|
|
| (149 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| ===Pathophysiology=== | | ==Physical examination== |
| * The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of scar tissue that replaces normal [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of portal blood flow and disturbance of normal liver function.
| | ==References== |
| * The development of [[fibrosis]] requires several months, or even years, of ongoing injury.
| | {{reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| * The [[Ito cell|stellate cell]], a cell type that normally stores [[vitamin A]], plays a pivotal role in the development of cirrhosis.
| | {{WH}} |
| * Damage to the hepatic [[parenchyma]] leads to activation of the stellate cell, which becomes contractile (called [[myofibroblast]]) and obstructs blood flow in the circulation.
| | {{WS}} |
| * The [[stellate cell]] secretes [[TGF beta 1|TGF-β<sub>1</sub>]], which leads to a fibrotic response and proliferation of [[connective tissue]].
| |
| * Connective tissue proliferation leads to the formation of [[extracellular matrix]] around [[hepatocytes]] and is composed of [[collagen]]s (especially type I, III, IV), [[glycoprotein]] and [[proteoglycan]]s.
| |
|
| |
|
| * Sinusoidal endothelial cells are also important contributors of early fibrosis. [[Endothelial cell]]s from a normal liver produces collagen, [[laminin]] and [[fibronectin]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Maher JJ, McGuire RF |title=Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=86 |issue=5 |pages=1641–8 |year=1990 |month=November |pmid=2243137 |pmc=296914 |doi=10.1172/JCI114886 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Herbst H, Frey A, Heinrichs O, ''et al.'' |title=Heterogeneity of liver cells expressing procollagen types I and IV in vivo |journal=Histochem. Cell Biol. |volume=107 |issue=5 |pages=399–409 |year=1997 |month=May |pmid=9208331 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| | ==References== |
| | {{Reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| *The liver responds to injury with new blood vessel formation. Mediators involved in angiogenesis include:
| |
| **Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF)
| |
| **[[Vascular endothelial growth factor]] (VEGF)
| |
| **[[Nitric oxide]]
| |
| **[[Carbon monoxide]]
| |
| *[[Angiogenesis]] in cirrhosis results in the production of immature and permeable [[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]] induced neo-[[Blood vessel|vessels]] that further exacerbate [[liver]] injury. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Lee JS, Semela D, Iredale J, Shah VH |title=Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: a new function for the liver-specific pericyte? |journal=Hepatology |volume=45 |issue=3 |pages=817–25 |year=2007 |month=March |pmid=17326208 |doi=10.1002/hep.21564 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Rosmorduc O, Housset C |title=Hypoxia: a link between fibrogenesis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis in liver disease |journal=Semin. Liver Dis. |volume=30 |issue=3 |pages=258–70 |year=2010 |month=August |pmid=20665378 |doi=10.1055/s-0030-1255355 |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| * Stellate cell activation leads to disturbance of the balance between [[matrix metalloproteinase]]s and the naturally occurring inhibitors (TIMP 1 and 2). This is followed by [[matrix (biology)|matrix]] breakdown and replacement by connective tissue-secreted matrix.<ref>Iredale JP. Cirrhosis: new research provides a basis for rational and targeted treatments. [[British Medical Journal|BMJ]] 2003;327:143-7.[http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/327/7407/143 Fulltext.] PMID 12869458.</ref>
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| * [[Matrix metalloproteinase]] (MMP) are calcium dependent enzymes that specifically degrade [[collagen]] and non collagenous substrate.
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| * MMP-2 and stromyelysin-1 are produced by stellate cells.
