Tillaux fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 247: | Line 247: | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
'''''[[Salter-Harris classification]]''''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 253: | Line 253: | ||
!Descrpstion | !Descrpstion | ||
!Image | !Image | ||
|- | |- | ||
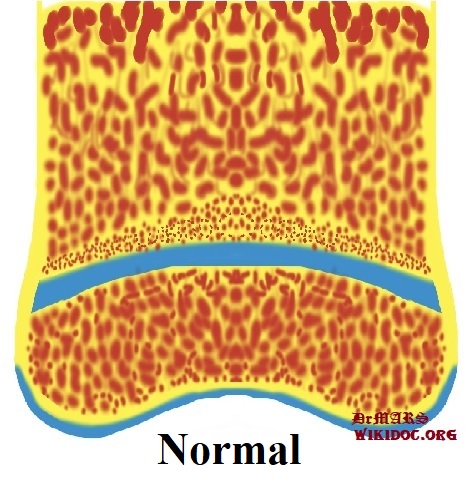
|Normal | |Normal | ||
| | | | ||
|[[File:Normal Bone.jpg|alt=courtesy of DrMars, <https://www.wikidoc.org>|thumb|'''''Normal Bone''''']] | |[[File:Normal Bone.jpg|alt=courtesy of DrMars, <https://www.wikidoc.org>|thumb|'''''Normal Bone''''']] | ||
|- | |- | ||
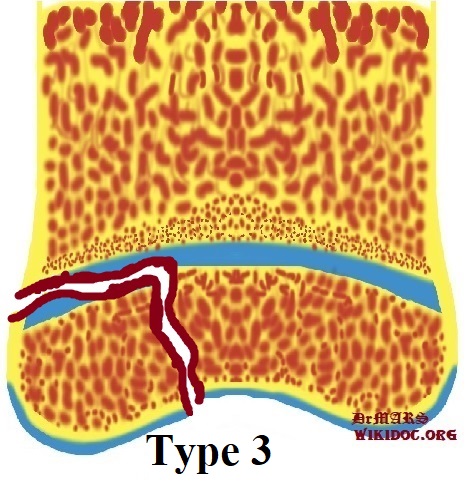
|Type | |'''Type III''' | ||
| | | | ||
* | * '''Frequency: 7-10%''' | ||
* '''cannot occur if the growth plate is fused cit''' | |||
* '''poorer prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interrupted''' | |||
* '''Mechanism: Fractured plane involved the growth plate through the epiphysis''' | |||
* '''Origin: through growth plate and epiphysis, sparing the metaphysis''' | |||
* poorer prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interrupted | |||
* Mechanism: Fractured plane involved the growth plate through the epiphysis | |||
* Origin: through growth plate and epiphysis, sparing the metaphysis | |||
|[[File:Type 3 Salter-Harris classification.jpg|alt=courtesy of DrMars, <https://www.wikidoc.org>|thumb|'''''Type 3 Salter-Harris classification''''']] | |[[File:Type 3 Salter-Harris classification.jpg|alt=courtesy of DrMars, <https://www.wikidoc.org>|thumb|'''''Type 3 Salter-Harris classification''''']] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Screening== | ==Screening== | ||
| Line 406: | Line 339: | ||
In the physical exam the orthopedic surgeon should check the vascular status and amount of swelling in the ankle. In MULTI-trauma patients or in comatose or obtunded patients a tense compartment with neurological signs or stretch pain should be considered as the [[compartment syndrome]], and the compartment pressures should be measured and monitored. Normally the pain and soft-tissue swelling are found at the injury site. This injury should be confirmed using a radiographic evaluations. | In the physical exam the orthopedic surgeon should check the vascular status and amount of swelling in the ankle. In MULTI-trauma patients or in comatose or obtunded patients a tense compartment with neurological signs or stretch pain should be considered as the [[compartment syndrome]], and the compartment pressures should be measured and monitored. Normally the pain and soft-tissue swelling are found at the injury site. This injury should be confirmed using a radiographic evaluations. | ||
==Physical Examination | ==Physical Examination== | ||
The related signs and symptoms include: | The related signs and symptoms include: | ||
* Edema of the ankle | * Edema of the ankle | ||
| Line 499: | Line 432: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Other Imaging Findings | ==Other Imaging Findings== | ||
There are no other imaging findings associated with [[Tillaux fracture]] | There are no other imaging findings associated with [[Tillaux fracture]] | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 18 May 2019

| Tillaux fracture | |
| ICD-10 | S42.2-S42.4 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 812 |
| eMedicine | emerg/199 orthoped/271 orthoped/199 |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Tillaux fracture |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Tillaux fracture Most cited articles on Tillaux fracture |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Tillaux fracture |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Tillaux fracture at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Tillaux fracture Clinical Trials on Tillaux fracture at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Tillaux fracture NICE Guidance on Tillaux fracture
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Tillaux fracture Discussion groups on Tillaux fracture Patient Handouts on Tillaux fracture Directions to Hospitals Treating Tillaux fracture Risk calculators and risk factors for Tillaux fracture
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Tillaux fracture |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohammadmain Rezazadehsaatlou[2].
Synonyms and Keywords: Tillaux fracture, Tillaux-Chaput avulsion fracture
Overview
Tillaux fracture is a Salter-Harris type III fracture of the anterolateral distal tibial epiphysis that is commonly seen in adolescents, with different amount of displacements.
Historical Perspective
In 1822, Sir Astley Cooper described a fracture of the lateral aspect of the distal tibia in the adult population.
In 1892, Paul Jules Tillaux, a French surgeon and anatomist, partially described an avulsion-type fracture of the lateral tibia.
In 1944, Kleiger and Mankin described an isolated-type fracture of the lateral side of the distal tibial in adolescents. Nowadays we known this fracture as is a Salter-Harris type III epiphyseal injury.
Causes
The Tillaux fractures most often result from high-energy trauma like: a car or motorcycle accident, fall from height, or skiing accident due to the rotational or axial-loading forces to the tibia bone. Meanwhile, there are other causes responsible for this type of fracture such as:
- Pressure during car accidents
- Twisted ankle side to side
- Rotated ankle side to side
- Rolling ankle in or out
- Hyper-flextion
- Hyper-Extention
- Tripping
- Falling from a height
- Jumping from a height
As a person age, two factors cause higher risk of fractures:
- Weaker bones
- Greater risk of falling
Stress fractures as a common causes of fractures can be found due to the repeated stresses and strains. Importantly children having more physically active lifestyles than adults, are also prone to fractures. People with any underlying diseases such as osteoporosis, infection, or a tumor affecting their bones having a higher risk of fractures. As mentioned in previous chapters, this type of fracture is known as a pathological fracture. Stress fractures, which result from repeated stresses and strains, commonly found among professional sports people, are also common causes of fractures.
Life-threatening Causes
- There are no life-threatening causes of Tillaux fracture, however complications resulting from Tillaux fracture is common.
Common Causes
Common causes of Tillaux fracture may include:
Less Common Causes
Less common causes of Tillaux fracture include conditions that predisposes to fracture:
Causes by Organ System
| Cardiovascular | No underlying causes |
| Chemical/Poisoning | No underlying causes |
| Dental | No underlying causes |
| Dermatologic | No underlying causes |
| Drug Side Effect | No underlying causes |
| Ear Nose Throat | No underlying causes |
| Endocrine | No underlying causes |
| Environmental | No underlying causes |
| Gastroenterologic | No underlying causes |
| Genetic | No underlying causes |
| Hematologic | No underlying causes |
| Iatrogenic | No underlying causes |
| Infectious Disease | No underlying causes |
| Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic | Osteoporosis and osteopenia. |
| Neurologic | No underlying causes |
| Nutritional/Metabolic | Osteoporosis and osteopenia. |
| Obstetric/Gynecologic | No underlying causes |
| Oncologic | No underlying causes |
| Ophthalmologic | No underlying causes |
| Overdose/Toxicity | No underlying causes |
| Psychiatric | No underlying causes |
| Pulmonary | No underlying causes |
| Renal/Electrolyte | No underlying causes |
| Rheumatology/Immunology/Allergy | No underlying causes |
| Sexual | No underlying causes |
| Trauma | Falling of car accident to on side of Ankle . |
| Urologic | No underlying causes |
| Miscellaneous | No underlying causes |
Causes in Alphabetical Order
List the causes of the disease in alphabetical order:
Pathophysiology
The main etiology of the Tillaux fracture is thought to excessive inversion stress to the ankle joint following a low-energy trauma.
Mechanism
In 80% of ankle fractures the foot is in supination position while, in 20% of fractures the foot is in pronation position. Meanwhlie the Tillaux fracture is caused by an abduction-external rotation mechanism; consequently, the anterior tibiofibular ligament avulses the anterolateral of the distal tibial epiphysis The form and severity of this fracture depends on the position of the ankle joint at the moment of the trauma. The ankle joint is flexible but the medial side of the ankle joint is rigid because the medial malleolus is attached to the tibia and also the medial collateral ligaments are very strong. Also, lateral wall of the ankle include: the fibula, syndesmosis and lateral collateral ligaments play important rolls in this flexibility. This lateral wall of the ankle allows the talus to move in lateral and dorsal sides easily. The fibula has no weight-bearing roll but it provide a flexible lateral support. The syndesmosis is formed by the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments which is the fibrous connection between the fibula and tibia.
Pathophysiology
The Tillaux fracture occurs following a low-energy trauma and mostly is associated with sliding injuries such as skateboard and baseball.
A lateral rotation force of the foot in neutral, supination, or a medial rotation on the fixed foot consequently cause an avulsion injury to the lateral epiphysis.
Meanwhile, the risk factor for insufficiency fractures is chronic metabolic disease such as steoporosis, osteopenia, eating-disordered behavior, higher age, prolonged corticosteroid usage, female gender, lower BMI, history of a recent falling, and prior fracture.
- The pattern of bone fracture and severity of injury depends on variety of factors such as:
- Patients age
- Patients Weight
- Patients past medical history specifically any bone diseases affecting the quality of bone (such as osteoporosis, malignancies)
- Energy of trauma
- Bone quality
- Position of the specific organ during the trauma
- The below-mentioned processes cause decreased bone mass density:
- Autophagy is the mechanism through which osteocytes evade oxidative stress.
- The capability of autophagy in cells decreases as they age, a major factor of aging.
- As osteocytes grow, viability of cells decrease thereby decreasing the bone mass density.
Differentiating Tillaux fracture from other Diseases
In the orthopedic medicine its important to know that the Tillaux fracture should be evaluated using radiography for both confirming diagnosis and also for evaluating the surrounding tissues.
- Acute compartment syndrome of ankle joint
- Ankle Dislocation
- Soft tissue Injury around the ankle ,
- Deep Venous thrombosis
- Thrombophlebitis
- Foot Fracture
- Gout
- Pseudogout
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Tibia Fracture
- Fibula Fracture
- bimalleolar fracture
- trimalleolar fracture
- triplane fracture
- Tillaux fracture
- Bosworth fracture
- Wagstaffe-Le Forte fracture
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: in cases with repeated Tillaux fractures
Epidemiology and Demographics
The Tillaux fracture accounts for around 1-10% of all fractures and 5-10 % of tibial fractures. It is more common in adults aged 30s to 40s due to the fall from height or a motor vehicle crash which is more common in this age group.
Risk Factors
There are different risk factors that predispose patient for the Tillaux fracture that include:
- High-risk contact sports
- Higher age (elderly adults are higher prone to such fractures)
- Reduced bone density (osteoporosis)
- Direct blow
- Road / traffic accidents
- Falling
- Direct trauma to the ankle
- Taking part in any rough or high-impact sport
- Street fights, gunshot wounds, and domestic violence, may also cause the Tillaux fracture
- Road traffic accidents.
Classification
Screening
Osteoporosis is an important risk factor for human affecting human bone especially in men with the age of older than 50 years old and postmenopausal and women.
Based on the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) there are three groups of patients need to be screened for the osteoporosis:
- · Men with no history of osteoporosis
- · Women with the age of 65≤ year old, with no previous history of pathological fracture due to the osteoporosis
- · Women with the age of <65 years, with 10-year fracture risk of not less than a 65-year-old white woman (who has not any other risk factor)
Accordingly women older than age of 50 are the main target for the osteoporosis screening. There is no specific recommendation to screen men for the osteoporosis.[1]
The USPSTF recommendations from 2002 included:
Meanwhile, there are two major modalities for the osteoporosis screening:
- · Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) of the hip and lumbar spine bones
- · Quantitative ultrasonography of the calcaneus
*It should be noted of the two above mentioned modalities for screening the ultrasonograhy is preferred to the DXA due to its lower cost, lower ionizing radiation, more availability.
After the primary evaluation of the osteoporosis, the further evaluation are required in some cases such as:
· Women with normal bone density or mild osteopenia: T-score of greater than −1.50 – should have screening for 15 years.
· Women with moderate osteopenia: T-score of −1.50 to −1.99 – should have screening for 5 years.
· Women with advanced osteopenia: T-score of −2.00 to −2.49 - should have screening for 1 year.
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Natural History
In cases with untreated Tillaux fracture the malunion and deformity of arm can be occurred.
Complications
The overall complication rate in the treatment of Tillaux fracture were found in around 40% of cases:
- Neurovascular compromise: such as Ulna nerve damage
- Compartment syndrome
- Chronic disability of the DRUJ
- Physeal Injury
- Malunion of the radius
- Nonunion
- Infection
- Refracture following plate removal
- Neural injury
- Instability of the DRUJ
- Loss of Motion (Stiffness)
- Posttraumatic Arthritis
- Heterotopic Ossification
Prognosis
Successful treatment of Tillaux fracture depends on the on-time interventions such as: accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment and referral. A low incidence of arthrosis was reported among cases with Tillaux fracture after having either cast treatment for undisplaced fractures or operative intervention. As it was mentioend before the Tillaux fracture is more common in adults than children so growth-plate damage in rare cases could cause deformity in these cases.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a Tillaux fracture should be confirmed using a radiographic examination.
History and Symptoms
The related signs and symptoms include:
- Deformity
- Skin lacerations
- Open fractures
- Erythema
- Edema
- Stiffness
- Decreased range of motion
- Tenderness
- Loss of function of the ankle
- Difficulties in detection of pulses
- Nerve damage
- Varus deformity
- Tibiotalar slant
- Rotational deformity (rare)
- Leg-length inequality (extremely rare)
- Avascular necrosis of the fragment
- Arthrofibrosis following arthroscopic procedures
In the physical exam the orthopedic surgeon should check the vascular status and amount of swelling in the ankle. In MULTI-trauma patients or in comatose or obtunded patients a tense compartment with neurological signs or stretch pain should be considered as the compartment syndrome, and the compartment pressures should be measured and monitored. Normally the pain and soft-tissue swelling are found at the injury site. This injury should be confirmed using a radiographic evaluations.
Physical Examination
The related signs and symptoms include:
- Edema of the ankle
- Most of the time the edema will be a non-pitting edema
- Depends on the edema extent, it may even lead to compartment syndrome in the anterior and internal compartment of the ankle
- Bruising
- As a manifestation of internal injury to the local vessels by trauma or fractures bone
- Decrease in range of motion of the ankle
- Movement of the ankle will be painful if possible at all
- Tenderness
- Deformity
- Fractured bone deformity may be touchable in the internal side of the ankle if the fracture is displaced
In the physical exam the orthopedic surgeon should check the vascular status and amount of swelling in the ankle. In polytrauma patients or in comatose or obtunded patients a tense compartment with neurological signs or stretch pain should be considered as the compartment syndrome, and the compartment pressures should be measured and monitored.
Physical examination of patients with Tillaux fracture is usually remarkable for swelling, tenderness, bruises, ecchymosis, deformity and restricted range of motion of the ankle.
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with Tillaux fracture usually appears normal unless the patients had a high energy trauma causing the open wound fracture.
