Deep perineal pouch
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The deep perineal pouch (also deep perineal space) is an anatomical term that refers to the partially enclosed space in the perineum, located superiorly to the perineal membrane.
Structure
Unlike the superficial perineal pouch, the deep perineal pouch lacks a superior border. It extends up into the pelvis.
Contents
The deep perineal pouch contains:
- muscles
- other
- Membranous portion of the urethra (males) / proximal portion of urethra (females)
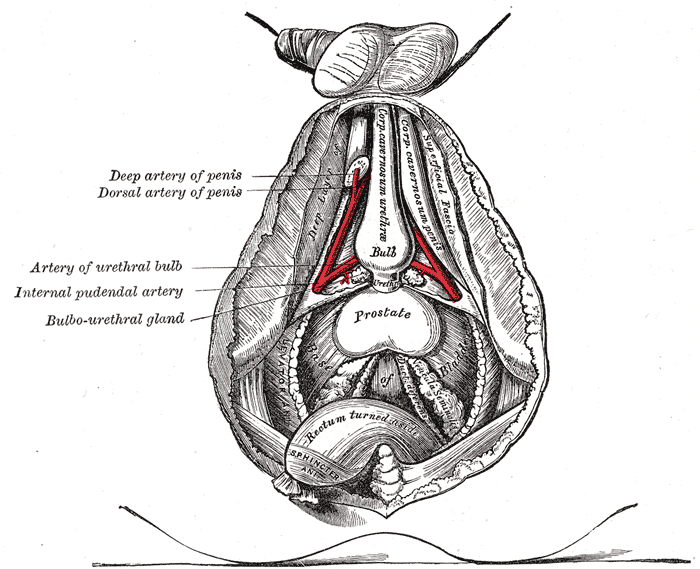
- Bulbourethral gland (males). (Note: The Bartholin gland is the female counterpart to the bulbourethral gland in males, but it is located in the superficial perineal pouch.)
- Vagina (females)
"Urogenital diaphragm"
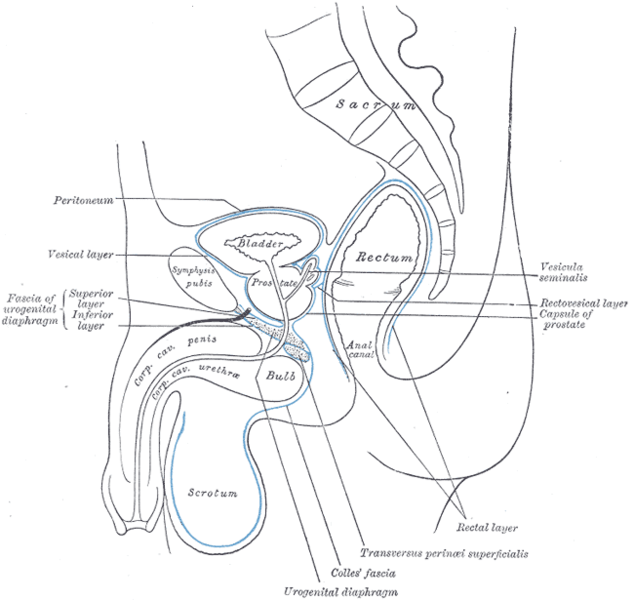
Older texts have asserted the existence of an "urogenital diaphragm", which was described as a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, lying between the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
While this term is used to refer to a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, such a discrete border of the sac probably does not exist.[1][2][3] [4][5]
While it has no official entry in Terminologia Anatomica, the term is still used occasionally to describe the muscular components of the deep perineal pouch[6] The urethra and the vagina, though part of the pouch, are usually said to be passing through the urogenital diaphragm, rather than part of the diaphragm itself. [2]
Some researchers still assert that such a diaphragm exists, [7] and the term is still used in the literature.[8]
The term "urogenital diaphragm" is often confused with the pelvic floor, which is a true diaphragm supporting many of the pelvic organs.
Additional images
-
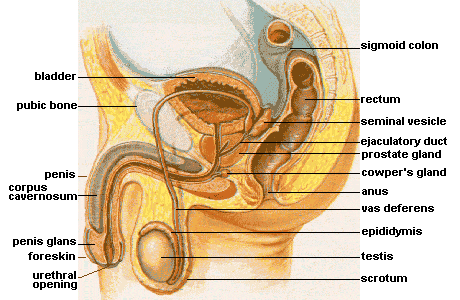
Male Anatomy
-
Median sagittal section of pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciæ.
-
The deeper branches of the internal pudendal artery.
See also
References
- ↑ Kaye K, Milne N, Creed K, van der Werf B (1997). "The 'urogenital diaphragm', external urethral sphincter and radical prostatectomy". Aust N Z J Surg. 67 (1): 40–4. PMID 9033375.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 "Chapter 38: The perineal region and external genitalia". Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- ↑ Oelrich TM (1980). "The urethral sphincter muscle in the male". Am. J. Anat. 158 (2): 229–46. doi:10.1002/aja.1001580211. PMID 7416058.
- ↑ Mirilas P, Skandalakis JE (2004). "Urogenital diaphragm: an erroneous concept casting its shadow over the sphincter urethrae and deep perineal space". J. Am. Coll. Surg. 198 (2): 279–90. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2003.07.022. PMID 14759786.
- ↑ Dorschner W, Biesold M, Schmidt F, Stolzenburg JU (1999). "The dispute about the external sphincter and the urogenital diaphragm". J. Urol. 162 (6): 1942–5. PMID 10569543.
- ↑ Template:Dorlands
- ↑ Herschorn S (2004). "Female pelvic floor anatomy: the pelvic floor, supporting structures, and pelvic organs". Rev Urol. 6 Suppl 5: S2–S10. PMID 16985905.
- ↑ Hruby S, Ebmer J, Dellon AL, Aszmann OC (2005). "Anatomy of pudendal nerve at urogenital diaphragm--new critical site for nerve entrapment". Urology. 66 (5): 949–52. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2005.05.032. PMID 16286101.
External links
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "The Female Perineum: The Perineal Nerve"
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "The Female Perineum - The Deep Perineal Pouch"
- Template:SUNYAnatomyFigs - "The urinary bladder and the urethra as seen in a frontal section of the female pelvis."
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "The Male Pelvis: The Prostate Gland"
- Template:NormanAnatomy (Template:NormanAnatomyFig)
- Template:DartmouthHumanAnatomy
- http://www.instantanatomy.net/abdomen/areas/perineum/mdeepperinealpouch.html