Diverticulosis endoscopy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category:Surgery]] | [[Category:Surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:26, 29 July 2020
|
Diverticulosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Diverticulosis endoscopy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Diverticulosis endoscopy |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Diverticulosis endoscopy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Seyedmahdi Pahlavani, M.D.
Overview
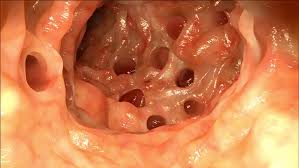
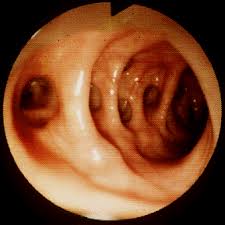
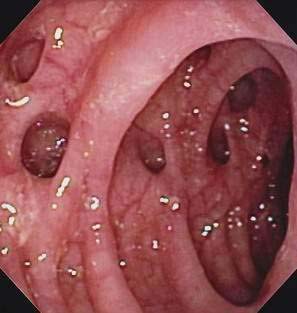
Colonoscopy is the optimal diagnostic procedure for the diagnosis of diverticulosis.
Colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy is the optimal diagnostic procedure for the diagnosis of diverticulosis.[1]
- Colonoscopy is both sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of diverticulosis, and it may additionally provide a therapeutic benefit.[1]
- Diverticula may be visualized as outpouchings of the wall that have the appearance of a blind sac.[2]
Gallery
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vernava AM, Moore BA, Longo WE, Johnson FE (1997). "Lower gastrointestinal bleeding". Dis. Colon Rectum. 40 (7): 846–58. PMID 9221865.
- ↑ Ghorai S, Ulbright TM, Rex DK (2003). "Endoscopic findings of diverticular inflammation in colonoscopy patients without clinical acute diverticulitis: prevalence and endoscopic spectrum". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98 (4): 802–6. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07383.x. PMID 12738459.