Vital Signs
- Weak pulse may be seen when associated with polytrauma.
- Low blood pressure with normal pulse pressure may be present due to compound fracture with blood loss.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with Tillaux fracture includes:
HEENT
- HEENT examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with Tillaux fracture is usually normal
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal
Back
- Back examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with Tillaux fracture usually normal
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with Tillaux fracture is usually normal
- However, some patients may develop neuropraxia of the branch of the Ulnar nerve resulting in decreased sensation of thumb, index and middle finger.
Laboratory Findings
There is a limited laboratory tests useful in the diagnosis of bone fractures such as the Tillaux fracture. Meanwhile, aged men and women may have some abnormalities in their laboratory findings suggestive of osteoporosis.
Laboratory tests for the diagnosis of osteoporosis are:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Serum total calcium level
- Serum Ionized calcium level
- Serum phosphate level
- Serum alkaline phosphatase level
- Serum 25-(OH)-vitamin D level
X Ray
The orthopedic surgeon should consider to have at least two radiographic projections (ie, anteroposterior [AP] and lateral) of the ankle. These show the fracture, the extent of displacement, and the extent of comminution. The orthopedic surgeon should pay serious attention toward finding any foreign bodies in open fractures and gunshot injuries. Also imperative is to include the elbow and wrist joint in the radiographs of Ankle fracture to ensure that the distal radioulnar joint injuries are not missed.
-
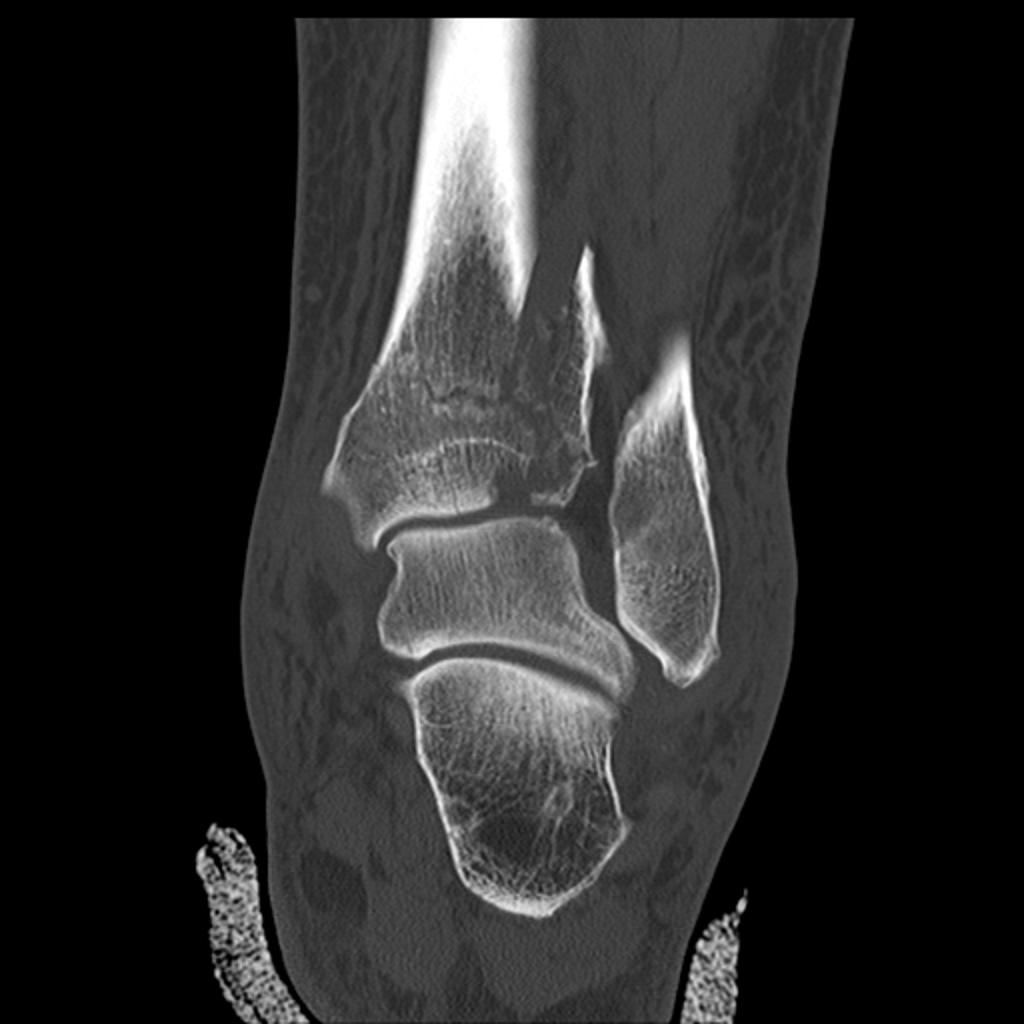
There is a comminuted distal tibial fracture extending into the tibial plafond, representing a Pilon fracture. There are also associated fractures of the talar dome and tip of the lateral malleolus.
