WBR1109
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Immunology, MainCategory::Pathophysiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Pulmonology |
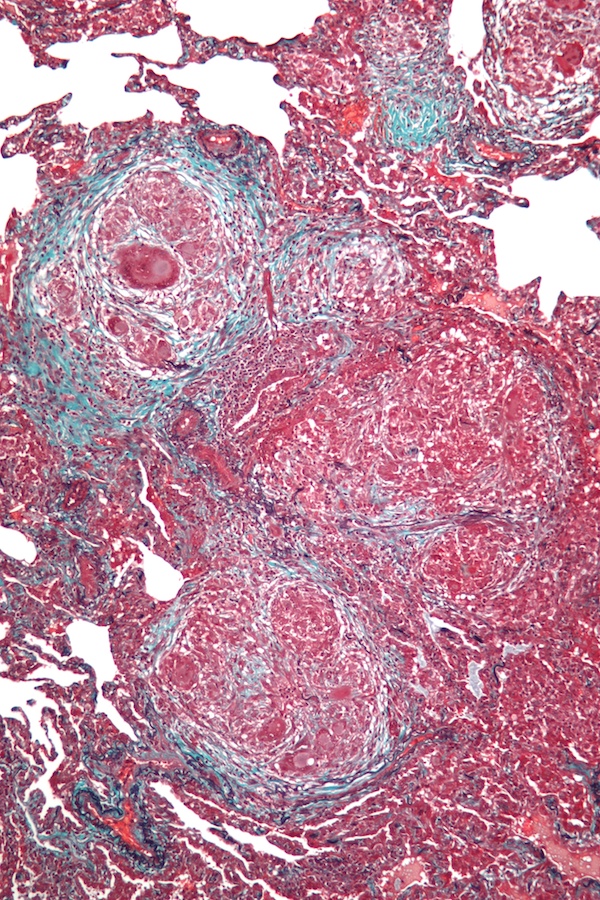
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 65-year-old woman presents to his primary care physician for shortness of breath and cough for the past month. Pulmonary function testing reveals decreased diffusion capacity of the lung, with an FEV1/FVC of 70%. Lung biopsy is shown below. The patient is taken off of amiodarone, but her symptoms do not resolve over the course of the following two weeks. She is readmitted and upon further questioning, reports starting a part-time job at a pet store. She reports that shortly after being exposed to pigeon droppings, she develops chest tightness. Her PaCO2 is 40 mmHg and PaO2 is 70 mmHg. Which of the following represent the patient’s A-a gradient and diagnosis respectively? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::30 mmHg; Chlamydia psittaci infection |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Chlamydia psittaci is a cause of pneumonia in individuals exposed to pigeon droppings. Chlamydia psittaci would not cause an acute exacerbation on exposure to pigeon droppings. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::15 mmHg; Chlamydia psittaci infection |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Chlamydia psittaci is a cause of pneumonia in individuals exposed to pigeon droppings. Chlamydia psittaci would not cause an acute exacerbation on exposure to pigeon droppings. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::30 mmHg ; Hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Recall that the equation for A-a gradient is PAO2-PaO2. PaO2 can be measured in the patient’s blood. PAO2 is given by the following equation: 150-PaCO2/0.8 = 150-40/0.8=100; 100-70=mmHg. The patient in this vignette has developed a subtype of hypersensitivity called Bird Fancier’s Lung.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::20 mmHg ; Hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::The calculation of A-a gradient in this answer is incorrect. Please see the explanation for a proper calculation. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::20 mmHg; Asthma exacerbation |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::While the acute exacerbation of the patient’s condition on exposure to an environmental antigen resembles an asthma exacerbation, the specific history in this case is telling. This patient has developed a subtype of hypersensitivity pneumonitis called Bird Fancier’s disease.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient in this vignette has contracted a subtype of hypersensitivity pneumonitis called “Bird Fancier’s Lung”. This disease is caused by the exposure to avian proteins present in the dry dust of the droppings and sometimes in the feathers of a variety of birds. People who work with birds or own many birds are at risk. Bird hobbyists and pet store workers may also be at risk. This question requires that test takers calculate the Aveolar-arterial (A-a) oxygen gradient. Recall that the equation for A-a gradient is PAO2 - PaO2. PaO2 can be measured in the patient’s blood. PAO2 is given by the following equation:
150 - (PaCO2/0.8) = 150 - (40/0.8) = 100 The A-a gradient is the PAO2 - PaO2: 100 - 70 = 30 mmHg |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Hypersensitivity, WBRKeyword::Pneumonitis, WBRKeyword::Pulmonary, WBRKeyword::Respiratory, WBRKeyword::Allergy |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |