Wide complex tachycardia overview: Difference between revisions
| (24 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
Wide complex tachycardia is a cardiac rhythm of more than 100 beats per minute with a [[QRS duration]] of 120 milliseconds or more. It is critical to differentiate whether the wide complex tachycardia is of ventricular origin and is [[ventricular tachycardia]] ([[VT]]), or if it is of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction ([[SVT]] with aberrancy). Rapid differentiation between these two causes of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for [[VT]] versus [[SVT]] with aberrancy. | Wide complex tachycardia is a cardiac rhythm of more than 100 beats per minute with a [[QRS duration]] of 120 milliseconds or more. It is critical to differentiate whether the wide complex tachycardia is of ventricular origin and is [[ventricular tachycardia]] ([[VT]]), or if it is of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction ([[SVT]] with aberrancy). Rapid differentiation between these two causes of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for [[VT]] versus [[SVT]] with aberrancy. '''Wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be due to [[ventricular tachycardia]] even in a hemodynamically stable patient unless proven otherwise,''' and first line treatment with [[verapamil]] should be avoided. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
A wide complex tachycardia is either of ventricular origin ([[ventricular tachycardia]] or [[VT]]), | A wide complex tachycardia is either of ventricular origin ([[ventricular tachycardia]] or [[VT]]), of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction ([[SVT]] with aberrancy), of supraventricular origin and is conducted down a [[bypass tract]] such as in [[Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome]] ([[WPW]]), or is due to a pacemaker malfunction. Approximately 80% of wide complex tachycardias are due to [[ventricular tachycardia]].<ref name="pmid16951728">{{cite journal |author=Lam P, Saba S |title=Approach to the evaluation and management of wide complex tachycardias |journal=[[Indian Pacing and Electrophysiology Journal]] |volume=2 |issue=4 |pages=120–6 |year=2002 |pmid=16951728 |pmc=1557420 |doi= |url=http://www.ipej.org/2/120 |issn= |accessdate=2013-08-04}}</ref> | ||
==Differential Diagnosis of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Distinguishing VT from SVT== | ==Differential Diagnosis of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Distinguishing VT from SVT== | ||
''For more detailed information regarding how to differentiate VT from SVT please view the [[Wide complex tachycardia differential diagnosis|differential diagnosis page]] or click [[Wide complex tachycardia differential diagnosis|here]].'' | |||
Differentiating between [[VT]] and [[SVT]] as the cause of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for [[VT]] versus [[SVT]] with aberrancy. | Differentiating between [[VT]] and [[SVT]] as the cause of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for [[VT]] versus [[SVT]] with aberrancy. | ||
===Ventricular Tachycardia=== | ===Ventricular Tachycardia=== | ||
The diagnosis of [[VT]] is more likely if: | The diagnosis of [[VT]] is more likely if: | ||
:*There is a history of [[myocardial infarction]] or [[structural heart disease]] | :*There is a history of [[myocardial infarction]], [[myocardial ischemia]], [[heart failure]] or [[structural heart disease]] | ||
:*The [[electrical axis]] is -90 to -180 degrees (a “northwest” or “superior” axis) | :*The [[electrical axis]] is -90 to -180 degrees (a “northwest” or “superior” axis) | ||
:*The [[QRS]] is > 140 msec | :*The [[QRS]] is > 140 msec | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
:*There are positive or negative [[QRS]] complexes in all the precordial leads | :*There are positive or negative [[QRS]] complexes in all the precordial leads | ||
:*The morphology of the [[QRS]] complexes resembles that of a previous [[premature ventricular contraction]] ([[PVC]]). | :*The morphology of the [[QRS]] complexes resembles that of a previous [[premature ventricular contraction]] ([[PVC]]). | ||