CT
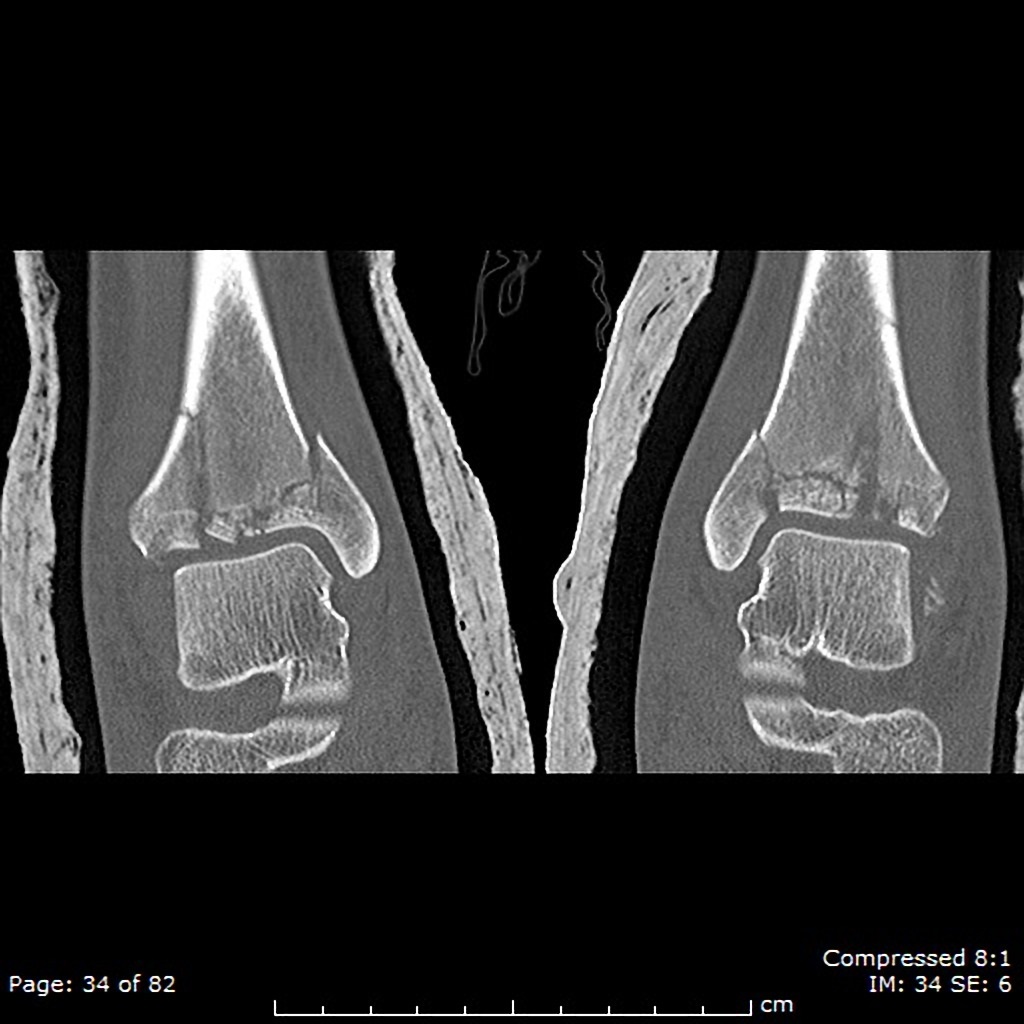
- CT-scan in the case of the Tillaux fractureis the best modality if you can not have an exclusive diagnosis by X-ray itself can not be made.
-
Severely comminuted tibial plafond fractures that extend into the metadiaphyseal regions which are bilateral and nearly symmetric. On the right, there is approximately 3mm of articular offest anteriorly, but otherwise the articular fragments are minimally displaced. There is 1mm medial offset of the medial malleolar fracture fragment on the left and 2mm on the right. There are several small sub-millimeter intraarticular fragments bilaterally.
-
There is a comminuted distal tibial fracture extending into the tibial plafond, representing a Pilon fracture. There are also associated fractures of the talar dome and tip of the lateral malleolus.
MRI
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an expensive technique that should not be used routinely.
- MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool to assess the abnormalities of the bone, ligaments and soft tissues associated with the Tillaux fracture, but it is known as a limited utility in radioulnar injuries and is not indicated in uncomplicated foankle earm fractures.
