Medical physics
|
WikiDoc Resources for Medical physics |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Medical physics Most cited articles on Medical physics |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Medical physics |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Medical physics at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Medical physics Clinical Trials on Medical physics at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Medical physics NICE Guidance on Medical physics
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Medical physics Discussion groups on Medical physics Patient Handouts on Medical physics Directions to Hospitals Treating Medical physics Risk calculators and risk factors for Medical physics
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Medical physics |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Overview
Medical physics is a branch of applied physics concerning the application of physics to medicine. It generally concerns physics as applied to medical imaging and radiotherapy, although a medical physicist may also work in many other areas of healthcare. A medical physics department may be based in either a hospital or a university and its work is likely to include research, technical development and clinical healthcare.
Of the large body of medical physicists in academia and clinics, roughly 85% practice or specialize in various forms of therapy, 10% in Diagnostic imaging, and 5% in nuclear medicine.[1] Areas of specialty in medical physics however are widely varied in scope and breadth.
Areas of specialty
Medical imaging

- Diagnostic radiology, including x-rays, fluoroscopy, mammography, Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, angiography and Computed tomography
- Ultrasound, including intravascular ultrasound
- Non-ionising radiation (Lasers, Ultraviolet etc.)
- Nuclear medicine, including SPECT and positron emission tomography (PET)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), including functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and other methods for functional neuroimaging of the brain.
- For example, nuclear magnetic resonance (often referred to as magnetic resonance imaging to avoid the common concerns about radiation), uses the phenomenon of nuclear resonance to image the human body.
- Magnetoencephalography
- Electrical impedance tomography
- Diffuse optical imaging
- Optical coherence tomography
Treatment of disease
- Defibrillation
- High intensity focussed ultrasound, including lithotripsy
- Interventional radiology
- Non-ionising radiation Lasers, Ultraviolet etc. including photodynamic therapy and LASIK
- Nuclear medicine, including unsealed source radiotherapy
- Photomedicine, the use of light to treat and diagnose disease
- Radiotherapy
- Sealed source radiotherapy
- Terahertz radiation
Physiological measurement techniques
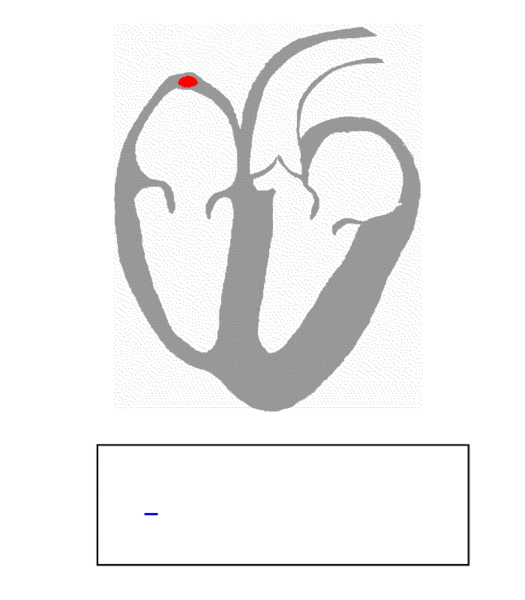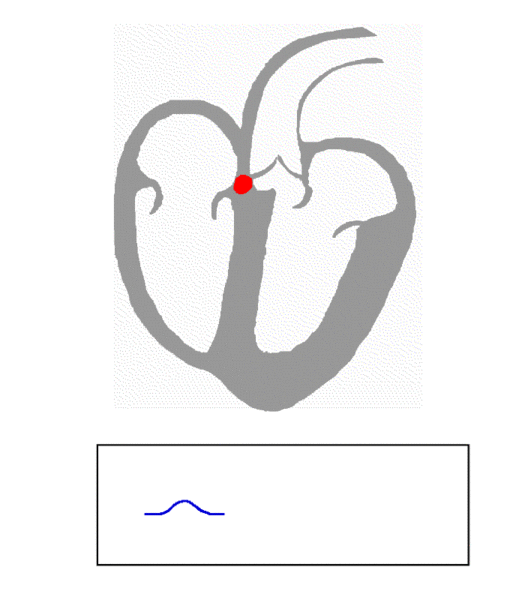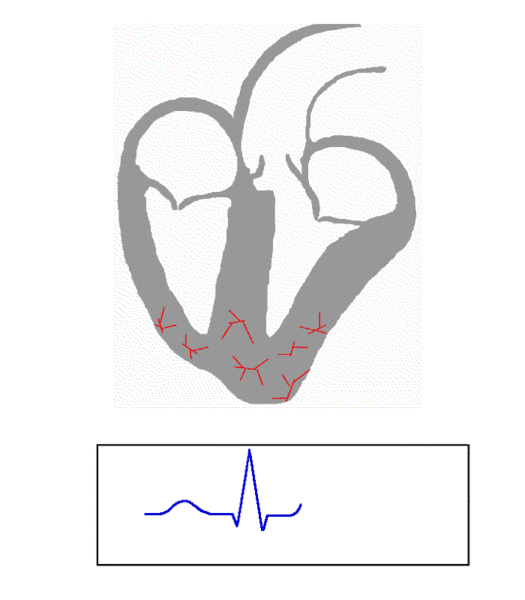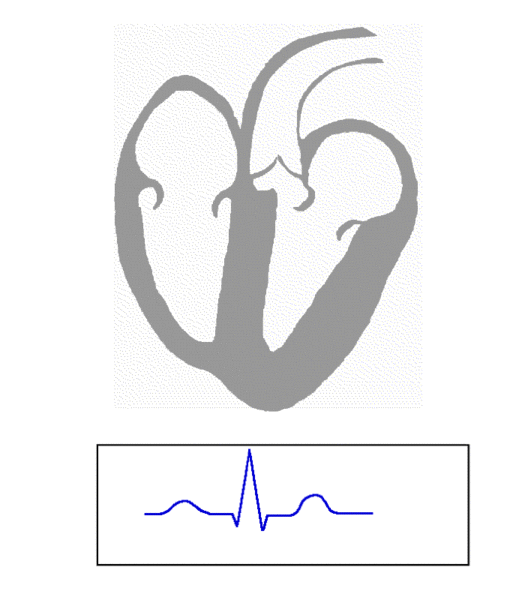