:*Patients with ventricular tachycardia can often be hemodynamically stable, and stable vital signs do not rule out ventricular tachycardia. This is often a major mistake on the part of clinicians and can lead to inappropriate treatment of [[VT]] as [[SVT]] with poor outcomes. <ref name="pmid4057488">{{cite journal |author=Morady F, Baerman JM, DiCarlo LA, DeBuitleir M, Krol RB, Wahr DW |title=A prevalent misconception regarding wide-complex tachycardias |journal=[[JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association]] |volume=254 |issue=19 |pages=2790–2 |year=1985 |month=November |pmid=4057488 |doi= |url=http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?volume=254&page=2790 |issn= |accessdate=2013-08-04}}</ref> | :*'''''Hemodynamic stability does not reliably differentiate [[VT]] from [[SVT]]'''''. Patients with ventricular tachycardia can often be hemodynamically stable, and stable vital signs do not rule out ventricular tachycardia. This is often a major mistake on the part of clinicians and can lead to inappropriate treatment of [[VT]] as [[SVT]] with poor outcomes. <ref name="pmid4057488">{{cite journal |author=Morady F, Baerman JM, DiCarlo LA, DeBuitleir M, Krol RB, Wahr DW |title=A prevalent misconception regarding wide-complex tachycardias |journal=[[JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association]] |volume=254 |issue=19 |pages=2790–2 |year=1985 |month=November |pmid=4057488 |doi= |url=http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?volume=254&page=2790 |issn= |accessdate=2013-08-04}}</ref> | ||
===Supraventricular Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction=== | ===Supraventricular Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
:*There is intermittently a short [[PR interval]] | :*There is intermittently a short [[PR interval]] | ||
===Paced Rhythms=== | |||
A paced rhythm as a cause of wide complex tachycardia is infrequent. This diagnosis is suggested if | |||
:*A pacemaker is in place and there is a [[LBBB]] pattern with superior left axis deviation, however, depending on the site of pacing this pattern can vary significantly | |||
:*A wide complex tachycardia can be due to an SVT if the pacemaker is tracking sensed atrial activity and is pacing the ventricles rapidly as result | |||
:*[[Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia]] may be present if there is retrograde conduction which triggers atrial activity during ventricular pacing. | |||
:*[[Runaway pacemaker syndrome]] in which the pacemaker fires at a rate of nearly 2000 bpm and captures intermittently | |||
:*[[Sensor induced tachycardia]] in which case the pacemaker fires at a rate of nearly 160-180 bpm in response to electrocautery, noise, vibration, limb movement or other stimuli. | |||
===Other Conditions=== | |||
* [[ECG artifact]] | |||
* [[Ventricular fibrillation]] is usually more chaotic | |||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
The underlying cause of wide complex tachycardia tends to be [[ventricular tachycardia]] ([[VT]]) in | The underlying cause of wide complex tachycardia tends to be [[ventricular tachycardia]] ([[VT]]) in patients > 35 years of age (sensitivity of 92% and a positive predictive value of 85% for VT) and [[supraventricular tachycardia]] ([[SVT]]) with aberrancy in patients <u><</u> 35 years of age (positive predictive value of approximately 70%).<ref name="pmid3800075">{{cite journal |author=Baerman JM, Morady F, DiCarlo LA, de Buitleir M |title=Differentiation of ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia with aberration: value of the clinical history |journal=[[Annals of Emergency Medicine]] |volume=16 |issue=1 |pages=40–3 |year=1987 |month=January |pmid=3800075 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0196-0644(87)80283-4 |issn= |accessdate=2013-08-04}}</ref> | ||
==Risk Factors== | ==Risk Factors== | ||
Risk factors for the ventricular tachycardia as a cause of wide complex tachycardia include a history of prior [[myocardial infarction]], a history of [[congestive heart failure]], and a history of recent [[angina pectoris]]. These three historical features have [[positive predictive values]] for [[VT]] of > 95% in a small study, but sensitivities of 66%, 24%, and 24%, respectively.<ref name="pmid3800075">{{cite journal |author=Baerman JM, Morady F, DiCarlo LA, de Buitleir M |title=Differentiation of ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia with aberration: value of the clinical history |journal=[[Annals of Emergency Medicine]] |volume=16 |issue=1 |pages=40–3 |year=1987 |month=January |pmid=3800075 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0196-0644(87)80283-4 |issn= |accessdate=2013-08-04}}</ref> Wide complex tachycardia will be due to [[VT]] in 98% of cases if there's a history of [[structural heart disease]]. Only 7% of patients with [[SVT]] with aberrancy will have had a prior [[myocardial infarction]] ([[MI]]). | |||
==Electrocardiogram== | ==Electrocardiogram== | ||
Wide complex tachycardia is defined as a heart rate > 100 beats per minute and a [[QRS duration]] > 120 ms. | |||
===Case 1=== | |||
VT with right bundle branch block morphology: [[AV dissociation]] is present, the [[QRS interval]] is greater than 140 ms, and the complexes are all up right in the anterior precordial leads consistent with [[ventricular tachycardia]] as the origin of the rhythm. | |||
[[File:VT with RBBB morphology.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
===Case 2:=== | |||