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| * MMP-2 degrades collagen and stromelysin-1 degrades [[proteoglycan]] and [[glycoprotein]].
| | |- |
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| * These mechanisms simultaneously occurring in the liver lead to fibrous tissue band (septa) and regenerative hepatocyte nodule formation, which eventually replace the entire liver architecture, leading to decreased blood flow throughout.
| |
| * Portal hypertension may develop as a consequence of cirrhosis.
| |
| * Due to portal hypertension, the [[spleen]] becomes congested, which leads to [[hypersplenism]] and increased [[platelet]] sequestration.
| |
| * [[Portal hypertension]] is responsible for the most severe complications of cirrhosis.
| |
|
| |
|
| * Pathogenesis of cirrhosis based upon its individual cause is as follows:
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| ** '''[[Alcoholic liver disease]]''': [[Alcohol]] seems to injure the [[liver]] by blocking the normal metabolism of [[protein]], [[fat]]s, and [[carbohydrate]]s. Patients may also have concurrent [[alcoholic hepatitis]] with [[fever]], [[hepatomegaly]], [[jaundice]], and anorexia.
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| ** '''Chronic hepatitis C''': Infection with the [[hepatitis C]] virus causes inflammation of and low grade damage to the [[liver]] that over several decades can lead to cirrhosis.
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| ** '''[[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease|Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis]]''' (NASH): In NASH, fat builds up in the liver and eventually causes scar tissue. This type of hepatitis appears to be associated with [[diabetes]], [[protein malnutrition]], [[obesity]], [[coronary artery disease]], and treatment with [[corticosteroid]] medications.
| | |- |
| ** '''[[Primary sclerosing cholangitis]]:''' PSC is a progressive cholestatic disorder presenting with [[pruritus]], [[steatorrhea]], fat soluble vitamin deficiencies, and [[metabolic bone disease]]. There is a strong association with [[inflammatory bowel disease]] (IBD), especially [[ulcerative colitis]].
| | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| ** '''[[Autoimmune hepatitis]]''': This disease is caused by the immunologic damage to the liver causing [[inflammation]] and eventually scarring and cirrhosis.
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Cirrhosis=== | | == History and Symptoms == |
|
| |
|
| Pathophysiology <ref name="pmid7932316">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ, Iredale JP |title=Hepatic lipocytes, TIMP-1 and liver fibrosis |journal=J R Coll Physicians Lond |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=200–8 |year=1994 |pmid=7932316 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8502273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedman SL |title=Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=328 |issue=25 |pages=1828–35 |year=1993 |pmid=8502273 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199306243282508 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8682489">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Matrix turnover in fibrogenesis |journal=Hepatogastroenterology |volume=43 |issue=7 |pages=56–71 |year=1996 |pmid=8682489 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7959178">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gressner AM |title=Perisinusoidal lipocytes and fibrogenesis |journal=Gut |volume=35 |issue=10 |pages=1331–3 |year=1994 |pmid=7959178 |pmc=1374996 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17332881">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=117 |issue=3 |pages=539–48 |year=2007 |pmid=17332881 |pmc=1804370 |doi=10.1172/JCI30542 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| | * History should include: |
| * When an injured issue is replaced by a collagenous scar, it is termed as fibrosis.
| | ** Appearance of bowel movements |
| * When fibrosis of the liver reaches an advanced stage where distortion of the hepatic vasculature also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the liver.
| | ** Travel history |
| * The cellular mechanisms responsible for cirrhosis are similar regardless of the type of initial insult and site of injury within the liver lobule.
| | ** Associated symptoms |
| * Viral hepatitis involves the periportal region, whereas involvement in alcoholic liver disease is largely pericentral.
| | ** Immune status |
| * If the damage progresses, panlobular cirrhosis may result.
| | ** Woodland exposure |
| * Cirrhosis involves the following steps: <ref name="pmid7737629">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G |title=Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension |journal=Hepatology |volume=21 |issue=5 |pages=1238–47 |year=1995 |pmid=7737629 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | | ==References== |
| ** Inflammation | | {{reflist|2}} |
| ** Hepatic stellate cell activation
| |
| ** Angiogenesis
| |
| ** Fibrogenesis
| |
| * Kupffer cells are hepatic macrophages responsible for Hepatic Stellate cell activation during injury.
| |
| * The hepatic stellate cell (also known as the perisinusoidal cell or Ito cell) plays a key role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis.
| |
| * Hepatic stellate cells(HSC) are usually located in the subendothelial space of Disse and become activated to a myofibroblast-like phenotype in areas of liver injury. | |
| * Collagen and non collagenous matrix proteins responsible for fibrosis are produced by the activated Hepatic Stellate Cells(HSC). | |
| * Hepatocyte damage causes the release of lipid peroxidases from injured cell membranes leading to necrosis of parenchymal cells. | |
| * Activated HSC produce numerous cytokines and their receptors, such as PDGF and TGF-f31 which are responsible for fibrogenesis. | |
| * The matrix formed due to HSC activation is deposited in the space of Disse and leads to loss of fenestrations of endothelial cells, which is a process called capillarization. | |
| * Cirrhosis leads to hepatic microvascular changes characterised by <ref name="pmid19157625">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J |title=Angiogenesis in liver disease |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=50 |issue=3 |pages=604–20 |year=2009 |pmid=19157625 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.011 |url=}}</ref> | |
| ** formation of intra hepatic shunts (due to angiogenesis and loss of parenchymal cells)
| |
| ** hepatic endothelial dysfunction | |
| * The endothelial dysfunction is characterised by <ref name="pmid22504334">{{cite journal |vauthors=García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J |title=Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=458–61 |year=2012 |pmid=22504334 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| ** insufficient release of vasodilators, such as nitric oxide due to oxidative stress
| |
| ** increased production of vasoconstrictors (mainly adrenergic stimulation and activation of endothelins and RAAS)
| |
| * Fibrosis eventually leads to formation of septae that grossly distort the liver architecture which includes both the liver parenchyma and the vasculature. A cirrhotic liver compromises hepatic sinusoidal exchange by shunting arterial and portal blood directly into the central veins (hepatic outflow). Vascularized fibrous septa connect central veins with portal tracts leading to islands of hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous bands without central veins.<ref name="pmid18328931">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schuppan D, Afdhal NH |title=Liver cirrhosis |journal=Lancet |volume=371 |issue=9615 |pages=838–51 |year=2008 |pmid=18328931 |pmc=2271178 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15094237">{{cite journal |vauthors=Desmet VJ, Roskams T |title=Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=40 |issue=5 |pages=860–7 |year=2004 |pmid=15094237 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2004.03.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11079009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M |title=Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=124 |issue=11 |pages=1599–607 |year=2000 |pmid=11079009 |doi=10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<1599:ROHC>2.0.CO;2 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * The formation of fibrotic bands is accompanied by regenerative nodule formation in the hepatic parenchyma.
| |
| * Advancement of cirrhosis may lead to parenchymal dysfunction and development of portal hypertension.
| |
| * Portal HTN results from the combination of the following:
| |
| ** Structural disturbances associated with advanced liver disease account for 70% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
| |
| ** Functional abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction and increased hepatic vascular tone account for 30% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
| |
|
| |
|
| Pathogenesis of Cirrhosis due to Alcohol:
| | {{WH}} |
| * More than 66 percent of all American adults consume alcohol.
| | {{WS}} |
| * Cirrhosis due to alcohol accounts for approximately forty percent of mortality rates due to cirrhosis.
| |
| * Mechanisms of alcohol-induced damage include:
| |
| ** Impaired protein synthesis, secretion, glycosylation
| |
| * Ethanol intake leads to elevated accumulation of intracellular triglycerides by:
| |
| ** Lipoprotein secretion
| |
| ** Decreased fatty acid oxidation
| |
| ** Increased fatty acid uptake
| |
| * Alcohol is converted by Alcohol dehydrogenase to acetaldehyde.
| |
| * Due to the high reactivity of acetaldehyde, it forms acetaldehyde-protein adducts which cause damage to cells by:
| |
| ** Trafficking of hepatic proteins
| |
| ** Interrupting microtubule formation
| |
| ** Interfering with enzyme activities
| |
| * Damage of hepatocytes leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species that activate Kupffer cells.<ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *Kupffer cell activation leads to the production of profibrogenic cytokines that stimulates stellate cells.