- Meanwhile, the MRI can be useful in in following mentioned evaluations:
- Evaluation of occult fractures
- Evaluation of the post-traumatic or avascular necrosis of carpal bones
- Evaluation of tendons
- Evaluation of nerve
- Evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome
-
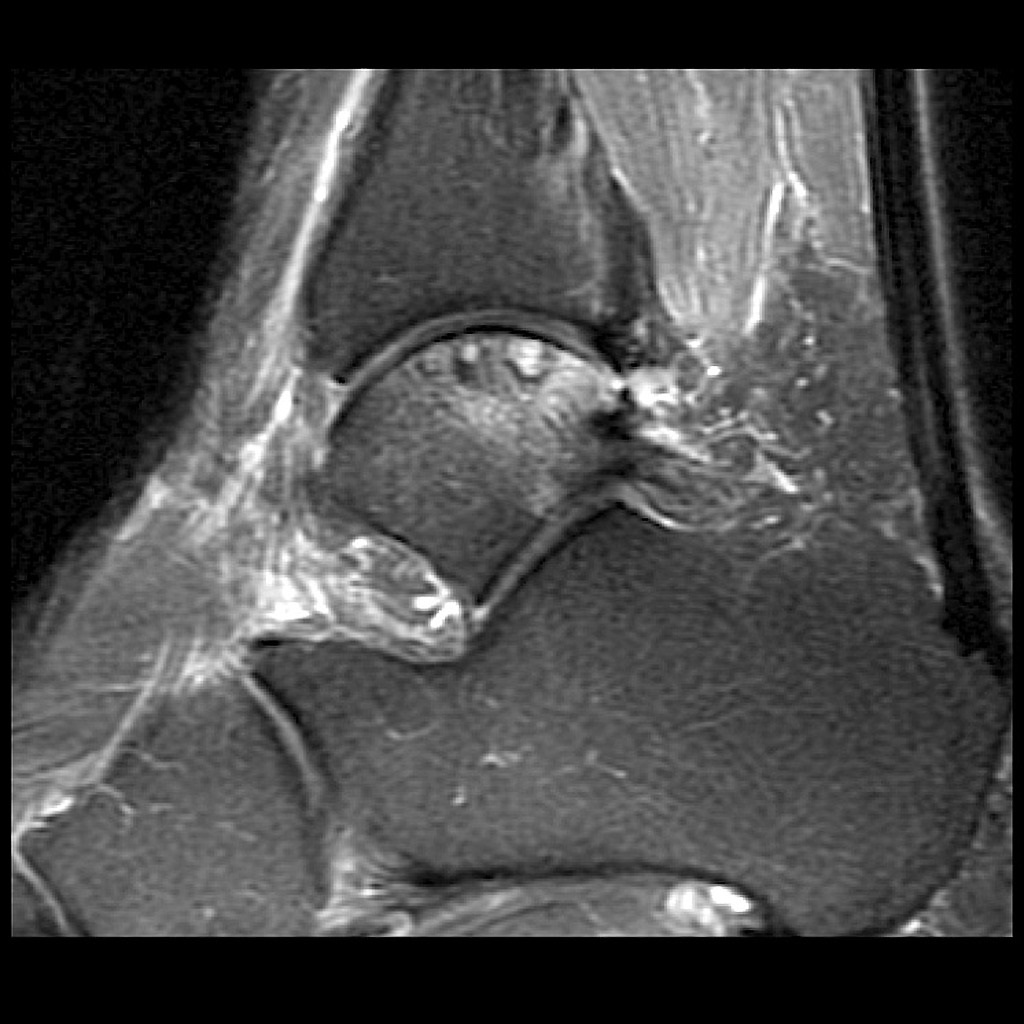
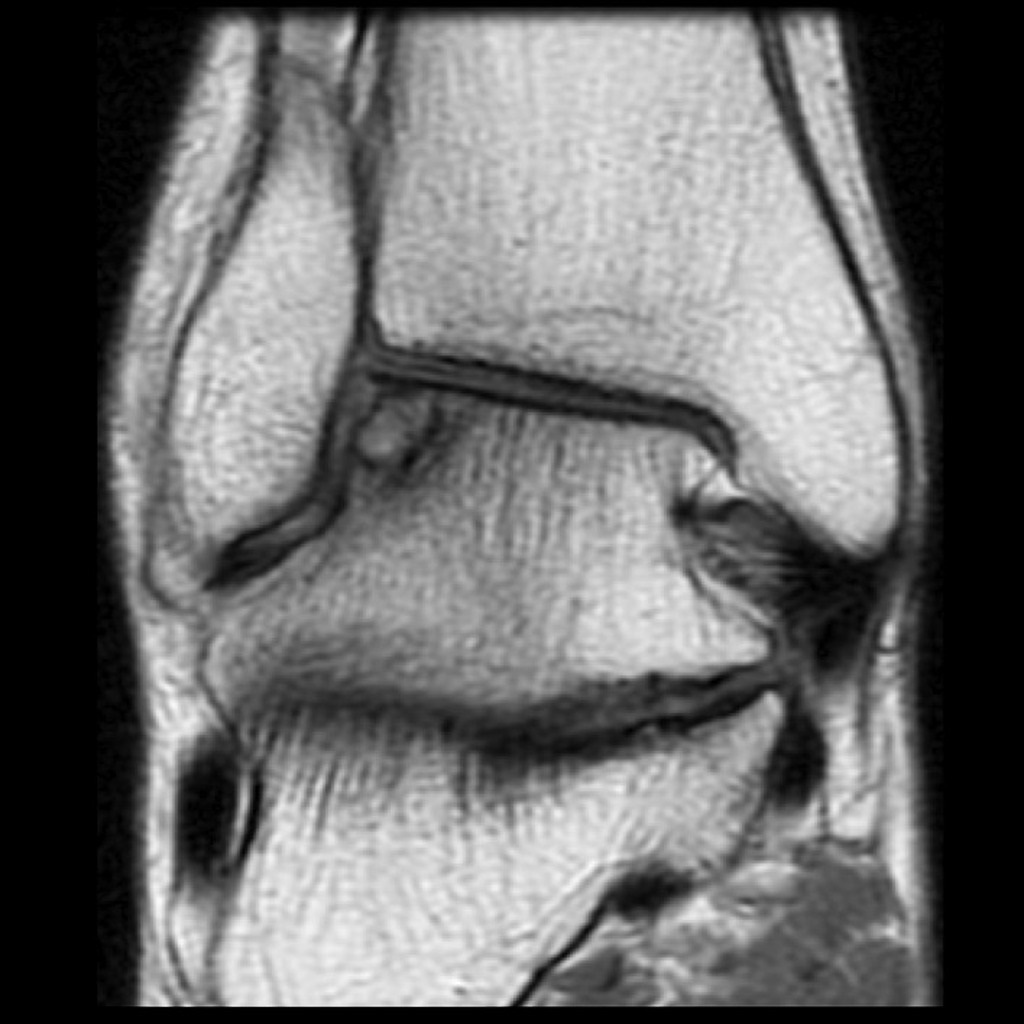
PD Subchondral fracture of the talar dome. Note the intact overlying cartilage.
