] | |||
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page | |||
---- | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 20:57, 12 March 2014
|
Right ventricular myocardial infarction Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Right ventricular myocardial infarction from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Pharmacological Reperfusion |
|
Mechanical Reperfusion |
|
Antithrombin Therapy |
|
Antiplatelet Agents |
|
Other Initial Therapy |
|
Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
FDA on Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram |
|
CDC on Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram |
|
Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram in the news |
|
Blogs on Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Right ventricular myocardial infarction |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Right ventricular myocardial infarction electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
A right ventricular MI is a heart attack or cessation of blood flow to the heart muscle that involves the right side of the heart. A right sided lead ECG should be ordered and clearly labeled among any patient with ST elevation in the inferior leads (II, III and aVF). The diagnosis of right ventricular MI can be made using a right-sided electrocardiogram, on which ST-segment elevation in leads V3R and V4R will be seen.
Electrocardiogram
- In addition to evidence of an acute inferior or inferoposterior myocardial infarction, the ECG may demonstrate ≥ 1 mm of doming ST elevation in the right sided precordial leads V4R to V6R.
- Right sided ST elevation, particularly in V4R, is indicative of acute right ventricular injury [1] [2] [3] and correlates closely with occlusion of the proximal right coronary artery.
- In one report of patients with acute inferior infarction, for example, ST elevation in V4R had 88 percent sensitivity and 78 percent specificity for concurrent right ventricular infarction. [4]
- Pulmonary embolism, pericarditis, and anteroseptal myocardial infarction also cause elevation of the ST segment in the right-sided precordial leads. As a result, an electrocardiographic diagnosis of right ventricular infarction cannot be made when one of these conditions is present. [5] [6]
EKG Examples
Shown below is an EKG image featuring ST elevation at V4R depicting right ventricular myocardial infarction.

Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is a 12 lead EKG image featuring ST elevation in II, III, aVF, V2, V3, V4 and V5 depicting inferior myocardial infarction and right ventricular myocardial infarction

Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is an EKG image featuring right ventricular myocardial infarction. Note the ST elevation in lead V1 and high R/S ratio in V1.
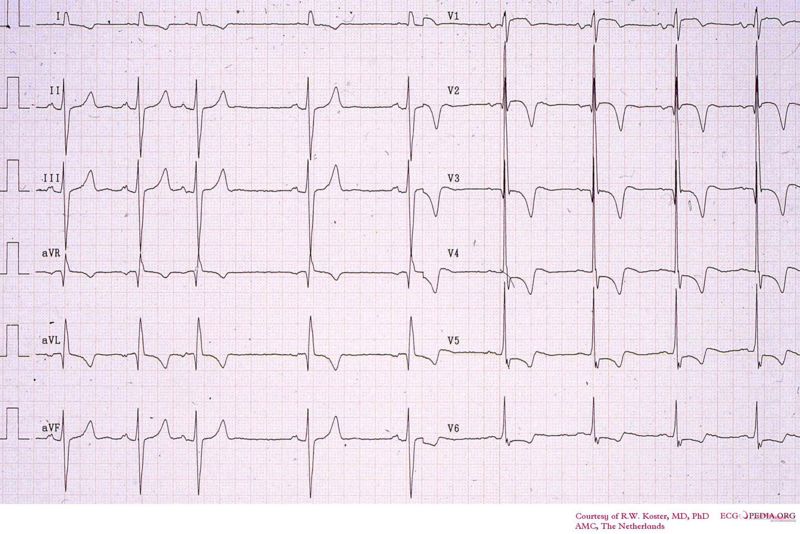
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/File:De-RV_MI.jpg
Shown below is an EKG featuring ST elevation in lead V1 depicting right ventricular myocardial infarction

Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
References
- ↑ Isner, JM. Right ventricular myocardial infarction. JAMA 1988; 259:712. PMID 3275819
- ↑ Kinch, JW, Ryan, TJ. Right ventricular infarction. N Engl J Med 1994; 330:1211. PMID 8139631
- ↑ Zehender, M, Kasper, W, Kauder, E, et al. Right ventricular infarction as an independent predictor of prognosis after acute inferior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:981. PMID 8450875
- ↑ Zehender, M, Kasper, W, Kauder, E, et al. Right ventricular infarction as an independent predictor of prognosis after acute inferior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:981. PMID 8450875.
- ↑ Williams, JF. Right ventricular infarction. Clin Cardiol 1990; 13:309. PMID 2189611
- ↑ Kahn, JK, Bernstein, M, Bengston, JR. Isolated right ventricular myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118:708. PMID 8460858