Capreomycin sulfate
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* The use of Capastat® Sulfate (Capreomycin for Injection, USP) in patients with renal insufficiency or preexisting auditory impairment must be undertaken with great caution, and the risk of additional cranial nerve VIII impairment or renal injury should be weighed against the benefits to be derived from therapy.
|
Overview
Capreomycin sulfate is an antitubercular drug that is FDA approved for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis, in combination with other antituberculosis agents, as second-line therapy. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include drug-induced eosinophilia, Ototoxicity, raised serum blood urea nitrogen.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Capastat Sulfate, which is to be used concomitantly with other appropriate antituberculosis agents, is indicated in pulmonary infections caused by capreomycin-susceptible strains of M. tuberculosis when the primary agents (isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, aminosalicylic acid, and streptomycin) have been ineffective or cannot be used because of toxicity or the presence of resistant tubercle bacilli.
- Susceptibility studies should be performed to determine the presence of a capreomycin-susceptible strain of M. tuberculosis.
Dosage
- Capastat Sulfate may be administered intramuscularly or intravenously following reconstitution. Reconstitution is achieved by dissolving the vial contents (1 g) in 2 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or Sterile Water for Injection. Two to 3 minutes should be allowed for complete dissolution.
- Intravenously — For intravenous infusion, reconstituted Capastat Sulfate should be diluted in 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection and administered over 60 minutes.
- Intramuscularly — Reconstituted Capastat Sulfate should be given by deep intramuscular injection into a large muscle mass, since superficial injection may be associated with increased pain and the development of sterile abscesses.
- For administration of a 1-g dose, the entire contents of the vial should be given. For doses lower than 1 g, the following dilution table may be used.
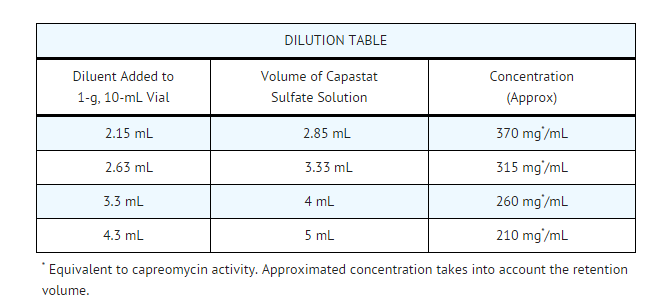
- The solution may acquire a pale straw color and darken with time, but this is not associated with loss of potency or the development of toxicity. After reconstitution, all solutions of Capastat Sulfate may be stored for up to 24 hours under refrigeration.
- Capreomycin is always administered in combination with at least 1 other antituberculosis agent to which the patient's strain of tubercle bacilli is susceptible. The usual dose is 1 g daily (not to exceed 20 mg/kg/day) given intramuscularly or intravenously for 60 to 120 days, followed by 1 g by either route 2 or 3 times weekly. (Note — Therapy for tuberculosis should be maintained for 12 to 24 months. If facilities for administering injectable medication are not available, a change to appropriate oral therapy is indicated on the patient's release from the hospital.)
- Patients with reduced renal function should have dosage reduction based on creatinine clearance using the guidelines included in TABLE below. These dosages are designed to achieve a mean steady-state capreomycin level of 10 μg/mL.
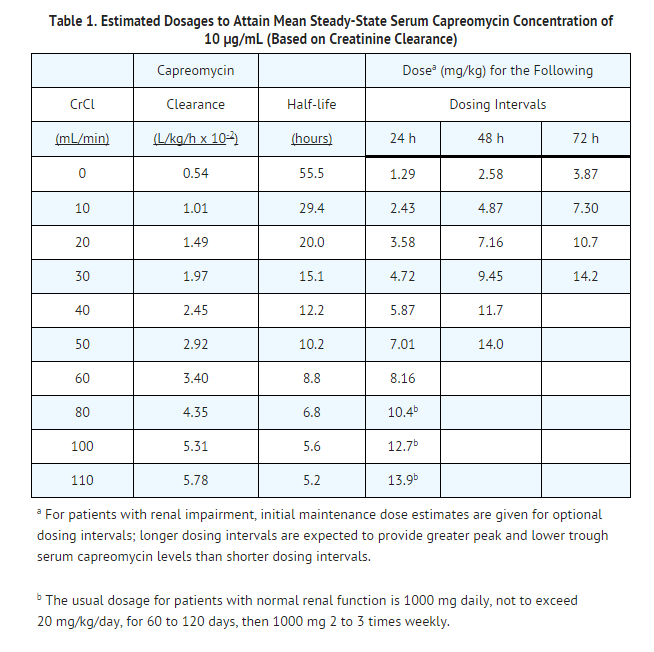
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Capreomycin sulfate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Capreomycin sulfate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Capreomycin sulfate in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Capreomycin sulfate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Capreomycin sulfate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Capastat Sulfate is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to capreomycin.