| |
| *Stellate cell activation leads to the production of extracellular matrix and collagen.
| |
| * Portal triads develop connections with central veins due to connective tissue formation in pericentral and periportal zones, leading to the formation of regenerative nodules.
| |
| * Shrinkage of the liver occurs over years due to repeated insults that lead to:
| |
| ** Loss of hepatocytes
| |
| ** Increased production and deposition of collagen
| |
|
| |
|
| | ==Other Imaging Findings== |
| | * [[Endoscopy]] |
| | * [[Barium enema]] |
| | * [[Colonoscopy]] |
| | * [[Sigmoidoscopy]] |
|
| |
|
| Pathology
| | ==Other diagnostic studies== |
| * There are four stages of Cirrhosis as it progresses:
| | == Other Diagnostic Studies == |
| ** Chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis - inflammation and necrosis of portal tracts with lymphocyte infiltration leading to the destruction of the bile ducts.
| |
| ** Development of biliary stasis and fibrosis
| |
| *Periportal fibrosis progresses to bridging fibrosis
| |
| *Increased proliferation of smaller bile ductules leading to regenerative nodule formation.
| |
|
| |
|
| | * Breath hydrogen test |
|
| |
|
| | * [[HIV test]]ing for those patients suspected of having HIV |
|
| |
|
| ===Causes===
| | == |
| {| class="wikitable"
| | |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Drugs and Toxins
| | ==Overview== |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Infections
| | |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Autoimmune
| | ==References== |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Metabolic
| | {{reflist|2}} |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Biliary obstruction(Secondary bilary cirrhosis)
| | |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Vascular
| | {{WH}} |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Miscellaneous
| | {{WS}} |
| |-
| |
| |Alcohol
| |
| |Hepatitis B
| |
| |Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
| |
| |Wilson's disease
| |
| |Cystic fibrosis
| |
| |Chronic RHF
| |
| |Sarcoidosis
| |
| |-
| |
| |Methotrexate
| |
| |Hepatitis C
| |
| |Autoimmune hepatitis
| |
| |Hemochromatosis
| |
| |Biliary atresia
| |
| |Budd-Chiari syndrome
| |
| |Intestinal
| |
|
| |
|
| bypass operations for obesity
| | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| | {| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" |
| |- | | |- |
| |Isoniazid | | | {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4|350}} |
| |Schistosoma japonicum | |
| |Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
| |
| |Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
| |
| |Bile duct strictures
| |
| |Veno-occlusive disease
| |
| |Cryptogenic: unknown | |
| |- | | |- |
| |Methyldopa
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |Porphyria
| |
| |Gallstones
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |Glycogen storage diseases (such as Galactosaemia, Abetalipoproteinaemia)
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |} | | |} |
| | | __NOTOC__ |
| ===Cirrhosis===
| | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| | | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
| Pathophysiology <ref name="pmid7932316">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ, Iredale JP |title=Hepatic lipocytes, TIMP-1 and liver fibrosis |journal=J R Coll Physicians Lond |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=200–8 |year=1994 |pmid=7932316 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8502273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedman SL |title=Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=328 |issue=25 |pages=1828–35 |year=1993 |pmid=8502273 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199306243282508 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8682489">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Matrix turnover in fibrogenesis |journal=Hepatogastroenterology |volume=43 |issue=7 |pages=56–71 |year=1996 |pmid=8682489 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7959178">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gressner AM |title=Perisinusoidal lipocytes and fibrogenesis |journal=Gut |volume=35 |issue=10 |pages=1331–3 |year=1994 |pmid=7959178 |pmc=1374996 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17332881">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=117 |issue=3 |pages=539–48 |year=2007 |pmid=17332881 |pmc=1804370 |doi=10.1172/JCI30542 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * When an injured issue is replaced by a collagenous scar, it is termed as fibrosis.
| |
| * When fibrosis of the liver reaches an advanced stage where distortion of the hepatic vasculature also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the liver.