Shown below is a patient with sinus tachycardia and [[WPW]] which mimics VT: A [[Delta wave]] consistent with pre-excitation is present. | |||
[[File:WPW with sinus tachycardia mimicking VT.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
==Laboratory Studies== | ==Laboratory Studies== | ||
[[Electroyte abnormalities]] such as [[hypokalemia]] (which can be associated with [[ventricular tachycardia]]), [[hypomagnesemia]] (which can lead to [[Torsade de Pointes]] | [[Electroyte abnormalities]] such as [[hypokalemia]] (which can be associated with [[ventricular tachycardia]]), and [[hypomagnesemia]] (which can lead to [[Torsade de Pointes]]) should be ruled out. | ||
==Medical Therapy== | ==Medical Therapy== | ||
The management of wide complex tachycardia should begin by assessing the patient's ABCs (airway, breathing, and circulation). If the patient is unstable and either [[hypotension]], [[altered mental status]], [[chest pain]], [[heart failure]] or [[seizures]] are present, then immediate synchronized [[cardioversion]] should be performed. If the patient is stable, the optimal management depends upon the differentiation of [[ventricular tachycardia]] versus [[supraventricular tachycardia]] with aberrant conduction as a cause of the wide complex tachycardia. Treatment targeted at the underlying cause can then be initiated. | The management of wide complex tachycardia should begin by assessing the patient's ABCs (airway, breathing, and circulation). If the patient is unstable and either [[hypotension]], [[altered mental status]], [[chest pain]], [[heart failure]] or [[seizures]] are present, then immediate synchronized [[cardioversion]] should be performed. If the patient is stable, the optimal management depends upon the differentiation of [[ventricular tachycardia]] versus [[supraventricular tachycardia]] with aberrant conduction as a cause of the wide complex tachycardia. Treatment targeted at the underlying cause can then be initiated. '''A wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be and managed as though it is due to ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise. This is true even in a hemodynamically stable patient until proven otherwise (VT can often be hemodynamically stable). The initial management strategy includes avoiding the use of a long acting [[AV nodal blocking agent]] and drugs that suppress [[left ventricular contractility]] such as [[verapamil]] which can induce [[hypotension]] in a previously stable patient.''' | ||
{{familytree/start |summary=PE diagnosis Algorithm.}} | {{familytree/start |summary=PE diagnosis Algorithm.}} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | | | A01='''Wide complex tachycardia'''<br>[[QRS]] ≥ 120ms}} | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | | | A01='''Wide complex tachycardia'''<br>[[QRS]] ≥ 120ms}} | ||
| Line 76: | Line 102: | ||
{{familytree/end}} | {{familytree/end}} | ||
''Algorithm based on [[ACLS]] guidelines for the management of tachycardia.'' | ''Algorithm based on the 2003 [[ACLS]] guidelines for the management of tachycardia.''<ref name="pmid14563598">{{cite journal| author=Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Camm AJ et al.| title=ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary. a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the European society of cardiology committee for practice guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias) developed in collaboration with NASPE-Heart Rhythm Society. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2003 | volume= 42 | issue= 8 | pages= 1493-531 | pmid=14563598 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14563598 }} </ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 10 August 2013
| Resident Survival Guide |
| File:Physician Extender Algorithms.gif |
|
Wide complex tachycardia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Wide complex tachycardia overview On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Wide complex tachycardia overview |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Wide complex tachycardia overview |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Wide complex tachycardia is a cardiac rhythm of more than 100 beats per minute with a QRS duration of 120 milliseconds or more. It is critical to differentiate whether the wide complex tachycardia is of ventricular origin and is ventricular tachycardia (VT), or if it is of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction (SVT with aberrancy). Rapid differentiation between these two causes of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for VT versus SVT with aberrancy. Wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be due to ventricular tachycardia even in a hemodynamically stable patient unless proven otherwise, and first line treatment with verapamil should be avoided.