Used to monitor and measure various physiological parameters. Many physiological measurement techniques are non-invasive and can be used in conjunction with, or as an alternative to, other invasive methods.
- Electrocardiography
- Electromyography
- Electroencephalography
- Electronystagmography
- Endoscopy
- Medical ultrasonography
- Non-ionising radiation (Lasers, Ultraviolet etc.)
- Near infrared spectroscopy
- Pulse oximetry
- Blood gas monitor
- Blood pressure measurement
Radiation protection
Medical computing and mathematics
- Medical informatics
- Telemedicine
- Picture archiving and communication systems (PACS)
- DICOM
- Tomographic reconstruction, an ill-posed inverse problem
- Advanced Digital Imaging Solutions Laboratory[ADISL]: [1]
Education and training
The primary clinical responsibility of the Qualified Medical Physicist is to "assure the safe and effective delivery of radiation to achieve a diagnostic or therapeutic result as prescribed in patient care (Medical Physics Scope of Practice)".[2] Various training programs exist to accommodate the demand for specialization in this field.
In North America
In the United States, the Consumer Assurance of Radiologic Excellence Act (H.R. 1426) also called the CARE Bill (under consideration by the U.S. congress in 2007) has required minimum training and qualifications for individuals to practice medical physics. The American Board of Radiology currently certifies medical physicists and desires that all candidates receive consistent training in a CAMPEP accredited clinical residency program. The American Association of Physicists in Medicine supports this desire.[3]
In North America, the degree of medical physics can be offered at a Masters level, doctorate level, and/or residency levels. Several large and established universities offer these degrees in Canada and the United States. Some programs such as the University of Texas Health Science Center Department of Radiology even offer Dual Medical Residency and Ph.D. degrees in medical physics.[4] Eleven universities in the United States, and four programs in Canada currently have graduate programs in Medical Physics that are accredited by The Commission on Accreditation of Medical Physics Education Programs (CAMPEP). As CAMPEP continues to gain support from bodies such as The American Association of Physicists in Medicine[5], the American Board of Radiology has specified that graduation from a CAMPEP accredited clinical training program be considered a requirement to sit for the ABR certification exams by 2012.[6][7][8]
The list of schools offering education in the field are:
- CAMPEP Accredited Graduate Programs in Medical Physics
- CAMPEP non-Accredited Graduate Programs in Medical Physics
- Other list of Canadian programs
In the United Kingdom
The person concerned must first gain a first or upper second-class honours degree in a physical or engineering science subject before they can start the Grade A medical physics training within the NHS.