-
T2 fat sat Subchondral fracture of the talar dome. Note the intact overlying cartilage.
Other Imaging Findings
There are no other imaging findings associated with Tillaux fracture
Other Diagnostic Studies[1]
There are no other Diagnostic studies associated with Tillaux fracture
Treatment
Immediate stabilization of patients is the first step. Then the radial fracture and the DRUJ stabilization is recommended in these cases. Open ankle fractures considered as a surgical emergency. Tillaux fracture occurs in younger patients who are skeletally immature; the normally they treated using a closed reduction and casting. Since closed reduction and cast application have led to unsatisfactory results. Then, Almost always the open reduction are necessary for the Tillaux fracture. There are controversies regarding the indications for intramedullary nailing of ankle fractures.
Non-Operative Treatment
- The first step in managing a patient with a fracture is to stabilize the patient if he/she is unstable due to blood loss, etc by giving them intravenous fluids and giving them some painkillers if the pain is severe.
- In children, the usual plan is to attempt closed reduction followed by cast immobilization. In adults, treatment with immobilization in a molded long arm cast can be used in those rare occasions of a non-displaced fracture of the ankle joint. If the fracture shifts in position, it may require surgery to put the bones back together.
- Rigid immobilization is suggested in preference to removable splints in nonoperative treatment for the management of the Tillaux fracture
- For all patients with Tillaux fracture, a post-reduction true lateral radiograph is suggested.
- Operative fixation is suggested in preference to cast fixation for fractures with post-reduction radial shortening greater than 3 mm, dorsal tilt greater than 10º, or intra-articular displacement or step-off greater than 2 mm.
- Patients probably do not need to begin early wrist motion routinely after stable fracture fixation.
- Adjuvant treatment of Tillaux fracture with vitamin C is suggested for the prevention of disproportionate pain
- Lateral epicondylar fractures should be immobilized for 7 days with patients elbow flexed at 90º, with the supinated ankle, and the extended wrist for relaxing the extensor muscles.
Complications of Non-surgical therapy
Failure of non-surgical therapy is common:
- Re-displacement to its original position even in a cast
- Stiffness
- Post traumatic osteoarthritis leading to wrist pain and loss of function
- Other risks specific to cast treatment include:
- Compression of the swollen arm causing compartment syndrome
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy is a serious complication
- Stiffness is universal following a prolonged period of immobilization and swelling
Surgery
Returning to the normal physical activity after Tillaux fracturecan take weeks to months of therapy under supervision an orthopedist. Meanwhile, a physiotherapy can be helpful for patient to achieve the normal wrist and elbow function caused by the immobilization. All adult Tillaux fracture should be considered to be treated with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
External fixation: For severe open fractures Open reduction and internal fixation: For distal Tillaux fracture which depending on each patients condition the following may be needed:
Nerve placement Bone grafting Osteotomy Arthrodesis
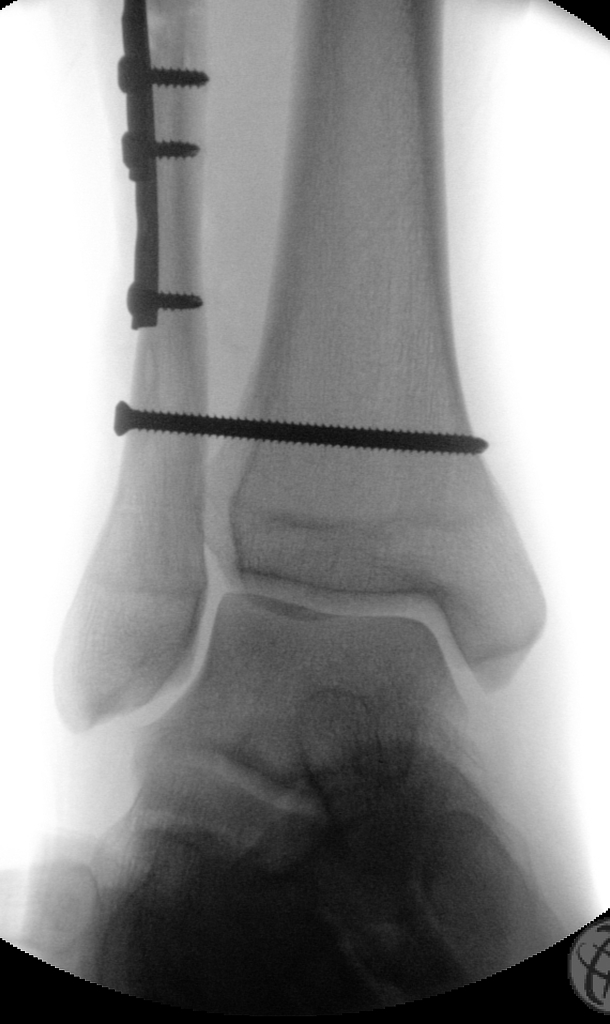
-
Screw-plate stabilization of the fibular fracture and trans-syndesmotic screw stabilizing the ankle mortise.