Causes
A wide complex tachycardia is either of ventricular origin (ventricular tachycardia or VT), of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction (SVT with aberrancy), of supraventricular origin and is conducted down a bypass tract such as in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW), or is due to a pacemaker malfunction. Approximately 80% of wide complex tachycardias are due to ventricular tachycardia.[1]
Differential Diagnosis of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Distinguishing VT from SVT
For more detailed information regarding how to differentiate VT from SVT please view the differential diagnosis page or click here.
Differentiating between VT and SVT as the cause of wide complex tachycardia is absolutely critical because the treatment options are quite different for VT versus SVT with aberrancy.
Ventricular Tachycardia
The diagnosis of VT is more likely if:
- There is a history of myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, heart failure or structural heart disease
- The electrical axis is -90 to -180 degrees (a “northwest” or “superior” axis)
- The QRS is > 140 msec
- There is AV dissociation
- There are positive or negative QRS complexes in all the precordial leads
- The morphology of the QRS complexes resembles that of a previous premature ventricular contraction (PVC).
- Hemodynamic stability does not reliably differentiate VT from SVT. Patients with ventricular tachycardia can often be hemodynamically stable, and stable vital signs do not rule out ventricular tachycardia. This is often a major mistake on the part of clinicians and can lead to inappropriate treatment of VT as SVT with poor outcomes. [2]
Supraventricular Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction
The diagnosis of atrial fibrillation with aberrant conduction should be considered if
- The heart rate is over 200 beats per minute
- If the rhythm is grossly irregularly irregular
Pre-Excitation
The diagnosis of rapid conduction down a bypass tract due to ventricular pre-excitation such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) should be considered if
- There is intermittent present of a Delta wave
- There is intermittently a short PR interval
Paced Rhythms
A paced rhythm as a cause of wide complex tachycardia is infrequent. This diagnosis is suggested if
- A pacemaker is in place and there is a LBBB pattern with superior left axis deviation, however, depending on the site of pacing this pattern can vary significantly
- A wide complex tachycardia can be due to an SVT if the pacemaker is tracking sensed atrial activity and is pacing the ventricles rapidly as result
- Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia may be present if there is retrograde conduction which triggers atrial activity during ventricular pacing.
- Runaway pacemaker syndrome in which the pacemaker fires at a rate of nearly 2000 bpm and captures intermittently
- Sensor induced tachycardia in which case the pacemaker fires at a rate of nearly 160-180 bpm in response to electrocautery, noise, vibration, limb movement or other stimuli.
Other Conditions
- ECG artifact
- Ventricular fibrillation is usually more chaotic
Epidemiology and Demographics
The underlying cause of wide complex tachycardia tends to be ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients > 35 years of age (sensitivity of 92% and a positive predictive value of 85% for VT) and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) with aberrancy in patients < 35 years of age (positive predictive value of approximately 70%).[3]
Risk Factors
Risk factors for the ventricular tachycardia as a cause of wide complex tachycardia include a history of prior myocardial infarction, a history of congestive heart failure, and a history of recent angina pectoris. These three historical features have positive predictive values for VT of > 95% in a small study, but sensitivities of 66%, 24%, and 24%, respectively.[3] Wide complex tachycardia will be due to VT in 98% of cases if there's a history of structural heart disease. Only 7% of patients with SVT with aberrancy will have had a prior myocardial infarction (MI).
Electrocardiogram
Wide complex tachycardia is defined as a heart rate > 100 beats per minute and a QRS duration > 120 ms.
Case 1
VT with right bundle branch block morphology: AV dissociation is present, the QRS interval is greater than 140 ms, and the complexes are all up right in the anterior precordial leads consistent with ventricular tachycardia as the origin of the rhythm.
