Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi- (talk | contribs) |
m Bot: Removing from Primary care |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{gonorrhea}} | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
| color = lightgrey | | color = lightgrey | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
}} | }} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{ | {{About0|gonorrhea}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''''', also known as '''''gonococci''''' (plural), or '''''gonococcus''''' (singular), is a species of [[Gram-negative]] coffee bean-shaped [[diplococci]] [[bacteria]] responsible for the [[sexually transmitted infection]] [[gonorrhea]].<ref name=Sherris>{{cite book |editor1-last=Ryan |editor1-first=KJ |editor2-last=Ray |editor2-first=CG |title=Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | isbn = 0-8385-8529-9 }}</ref> | |||
''N. gonorrhoeae'' was first described by [[Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser|Albert Neisser]] in 1879. | |||
'' | == Microbiology == | ||
''[[Neisseria]]'' are fastidious Gram-negative cocci that require nutrient supplementation to grow in laboratory cultures. To be specific, they grow on [[chocolate agar]] with [[carbon dioxide]]. These cocci are facultatively intracellular and typically appear in pairs (diplococci), in the shape of coffee beans. Of the eleven species of ''Neisseria'' that colonize humans, only two are pathogens. ''N. gonorrhoeae'' is the causative agent of [[gonorrhea]] (also called "The Clap") and is transmitted via sexual contact.<ref name= GencoWetzler>{{cite book |editor1-last=Genco |editor1-first=C |editor2-last=Wetzler |editor2-first=L |year=2010 |title=Neisseria: Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis |publisher=Caister Academic Press |isbn=978-1-904455-51-6}}</ref> | |||
''Neisseria'' is usually isolated on [[Thayer-Martin agar]] (or VPN agar)—an [[agar plate]] containing [[antibiotic]]s ([[vancomycin]], [[colistin]], [[nystatin]], and [[trimethoprim]]) and nutrients that facilitate the growth of ''Neisseria'' species while inhibiting the growth of contaminating bacteria and fungi. Further testing to differentiate the species includes testing for [[oxidase]] (all clinically relevant ''Neisseria'' show a positive reaction) and the [[carbohydrates]] [[maltose]], [[sucrose]], and [[glucose]] test in which ''N. gonorrhoeae'' will oxidize (that is, utilize) only the glucose. | |||
''N. gonorrhoeae'' are non-motile and possess type IV pili to adhere to surfaces. The type IV pili operate mechanistically similar to a grappling hook. Pili extend and attach to a [[Substrate (biology)|substrate]] that signals the pilus to retract, dragging the cell forward. ''N. gonorrhoeae'' are able to pull 100,000 times their own weight, and it has been claimed that the pili used to do so are the strongest biological motor known to date, exerting one nanonewton.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Biais N, Ladoux B, Higashi D, So M, Sheetz M |title=Cooperative retraction of bundled type IV pili enables nanonewton force generation |journal=PLoS Biol. |volume=6 |issue=4 |pages=e87 |year=2008 |pmid=18416602 |pmc=2292754 |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.0060087 |url=http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060087 |laysummary=http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg19826525.300-mighty-microbe-pulls-100000-times-its-bodyweight.html |laydate=19 April 2008 |laysource=New Scientist}}</ref> | |||
''N. gonorrhoeae'' has surface proteins called Opa proteins, which bind to receptors on immune cells. In so doing, ''N. gonorrhoeae'' is able to prevent an immune response. The host is also unable to develop an immunological memory against ''N. gonorrhoeae'' – which means that future reinfection is possible. ''N. gonorrhoeae'' can also evade the immune system through a process called [[antigenic variation]], in which the ''N. gonorrhoeae'' bacterium is able to alter the antigenic determinants (sites where antibodies bind) such as the Opa proteins<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1|pmid=3093085|title=Opacity genes in ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'': Control of phase and antigenic variation|journal=Cell|volume=47|issue=1|pages=61–71|year=1986|last1=Stern|first1=Anne|last2=Brown|first2=Melissa|last3=Nickel|first3=Peter|last4=Meyer|first4=Thomas F.}}</ref> and Type IV pili<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07773.x|pmid=21812841|title=Focusing homologous recombination: Pilin antigenic variation in the pathogenic Neisseria|journal=Molecular Microbiology|volume=81|issue=5|pages=1136–43|year=2011|last1=Cahoon|first1=Laty A.|last2=Seifert|first2=H. Steven}}</ref> that adorn its surface. The many permutations of surface proteins make it more difficult for immune cells to recognize ''N. gonorrhoeae'' and mount a defense.<ref>[http://blog.advocatesaz.org/2011/04/11/sti-awareness-gonorrhea/ STI Awareness: Gonorrhea]. Planned Parenthood Advocates of Arizona. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 31 August 2011.</ref> | |||
== | ''N. gonorrhoeae'' is naturally competent for DNA transformation as well as being capable of conjugation. These processes allow for the DNA of ''N. gonorrhoeae'' to acquire or spread new genes. Especially dangerous from the aspect of healthcare is the ability to conjugate, since this can lead to antibiotic resistance.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03193.x|pmid=12410832|title=Competence for natural transformation in ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'': Components of DNA binding and uptake linked to type IV pilus expression|journal=Molecular Microbiology|volume=46|issue=3|pages=749–60|year=2002|last1=Aas|first1=Finn Erik|last2=Wolfgang|first2=Matthew|last3=Frye|first3=Stephan|last4=Dunham|first4=Steven|last5=Løvold|first5=Cecilia|last6=Koomey|first6=Michael}}</ref> | ||
=== | |||
<gallery widths=300px> | <gallery widths=300px> | ||
N. gonorrhea (GN diplococci).jpg | N. gonorrhea ( | N. gonorrhea (GN diplococci).jpg | N. gonorrhea (Gram-negative diplococci) in conjunctivitis.<ref>http://picasaweb.google.com/mcmumbi/USMLEIIImages</ref> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Genome == | |||
The genomes of several strains of ''N''. ''gonorrhoeae ''have been sequenced. Most of them are about 2.1 Mb in size and encode 2,100 to 2,600 proteins (although most seem to be in the lower range).<ref>[https://www.broadinstitute.org/annotation/genome/neisseria_gonorrhoeae/GenomeStats.html ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' genome statistics, Broad Institute]</ref> For instance, '''strain NCCP11945''' consists of one circular chromosome (2,232,025 bp) encoding 2,662 predicted [[open reading frame|ORFs]] and one [[plasmid]] (4,153 bp) encoding 12 predicted ORFs. The estimated coding density over the entire genome is 87%, and the average G+C content is 52.4%, values that are similar to those of strain FA1090. The NCCP11945 genome encodes 54 tRNAs and four copies of 16S-23S-5S rRNA operons.<ref name="Chung2008">{{Cite pmid| 18586945}}</ref> | |||
== | In 2011, researchers at Northwestern University found evidence of a human DNA fragment in a ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' genome, the first example of [[horizontal gene transfer]] from humans to a bacterial pathogen.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.4161/mge.1.1.15868 |pmid=22016852 |pmc=3190277 |laysummary=http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/02/110213174143.htm |laysource=ScienceDaily |laydate=February 14, 2011|title=''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' and humans perform an evolutionary LINE dance |journal=Mobile Genetic Elements |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=85–87 |year=2014 |last1=Anderson |first1=Mark T. |last2=Seifert |first2=H. Steven }}</ref><ref name=anderson2011>{{cite journal |doi=10.1128/mBio.00005-11 |pmid=21325040|pmc=3042738|author1=Anderson|first1=M. T.|title=Opportunity and Means: Horizontal Gene Transfer from the Human Host to a Bacterial Pathogen|journal=MBio|volume=2|issue=1|pages=e00005–11|last2=Seifert|first2=H. S.|year=2011}}</ref> | ||
==Transmission== | |||
''N. gonorrhoeae'' is transmitted from person to person during sexual relations. Traditionally, the bacteria was thought to move attached to [[spermatozoon]], but this hypothesis did not explain female to male transmission of the disease. A recent study suggests that rather than “surf” on wiggling [[sperm]], ''N. gonorrhoeae'' bacteria uses hairlike structures called [[pilus|pili]] to anchor onto proteins in the sperm and move through coital liquid.<ref name=Anderson2014>{{cite journal |doi=10.1128/mBio.01004-13|pmid=24595372|title=Seminal Plasma Initiates a ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' Transmission State|journal=MBio|volume=5|issue=2|pages=e01004–13|year=2014|last1=Anderson|first1=M. T.|last2=Dewenter|first2=L.|last3=Maier|first3=B.|last4=Seifert|first4=H. S.}}</ref> | |||
==Survival of gonococci== | |||
The exudates from infected individuals contain many polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) with ingested ''gonococci''. These ''gonococci'' stimulate the PMN to release an internal oxidative burst involving reactive oxygen species in order to kill the ''gonococci''.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1128/iai.73.4.1971-1977.2005|pmid=15784537|pmc=1087443|title=Interactions of ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' with Adherent Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes|journal=Infection and Immunity|volume=73|issue=4 |pages=1971–7|year=2005|last1=Simons|first1=M. P.|last2=Nauseef|first2=W. M.|last3=Apicella|first3=M. A.}}</ref> However, a significant fraction of the ''gonococci'' can resist killing and are able to reproduce within the PMN phagosomes. | |||
Stohl and Seifert showed that the bacterial RecA protein, that mediates recombinational repair of DNA damage, plays an important role in ''gonococcal'' survival.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1128/JB.00801-06|pmid=16936020|pmc=1636252|title=''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' DNA Recombination and Repair Enzymes Protect against Oxidative Damage Caused by Hydrogen Peroxide|journal=Journal of Bacteriology|volume=188|issue=21 |pages=7645–51|year=2006|last1=Stohl|first1=E. A.|last2=Seifert|first2=H. S.}}</ref> The protection afforded by RecA protein may be linked to transformation, the process by which recipient ''gonococci'' take up DNA from neighboring ''gonococci'' and integrate this DNA into the recipient genome through recombination. Michod et al. have suggested that an important benefit of transformation in ''N. gonorrhoeae'' may be recombinational repair of oxidative DNA damages caused by oxidative attack by the hosts phagocytic cells.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002|pmid=18295550|title=Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens|journal=Infection, Genetics and Evolution|volume=8|issue=3 |pages=267–85|year=2008|last1=Michod|first1=Richard E.|last2=Bernstein|first2=Harris|last3=Nedelcu|first3=Aurora M.}}</ref> | |||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
: | Image: Gonorrhea10.jpeg| Photomicrograph of Gram-negative Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria, accompanied by a number of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp From Public Health Image Library (PHIL).] ''<ref name=PHIL> {{Cite web | title = Public Health Image Library (PHIL) | url = http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp}}</ref></SMALL></SMALL> | ||
: | Image: Gonorrhea02.jpeg| 3D computer-generated image of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae diplococcal bacteria. <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp From Public Health Image Library (PHIL).] ''<ref name=PHIL> {{Cite web | title = Public Health Image Library (PHIL) | url = http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp}}</ref></SMALL></SMALL> | ||
Image: Gonorrhea06.jpeg| Gram-stained photomicrograph revealed gram-negative diplococcal bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoea. <SMALL><SMALL>''[http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp From Public Health Image Library (PHIL).] ''<ref name=PHIL> {{Cite web | title = Public Health Image Library (PHIL) | url = http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp}}</ref></SMALL></SMALL> | |||
: | |||
: | |||
: | |||
: | |||
: | |||
</gallery> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist| | {{refbegin}} | ||
{{Reflist}} | |||
*{{cite web |first=Kenneth |last=Todar |title=Pathogenic Neisseriae: Gonorrhea, Neonatal Ophthalmia and Meningococcal Meningitis |work=Todar's Online Textbook of Bacteriology |url=http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/neisseria.html}} | |||
*{{EMedicine|article|218059|Gonorrhea}} | |||
{{Gram-negative bacterial diseases}} | |||
[[Category:Infectious Disease Project]] | [[Category:Infectious Disease Project]] | ||
[[Category:Gynecology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:56, 29 July 2020
|
Gonorrhea Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
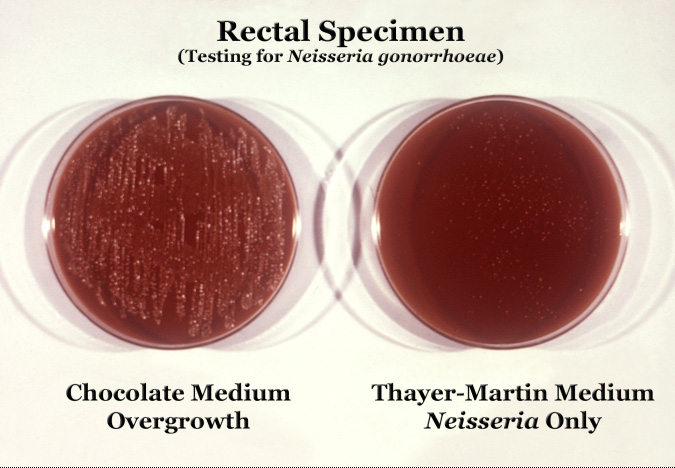 Neisseria gonorrhoeae cultured on two different media types.
| ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae Zopf, 1885 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, also known as gonococci (plural), or gonococcus (singular), is a species of Gram-negative coffee bean-shaped diplococci bacteria responsible for the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea.[1] N. gonorrhoeae was first described by Albert Neisser in 1879.