Operation
- There are a variety of methods and implants useful to stabilize the Tillaux fracturee, ranging from closed reduction and percutaneous pin fixation to the use of intra-medullary devices.
- However, the most common fixation methods to treat complex Tillaux fracture include external fixation, and open reduction and internal fixation.
External Fixation With or Without Percutaneous Pin Fixation
- Ankle spanning external fixation employs ligamentotaxis to restore and maintain length, alignment, and rotation of bone.
- Reduction is typically obtained through closed or minimally open methods and preserves the fracture biology.
- The addition of percutaneous pins enhances the ability to reduce and stabilize fracture fragments.
Complications of External Fixation
- Pin tract infection
- Injury to the Superficial branch of the nerve
- Complex regional pain syndrome
Open reduction and internal fixation with plates and screws
- This is the most common type of surgical repair for Tillaux fracture
- During this type of procedure, the bone fragments are first repositioned (reduced) into their normal alignment.
- The bones held together with special screws and metal plates attached to the outer surface of the bone.
Complications of open reduction and internal fixation with plates and screws =
- Infection
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels
- Synostosis
- Nonunion
Pain Management
Pain after an injury or surgery is a natural part of the healing process.
Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery or an injury such as:
- opioids
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- local anesthetics
Be aware that although opioids help relieve pain after surgery or an injury, they are a narcotic and can be addictive. It is important to use opioids only as directed by doctor.
Interventions
The following options can be helpful for patients to rehabilitate after their fracture :
- Joints mobilization
- compression bandage
- Soft tissue massage
- Exercises and Activity modification
Postoperative Rehabilitation
- Complex Tillaux fracture warrant individualized immobilization and rehabilitation strategies.
- Because most multifragmentary Tillaux fracture are the result of high-energy injuries, a prolonged period of wrist immobilization and soft-tissue rest may be beneficial and has not been shown to affect clinical outcomes.
- The ankle is typically immobilized for 6 weeks post-operatively in a splint with Full weight bearing commences at approximately 3 months post-operatively after consolidation of the fracture is noted on radiographs.
- The presence of varying degrees of ankle stiffness is inevitable and may result from poor pain control, lack of effort in controlled mobilization, edema, concomitant ipsilateral lower extremity fractures, or peripheral nerve injuries. Early stretching and mobilization of the intrinsic and extrinsic tendons of the hand is important to prevent finger stiffness. Edema control can be initiated with compression gloves, digital massage, and active and passive ROM of the ankle. A home exercise program or outpatient occupational therapy is started immediately post-operatively to maintain full range of motion of the ankle and limit the development of intrinsic muscle tightnes
Primary Prevention
There are various preventive options to reduce the incidence of the Tillaux fracture
- Using ankle guards during practicing sports (skating, biking)
- Using ankle guards during driving motorbikes
- Avoid falls in elderly individuals
- Prevention and/or treatment of osteoporosis
- Healthy diet
Secondary Prevention
It should be noted that the Post-menopausal women specially older than the age of 65 are at the higher risk of osteoporosis consequently these type of patients at greater risk for the pathological fractures .
So the Calcium and vitamin D supplementation play important role in increasing the bone mineral density (BMD) consequently decrease the risk of fracture in these type of patients. Also, avoiding excessive alcohol and quitting smoking play important role in this regard.
Detecting osteoporosis
- DEXA(dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) scan
- Serum calcium and vitamin D levels
- Ultrasonography of the calcaneus
Pharmacological therapy
- The primary goal for the treatment of osteoporosis is to reduce longtime fracture risk in patients. Increasing bone mineral density (BMD) in response to the treatment is far less important than improvement of clinical aspects of osteoporosis, i.e., osteoporoticfracture. Therefore, most of the drugs efficacy is measured by the extent they improve the fracture risk instead of increasing BMD.
- During the treatment, if a single fracture happens, it does not necessarily indicate treatment failure or the need to be started on an alternative treatment or patient referral to a specialist.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation have been found to be effective in reducing the long term fracture risk, significantly. In order to suggest the people to use vitamin D and calcium supplements, the physician needs to make sure that patient is not able to obtain the nutrients through the daily intake. The available supplemental ions of calcium include calcium carbonate, calcium citrate, and vitamin D3 in various dosage forms.
Life style modifications
- Exercise: Exercise promotes the mineralization of bone and bone accumulation particularly during growth. High impact exercise, in particular, has been shown to prevent the development of osteoporosis. However, it can have a negative effect on bone mineralization in cases of poor nutrition, such as anorexia nervosa and celiac disease.
- Nutrition: A diet high in calcium and vitamin D prevents bone loss. Patients at risk for osteoporosis, such as persons with chronic steroid use are generally treated with vitamin D and calcium supplementation. In renal disease, more active forms of vitamin D, such as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or calcitriol are used; as the kidney cannot adequately generate calcitriol from calcidiol (25-hydroxycholecalciferol), which is the storage form of vitamin D.
- By quitting smoking, osteoporosis as well as other diseases can be prevented.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol intake or drinking only in moderation.
See also
- Bosworth fracture
- pilon fracture
- Wagstaffe-Le Forte fracture
- Maisonneuve Fracture
References
- ↑ Klaue K, Cronier P (September 2015). "[Pilon fractures]". Unfallchirurg (in German). 118 (9): 795–801, quiz 802–3. doi:10.1007/s00113-015-0054-3. PMID 26293486.