Warnings
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* The use of Capastat® Sulfate (Capreomycin for Injection, USP) in patients with renal insufficiency or preexisting auditory impairment must be undertaken with great caution, and the risk of additional cranial nerve VIII impairment or renal injury should be weighed against the benefits to be derived from therapy.
|
There is limited information regarding Capreomycin sulfate Warnings' in the drug label.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Nephrotoxicity:
- In 36% of 722 patients treated with Capastat Sulfate, elevation of the BUN above 20 mg/100 mL has been observed. In many instances, there was also depression of PSP excretion and abnormal urine sediment. In 10% of this series, the BUN elevation exceeded 30 mg/100 mL.
- Toxic nephritis was reported in 1 patient with tuberculosis and portal cirrhosis who was treated with Capastat Sulfate (1 g) and aminosalicylic acid daily for 1 month. This patient developed renal insufficiency and oliguria and died. Autopsy showed subsiding acute tubular necrosis.
- Electrolyte disturbances including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia, sometimes serious in nature, have been reported.
Ototoxicity:
- Subclinical auditory loss was noted in approximately 11% of 722 patients undergoing treatment with Capastat Sulfate. This was a 5- to 10-decibel loss in the 4000- to 8000-CPS range. Clinically apparent hearing loss occurred in 3% of the 722 subjects. Some audiometric changes were reversible. Other cases with permanent loss were not progressive following withdrawal of Capastat Sulfate.
Liver:
- Serial tests of liver function have demonstrated a decrease in BSP excretion without change in AST (SGOT) or ALT (SGPT) in the presence of preexisting liver disease. Abnormal results in liver function tests have occurred in many persons receiving Capastat Sulfate in combination with other antituberculosis agents that also are known to cause changes in hepatic function. The role of Capastat Sulfate in producing these abnormalities is not clear; however, periodic determinations of liver function are recommended.
Blood:
Leukocytosis and leukopenia have been observed. The majority of patients treated have had eosinophilia exceeding 5% while receiving daily injections of Capastat Sulfate. This has subsided with reduction of the Capastat Sulfate dosage to 2 or 3 g weekly.
- Pain and induration at the injection site have been observed. Excessive bleeding at the injection site has been reported. Sterile abscesses have been noted. Rare cases of thrombocytopenia have been reported.
Hypersensitivity:
- Urticaria and maculopapular skin rashes associated in some cases with febrile reactions have been reported when Capastat Sulfate and other antituberculosis drugs were given concomitantly.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Capreomycin sulfate Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Pregnancy Category C
- Capastat Sulfate has been shown to be teratogenic in rats when given in doses 3 1/2 times the human dose. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Capastat Sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Capreomycin sulfate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Capreomycin sulfate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Capastat Sulfate is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of Capastat Sulfate did not analyze the safety and efficacy of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
- Capastat Sulfate is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. Patients with reduced renal function should have dosage reduction based on creatinine clearance using the guidelines included in TABLE .
- The geriatric population is also more likely to have impaired hearing at baseline. Audiometric measurements and assessment of vestibular function should be performed prior to initiation of therapy with Capastat Sulfate and at regular intervals during treatment
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Capreomycin sulfate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Capreomycin sulfate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Capreomycin sulfate in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Capreomycin sulfate in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Capreomycin sulfate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Capreomycin sulfate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Intravenous
- Intramuscular
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms
- Nephrotoxicity following the parenteral administration of Capastat Sulfate is most closely related to the area under the curve of the serum concentration versus time graph. The elderly patient, patients with abnormal renal function or dehydration, and patients receiving other nephrotoxic drugs are at much greater risk for developing acute tubular necrosis.
- Damage to the auditory and vestibular divisions of cranial nerve VIII has been associated with Capastat Sulfate given to patients with abnormal renal function or dehydration and in those receiving medications with additive auditory toxicities. These patients often experience dizziness, tinnitus, vertigo, and a loss of high-tone acuity.
- Neuromuscular blockage or respiratory paralysis may occur following rapid intravenous infusion.
If capreomycin is ingested, toxicity would be unlikely because it is poorly absorbed (less than 1%) from an intact gastrointestinal system.
- Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and an electrolyte disturbance resembling Bartter's syndrome have been reported to occur in patients with capreomycin toxicity.
- The subcutaneous median lethal dose in mice was 514 mg/kg.
Treatment
- To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is your certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR). In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs, and unusual drug kinetics in your patient.
- Protect the patient's airway and support ventilation and perfusion. Meticulously monitor and maintain, within acceptable limits, the patient's vital signs, blood gases, serum electrolytes, etc. Absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract may be decreased by giving activated charcoal, which, in many cases, is more effective than emesis or lavage; consider charcoal instead of or in addition to gastric emptying. Repeated doses of charcoal over time may hasten elimination of some drugs that have been absorbed. Safeguard the patient's airway when employing gastric emptying or charcoal.
- Patients who have received an overdose of capreomycin and have normal renal function should be carefully hydrated to maintain a urine output of 3 to 5 mL/kg/h. Fluid balance, electrolytes, and creatinine clearance should be carefully monitored.
- Hemodialysis may be effectively used to remove capreomycin in patients with significant renal disease.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Capreomycin sulfate Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
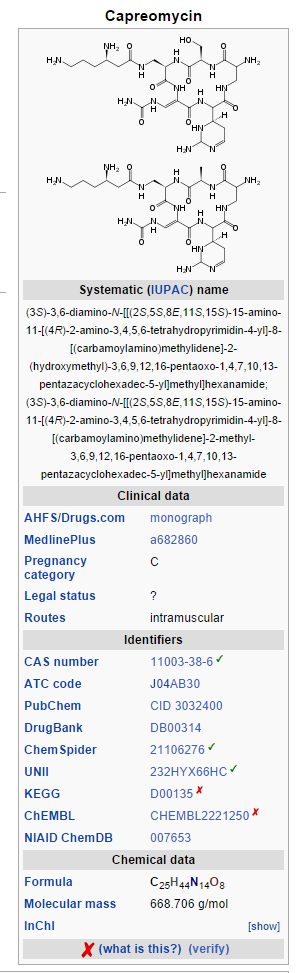
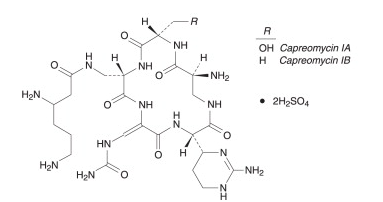
- Capastat Sulfate is a polypeptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces capreolus. It is a complex of 4 microbiologically active components which have been characterized in part; however, complete structural determination of all the components has not been established.
- Capreomycin is supplied as the disulfate salt and is soluble in water. In complete solution, it is almost colorless.
- Each vial contains the equivalent of 1 g capreomycin activity.
- The structural formula is as follows:
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Studies have not been performed to determine potential for carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Capastat® Sulfate, Capreomycin for Injection, USP, is available in:
Vials: 1 g*, 10 mL size (No. 718) (1s) NDC 17478-080-50
Storage
- Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) prior to reconstitution.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Capreomycin sulfate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Capreomycin sulfate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Capreomycin sulfate in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Capreomycin sulfate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- CAPASTAT SULFATE
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Capreomycin sulfate Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Capreomycin sulfate
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Capreomycin sulfate |Label Name=Capreomycin image1.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Capreomycin sulfate |Label Name=Capreomycin image2.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Capreomycin sulfate |Label Name=Capreomycin ingredients and appearance.png
}}