Microbiology
Neisseria are fastidious Gram-negative cocci that require nutrient supplementation to grow in laboratory cultures. To be specific, they grow on chocolate agar with carbon dioxide. These cocci are facultatively intracellular and typically appear in pairs (diplococci), in the shape of coffee beans. Of the eleven species of Neisseria that colonize humans, only two are pathogens. N. gonorrhoeae is the causative agent of gonorrhea (also called "The Clap") and is transmitted via sexual contact.[2]
Neisseria is usually isolated on Thayer-Martin agar (or VPN agar)—an agar plate containing antibiotics (vancomycin, colistin, nystatin, and trimethoprim) and nutrients that facilitate the growth of Neisseria species while inhibiting the growth of contaminating bacteria and fungi. Further testing to differentiate the species includes testing for oxidase (all clinically relevant Neisseria show a positive reaction) and the carbohydrates maltose, sucrose, and glucose test in which N. gonorrhoeae will oxidize (that is, utilize) only the glucose.
N. gonorrhoeae are non-motile and possess type IV pili to adhere to surfaces. The type IV pili operate mechanistically similar to a grappling hook. Pili extend and attach to a substrate that signals the pilus to retract, dragging the cell forward. N. gonorrhoeae are able to pull 100,000 times their own weight, and it has been claimed that the pili used to do so are the strongest biological motor known to date, exerting one nanonewton.[3]
N. gonorrhoeae has surface proteins called Opa proteins, which bind to receptors on immune cells. In so doing, N. gonorrhoeae is able to prevent an immune response. The host is also unable to develop an immunological memory against N. gonorrhoeae – which means that future reinfection is possible. N. gonorrhoeae can also evade the immune system through a process called antigenic variation, in which the N. gonorrhoeae bacterium is able to alter the antigenic determinants (sites where antibodies bind) such as the Opa proteins[4] and Type IV pili[5] that adorn its surface. The many permutations of surface proteins make it more difficult for immune cells to recognize N. gonorrhoeae and mount a defense.[6]
N. gonorrhoeae is naturally competent for DNA transformation as well as being capable of conjugation. These processes allow for the DNA of N. gonorrhoeae to acquire or spread new genes. Especially dangerous from the aspect of healthcare is the ability to conjugate, since this can lead to antibiotic resistance.[7]
-
N. gonorrhea (Gram-negative diplococci) in conjunctivitis.[8]
Genome
The genomes of several strains of N. gonorrhoeae have been sequenced. Most of them are about 2.1 Mb in size and encode 2,100 to 2,600 proteins (although most seem to be in the lower range).[9] For instance, strain NCCP11945 consists of one circular chromosome (2,232,025 bp) encoding 2,662 predicted ORFs and one plasmid (4,153 bp) encoding 12 predicted ORFs. The estimated coding density over the entire genome is 87%, and the average G+C content is 52.4%, values that are similar to those of strain FA1090. The NCCP11945 genome encodes 54 tRNAs and four copies of 16S-23S-5S rRNA operons.[10]
In 2011, researchers at Northwestern University found evidence of a human DNA fragment in a Neisseria gonorrhoeae genome, the first example of horizontal gene transfer from humans to a bacterial pathogen.[11][12]
Transmission
N. gonorrhoeae is transmitted from person to person during sexual relations. Traditionally, the bacteria was thought to move attached to spermatozoon, but this hypothesis did not explain female to male transmission of the disease. A recent study suggests that rather than “surf” on wiggling sperm, N. gonorrhoeae bacteria uses hairlike structures called pili to anchor onto proteins in the sperm and move through coital liquid.[13]
Survival of gonococci
The exudates from infected individuals contain many polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) with ingested gonococci. These gonococci stimulate the PMN to release an internal oxidative burst involving reactive oxygen species in order to kill the gonococci.[14] However, a significant fraction of the gonococci can resist killing and are able to reproduce within the PMN phagosomes.