Trainees can complete Grade A training in fifteen months provided they hold an MSc from an IPEM accredited center in the United Kingdom or the Republic of Ireland. For these candidates, the grade A training consists of pure clinical experience. Trainees applying for grade A trainee holding only a degree in a physical or engineering science subject must undertake a combined study and clinical training program. This program consists of two years of clinical placement, during which the trainee will study for an MSc in Medical Physics which is approved by the Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (IPEM). The MSc will be either at Swansea, Sheffield, Surrey, Birmingham, Leeds, Manchester, Aberdeen, King's or Queen Mary's. Successful completion of the Grade A training programme leads to an IPEM Diploma. The trainee can then apply for a Grade B position, which will consists of the IPEM's Programme of Advanced Training (PAT) which takes a further two years and leads to Corporate Membership of the IPEM. At this stage the physicist is eligible for Senior Grade B positions.
Other programs around the world
Some major involved organizations around the world
Professional
- IOMP: International Organisation for Medical Physics (link)
- ASTRO: American Society for Therapeutic Radiology And Oncology (link)
- RSNA: Radiological Society of North America
- ACMP: American College of Medical Physics (link)
- ISMRM: International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (link)
- AAPM: American Association of Physicists in Medicine
- EFOMP: European Federation of Organisations for Medical Physics (link)
- ABR: American Board of Radiology (link)
- APSM: Association of physical scientists in medicine (link)
- COMP: Canadian Organization of Medical Physicists (link)
- IPEM: Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (link)
- ABMP: American Board of Medical Physics (link)
- SFPM: French society of Medical Physicists (link)
- APSM: Association of physical scientists in medicine (Ireland) (link)
- ACPSEM: Australasian college of physical scientists and engineers in medicine (link)
Legislative and advisory
- ICRU: International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements
- ICRP: International Commission on Radiological Protection
- NCRP: National Council on Radiation Protection & Measurements
- NRC: Nuclear Regulatory Commission
- FDA: Food and Drug Administration
- IAEA: International Atomic Energy Agency
Some major journals
- Medical Physics
- JMP: The official journal of Association of Medical Physicists of India
- Medical Engineering and Physics
- Physica Medica
- JACMP: Journal of Applied Clinical Physics
- JMRI: Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Radiology
- JRAD: Journal of Radiology
- The British Journal of Radiology
- European Journal of Radiology
- Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging
References
- ↑ Alternative Clinical Medical Physics Training Pathways: Report of AAPM Task Group 133, p.21
- ↑ Alternative Clinical Medical Physics Training Pathways: Report of AAPM Task Group 133, p.4
- ↑ Alternative Clinical Medical Physics Training Pathways: Report of AAPM Task Group 133, p.24
- ↑ http://www.uthscsa.edu/hscnews/singleformat.asp?newID=2477
- ↑ AAPM stated policy: http://www.aapm.org/org/policies/details.asp?id=242&type=AP
- ↑ Hendee, W.R., Accreditation, Certification and Maintenance of Certification in Medical Physics: The Need for Convergence. NCCAAPM meeting, Nov 19,, 2004.
- ↑ Alternative Clinical Medical Physics Training Pathways: Report of AAPM Task Group 133, p.6
- ↑ AAPM presentation report p.8
See also
- Biomedical engineering
- Biomechanics
- Functional electrical stimulation
- Dialysis
- Gait analysis
- Prosthetics
- Cochlear implants
- Nanomedicine
- important publications in medical physics
External links
- medicalphysicsweb.org - a community website from the Institute of Physics
- AIP Medical Physics portal
- Resources for physics students and clinical medical physicists
ar:فيزياء طبية bg:Медицинска физика de:Medizinische Physik fa:فیزیک پزشکی gl:Física médica nl:Medische fysica fi:Lääketieteellinen fysiikka Template:WH Template:WikiDoc Sources