| |
| * The cellular mechanisms responsible for cirrhosis are similar regardless of the type of initial insult and site of injury within the liver lobule.
| |
| * Viral hepatitis involves the periportal region, whereas involvement in alcoholic liver disease is largely pericentral.
| |
| * If the damage progresses, panlobular cirrhosis may result.
| |
| * Cirrhosis involves the following steps: <ref name="pmid7737629">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G |title=Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension |journal=Hepatology |volume=21 |issue=5 |pages=1238–47 |year=1995 |pmid=7737629 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| ** Inflammation
| |
| ** Hepatic stellate cell activation
| |
| ** Angiogenesis
| |
| ** Fibrogenesis
| |
| * Kupffer cells are hepatic macrophages responsible for Hepatic Stellate cell activation during injury.
| |
| * The hepatic stellate cell (also known as the perisinusoidal cell or Ito cell) plays a key role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis.
| |
| * Hepatic stellate cells(HSC) are usually located in the subendothelial space of Disse and become activated to a myofibroblast-like phenotype in areas of liver injury.
| |
| * Collagen and non collagenous matrix proteins responsible for fibrosis are produced by the activated Hepatic Stellate Cells(HSC).
| |
| * Hepatocyte damage causes the release of lipid peroxidases from injured cell membranes leading to necrosis of parenchymal cells.
| |
| * Activated HSC produce numerous cytokines and their receptors, such as PDGF and TGF-f31 which are responsible for fibrogenesis.
| |
| * The matrix formed due to HSC activation is deposited in the space of Disse and leads to loss of fenestrations of endothelial cells, which is a process called capillarization.
| |
| * Cirrhosis leads to hepatic microvascular changes characterised by <ref name="pmid19157625">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J |title=Angiogenesis in liver disease |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=50 |issue=3 |pages=604–20 |year=2009 |pmid=19157625 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.011 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| ** formation of intra hepatic shunts (due to angiogenesis and loss of parenchymal cells)
| |
| ** hepatic endothelial dysfunction
| |
| * The endothelial dysfunction is characterised by <ref name="pmid22504334">{{cite journal |vauthors=García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J |title=Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=458–61 |year=2012 |pmid=22504334 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| ** insufficient release of vasodilators, such as nitric oxide due to oxidative stress
| |
| ** increased production of vasoconstrictors (mainly adrenergic stimulation and activation of endothelins and RAAS)
| |
| * Fibrosis eventually leads to formation of septae that grossly distort the liver architecture which includes both the liver parenchyma and the vasculature. A cirrhotic liver compromises hepatic sinusoidal exchange by shunting arterial and portal blood directly into the central veins (hepatic outflow). Vascularized fibrous septa connect central veins with portal tracts leading to islands of hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous bands without central veins.<ref name="pmid18328931">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schuppan D, Afdhal NH |title=Liver cirrhosis |journal=Lancet |volume=371 |issue=9615 |pages=838–51 |year=2008 |pmid=18328931 |pmc=2271178 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15094237">{{cite journal |vauthors=Desmet VJ, Roskams T |title=Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=40 |issue=5 |pages=860–7 |year=2004 |pmid=15094237 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2004.03.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11079009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M |title=Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=124 |issue=11 |pages=1599–607 |year=2000 |pmid=11079009 |doi=10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<1599:ROHC>2.0.CO;2 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * The formation of fibrotic bands is accompanied by regenerative nodule formation in the hepatic parenchyma.
| |
| * Advancement of cirrhosis may lead to parenchymal dysfunction and development of portal hypertension.
| |
| * Portal HTN results from the combination of the following:
| |
| ** Structural disturbances associated with advanced liver disease account for 70% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
| |
| ** Functional abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction and increased hepatic vascular tone account for 30% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
| |
| | |
| Pathogenesis of Cirrhosis due to Alcohol:
| |
| * More than 66 percent of all American adults consume alcohol.
| |
| * Cirrhosis due to alcohol accounts for approximately forty percent of mortality rates due to cirrhosis.
| |
| * Mechanisms of alcohol-induced damage include:
| |
| ** Impaired protein synthesis, secretion, glycosylation
| |
| * Ethanol intake leads to elevated accumulation of intracellular triglycerides by:
| |
| ** Lipoprotein secretion
| |
| ** Decreased fatty acid oxidation
| |
| ** Increased fatty acid uptake
| |
| * Alcohol is converted by Alcohol dehydrogenase to acetaldehyde.
| |
| * Due to the high reactivity of acetaldehyde, it forms acetaldehyde-protein adducts which cause damage to cells by:
| |
| ** Trafficking of hepatic proteins
| |
| ** Interrupting microtubule formation
| |
| ** Interfering with enzyme activities
| |
| * Damage of hepatocytes leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species that activate Kupffer cells.<ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *Kupffer cell activation leads to the production of profibrogenic cytokines that stimulates stellate cells.
| |
| *Stellate cell activation leads to the production of extracellular matrix and collagen.
| |
| * Portal triads develop connections with central veins due to connective tissue formation in pericentral and periportal zones, leading to the formation of regenerative nodules.
| |
| * Shrinkage of the liver occurs over years due to repeated insults that lead to:
| |
| ** Loss of hepatocytes
| |
| ** Increased production and deposition of collagen
| |
| | |
| | |
| Pathology
| |
| * There are four stages of Cirrhosis as it progresses:
| |
| ** Chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis - inflammation and necrosis of portal tracts with lymphocyte infiltration leading to the destruction of the bile ducts.
| |
| ** Development of biliary stasis and fibrosis
| |
| *Periportal fibrosis progresses to bridging fibrosis
| |
| *Increased proliferation of smaller bile ductules leading to regenerative nodule formation. __NOTOC__
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Video codes== | | ==Video codes== |
| Line 219: |
Line 85: |
| ===Normal video=== | | ===Normal video=== |
| {{#ev:youtube|x6e9Pk6inYI}} | | {{#ev:youtube|x6e9Pk6inYI}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|4uSSvD1BAHg}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|PQXb5D-5UZw}} |
| | {{#ev:youtube|UVJYQlUm2A8}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Video in table=== | | ===Video in table=== |
| Line 250: |
Line 119: |
| ===Image and text to the right=== | | ===Image and text to the right=== |
|
| |
|
| <figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline>[[File:Global distribution of leptospirosis.jpg|577x577px]]</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017. | | <figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline>[[File:Global distribution of leptospirosis.jpg|577x577px]]</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017. |
|
| |
|
| ===Gallery=== | | ===Gallery=== |
| Line 265: |
Line 134: |
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |
|
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
| [[Category:Hepatology]]
| |
| [[Category:Disease]]
| |
|
| |
| {{WS}} | | {{WS}} |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| Line 276: |
Line 140: |
| REFERENCES | | REFERENCES |
| <references /> | | <references /> |
| | |
| | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] |
| | [[Category:Needs overview]] |
| | [[Category:Hepatology]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |
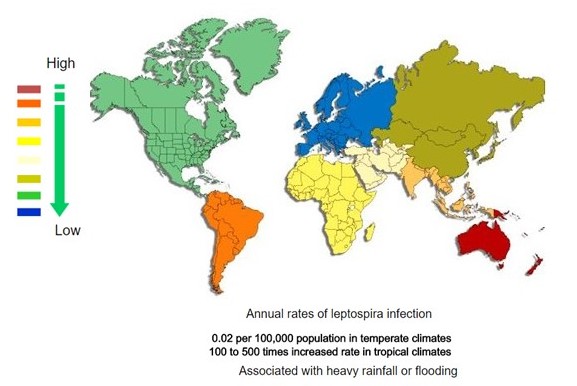 </figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/2/2f/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_2.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Chromogranin A immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/a/a3/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histopathology_3.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Insulin immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/d/d5/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_4.JPG)