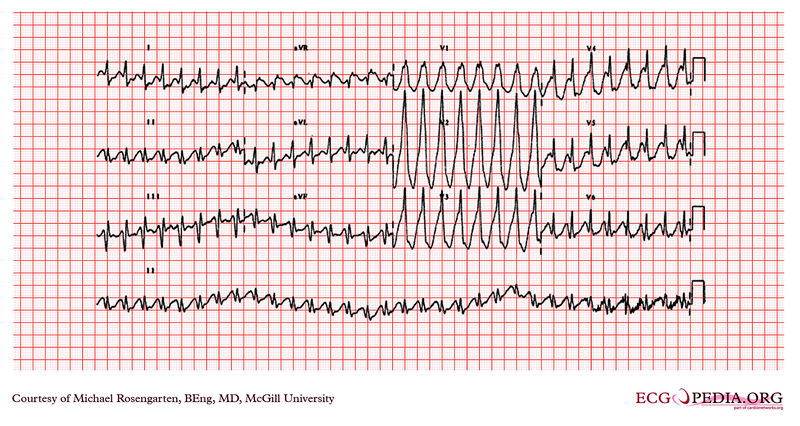
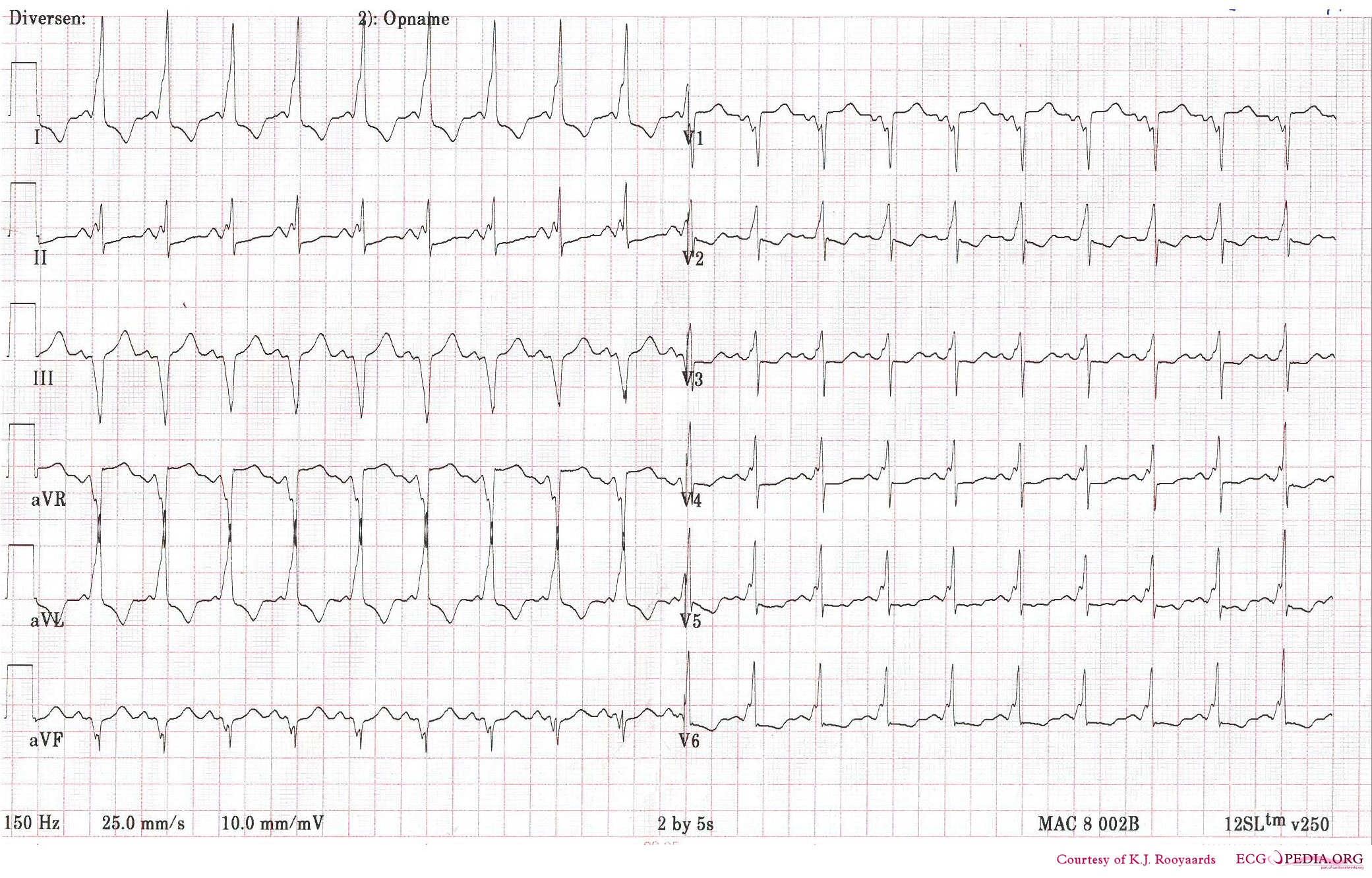
Case 2:
Shown below is a patient with sinus tachycardia and WPW which mimics VT: A Delta wave consistent with pre-excitation is present.
Laboratory Studies
Electroyte abnormalities such as hypokalemia (which can be associated with ventricular tachycardia), and hypomagnesemia (which can lead to Torsade de Pointes) should be ruled out.
Medical Therapy
The management of wide complex tachycardia should begin by assessing the patient's ABCs (airway, breathing, and circulation). If the patient is unstable and either hypotension, altered mental status, chest pain, heart failure or seizures are present, then immediate synchronized cardioversion should be performed. If the patient is stable, the optimal management depends upon the differentiation of ventricular tachycardia versus supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant conduction as a cause of the wide complex tachycardia. Treatment targeted at the underlying cause can then be initiated. A wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be and managed as though it is due to ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise. This is true even in a hemodynamically stable patient until proven otherwise (VT can often be hemodynamically stable). The initial management strategy includes avoiding the use of a long acting AV nodal blocking agent and drugs that suppress left ventricular contractility such as verapamil which can induce hypotension in a previously stable patient.
| Wide complex tachycardia QRS ≥ 120ms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Do the following simultaneously: - Assess and support ABC's as needed - Give oxygen - Monitor ECG, BP, oxymetry - Identify and treat reversible causes (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Is the patient stable? Unstable signs include: - Chest pain - Congestive heart failure - Hypotension - Loss of consciousness - Seizures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Is the rhythm regular? | Immediate synchronized cardioversion -Establish IV access - Give IV sedation if the patient is conscious - Consider expert consultation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regular rhythm | Irregular rhythm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular tachycardia or uncertain rhythm? | Confirmed SVT with aberrancy? | Afib with aberrancy? | Pre-excited Afib (Afib + WPW)? | Recurrent polymorphic VT? | Torsade de pointes? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| - Give amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 min - Repeat amiodarone as needed for a maximal dose of 2.2g/24h - Prepare for elective synchronized cardioversion | - If certain VT is not present, give adenosine 6 mg rapid IV push - If no conversion give 12 mg IV push - May repeat 12 mg dose once | - Consider expert consultation - Control rate e.g diltiazem or beta blockers Use beta blockers with caution in pulmonary diseases or CHF | - Consider expert consultation - Avoid AV nodal blocking agents e.g adenosine, digoxin, diltiazem and verapamil - Consider amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 min | Consider expert consultation | Load with Magnesium 1-2 g over 5-60 min, then infusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Algorithm based on the 2003 ACLS guidelines for the management of tachycardia.[4]
References
- ↑ Lam P, Saba S (2002). "Approach to the evaluation and management of wide complex tachycardias". Indian Pacing and Electrophysiology Journal. 2 (4): 120–6. PMC 1557420. PMID 16951728. Retrieved 2013-08-04.
- ↑ Morady F, Baerman JM, DiCarlo LA, DeBuitleir M, Krol RB, Wahr DW (1985). "A prevalent misconception regarding wide-complex tachycardias". JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association. 254 (19): 2790–2. PMID 4057488. Retrieved 2013-08-04. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 3.0 3.1 Baerman JM, Morady F, DiCarlo LA, de Buitleir M (1987). "Differentiation of ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia with aberration: value of the clinical history". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 16 (1): 40–3. PMID 3800075. Retrieved 2013-08-04. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Camm AJ; et al. (2003). "ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary. a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the European society of cardiology committee for practice guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias) developed in collaboration with NASPE-Heart Rhythm Society". J Am Coll Cardiol. 42 (8): 1493–531. PMID 14563598.