Stohl and Seifert showed that the bacterial RecA protein, that mediates recombinational repair of DNA damage, plays an important role in gonococcal survival.[15] The protection afforded by RecA protein may be linked to transformation, the process by which recipient gonococci take up DNA from neighboring gonococci and integrate this DNA into the recipient genome through recombination. Michod et al. have suggested that an important benefit of transformation in N. gonorrhoeae may be recombinational repair of oxidative DNA damages caused by oxidative attack by the hosts phagocytic cells.[16]
Gallery
-
Photomicrograph of Gram-negative Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria, accompanied by a number of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]
-
3D computer-generated image of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae diplococcal bacteria. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]
-
Gram-stained photomicrograph revealed gram-negative diplococcal bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoea. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]
References
- ↑ Ryan, KJ; Ray, CG, eds. (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- ↑ Genco, C; Wetzler, L, eds. (2010). Neisseria: Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-51-6.
- ↑ Biais N, Ladoux B, Higashi D, So M, Sheetz M (2008). "Cooperative retraction of bundled type IV pili enables nanonewton force generation". PLoS Biol. 6 (4): e87. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060087. PMC 2292754. PMID 18416602. Lay summary – New Scientist (19 April 2008).
- ↑ Stern, Anne; Brown, Melissa; Nickel, Peter; Meyer, Thomas F. (1986). "Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Control of phase and antigenic variation". Cell. 47 (1): 61–71. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. PMID 3093085.
- ↑ Cahoon, Laty A.; Seifert, H. Steven (2011). "Focusing homologous recombination: Pilin antigenic variation in the pathogenic Neisseria". Molecular Microbiology. 81 (5): 1136–43. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07773.x. PMID 21812841.
- ↑ STI Awareness: Gonorrhea. Planned Parenthood Advocates of Arizona. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ↑ Aas, Finn Erik; Wolfgang, Matthew; Frye, Stephan; Dunham, Steven; Løvold, Cecilia; Koomey, Michael (2002). "Competence for natural transformation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Components of DNA binding and uptake linked to type IV pilus expression". Molecular Microbiology. 46 (3): 749–60. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03193.x. PMID 12410832.
- ↑ http://picasaweb.google.com/mcmumbi/USMLEIIImages
- ↑ Neisseria gonorrhoeae genome statistics, Broad Institute
- ↑ PMID 18586945 (PMID 18586945)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Anderson, Mark T.; Seifert, H. Steven (2014). "Neisseria gonorrhoeae and humans perform an evolutionary LINE dance". Mobile Genetic Elements. 1 (1): 85–87. doi:10.4161/mge.1.1.15868. PMC 3190277. PMID 22016852. Lay summary – ScienceDaily (February 14, 2011).
- ↑ Anderson, M. T.; Seifert, H. S. (2011). "Opportunity and Means: Horizontal Gene Transfer from the Human Host to a Bacterial Pathogen". MBio. 2 (1): e00005–11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00005-11. PMC 3042738. PMID 21325040.
- ↑ Anderson, M. T.; Dewenter, L.; Maier, B.; Seifert, H. S. (2014). "Seminal Plasma Initiates a Neisseria gonorrhoeae Transmission State". MBio. 5 (2): e01004–13. doi:10.1128/mBio.01004-13. PMID 24595372.
- ↑ Simons, M. P.; Nauseef, W. M.; Apicella, M. A. (2005). "Interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with Adherent Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes". Infection and Immunity. 73 (4): 1971–7. doi:10.1128/iai.73.4.1971-1977.2005. PMC 1087443. PMID 15784537.
- ↑ Stohl, E. A.; Seifert, H. S. (2006). "Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA Recombination and Repair Enzymes Protect against Oxidative Damage Caused by Hydrogen Peroxide". Journal of Bacteriology. 188 (21): 7645–51. doi:10.1128/JB.00801-06. PMC 1636252. PMID 16936020.
- ↑ Michod, Richard E.; Bernstein, Harris; Nedelcu, Aurora M. (2008). "Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 8 (3): 267–85. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002. PMID 18295550.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "Public Health Image Library (PHIL)".
- Todar, Kenneth. "Pathogenic Neisseriae: Gonorrhea, Neonatal Ophthalmia and Meningococcal Meningitis". Todar's Online Textbook of Bacteriology.
- Gonorrhea at eMedicine
![N. gonorrhea (Gram-negative diplococci) in conjunctivitis.[8]](/images/8/8a/N._gonorrhea_%28GN_diplococci%29.jpg)
![Photomicrograph of Gram-negative Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria, accompanied by a number of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]](/images/0/00/Gonorrhea10.jpeg)
![3D computer-generated image of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae diplococcal bacteria. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]](/images/b/b7/Gonorrhea02.jpeg)
![Gram-stained photomicrograph revealed gram-negative diplococcal bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoea. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [17]](/images/a/a7/Gonorrhea06.jpeg)