Rifampin (oral)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Rifampin (oral) is a {{{drugClass}}} that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of {{{indication}}}. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- In the treatment of both tuberculosis and the meningococcal carrier state, the small number of resistant cells present within large populations of susceptible cells can rapidly become the predominant type. Bacteriologic cultures should be obtained before the start of therapy to confirm the susceptibility of the organism to rifampin and they should be repeated throughout therapy to monitor the response to treatment. Since resistance can emerge rapidly, susceptibility tests should be performed in the event of persistent positive cultures during the course of treatment. If test results show resistance to rifampin and the patient is not responding to therapy, the drug regimen should be modified.
Tuberculosis Rifampin is indicated in the treatment of all forms of tuberculosis.
A three-drug regimen consisting of rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide [e.g., RIFATER®]5 is recommended in the initial phase of short-course therapy which is usually continued for 2 months. The Advisory Council for the Elimination of Tuberculosis, the American Thoracic Society, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that either streptomycin or ethambutol be added as a fourth drug in a regimen containing isoniazid (INH), rifampin, and pyrazinamide for initial treatment of tuberculosis unless the likelihood of INH resistance is very low. The need for a fourth drug should be reassessed when the results of susceptibility testing are known. If community rates of INH resistance are currently less than 4%, an initial treatment regimen with less than four drugs may be considered.
Following the initial phase, treatment should be continued with rifampin and isoniazid [e.g., RIFAMATE®]6 for at least 4 months. Treatment should be continued for longer if the patient is still sputum or culture positive, if resistant organisms are present, or if the patient is HIV positive.
Meningococcal Carriers Rifampin is indicated for the treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis to eliminate meningococci from the nasopharynx. Rifampin is not indicated for the treatment of meningococcal infection because of the possibility of the rapid emergence of resistant organisms. (See WARNINGS).
Rifampin should not be used indiscriminately, and therefore, diagnostic laboratory procedures, including serotyping and susceptibility testing, should be performed for establishment of the carrier state and the correct treatment. So that the usefulness of rifampin in the treatment of asymptomatic meningococcal carriers is preserved, the drug should be used only when the risk of meningococcal disease is high.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of rifampin and other antibacterial drugs, rifampin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Rifampin is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to rifampin or any of the components, or to any of the rifamycins.
- Rifampin is contraindicated in patients who are also receiving ritonavir-boosted saquinavir due to an increased risk of severe hepatocellular toxicity.
- Rifampin is contraindicated in patients who are also receiving atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, saquinavir, or tipranavir due to the potential of rifampin to substantially decrease plasma concentrations of these antiviral drugs, which may result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
Warnings
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Warnings' in the drug label.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Gastrointestinal
Heartburn, epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, flatulence, cramps, and diarrhea have been noted in some patients. Although Clostridium difficile has been shown in vitro to be sensitive to rifampin, pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with the use of rifampin (and other broad spectrum antibiotics). Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who develop diarrhea in association with antibiotic use.
Hepatic
Transient abnormalities in liver function tests (e.g., elevations in serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, serum transaminases) have been observed. Rarely, hepatitis or a shock-like syndrome with hepatic involvement and abnormal liver function tests has been reported.
Hematologic
Thrombocytopenia has occurred primarily with high dose intermittent therapy, but has also been noted after resumption of interrupted treatment. It rarely occurs during well supervised daily therapy. This effect is reversible if the drug is discontinued as soon as purpura occurs. Cerebral hemorrhage and fatalities have been reported when rifampin administration has been continued or resumed after the appearance of purpura.
Rare reports of disseminated intravascular coagulation have been observed.
Leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, and decreased hemoglobin have been observed.
Agranulocytosis has been reported very rarely.
Central Nervous System
Headache, fever, drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, dizziness, inability to concentrate, mental confusion, behavioral changes, muscular weakness, pains in extremities, and generalized numbness have been observed.
Psychoses have been rarely reported.
Rare reports of myopathy have also been observed.
Ocular
Visual disturbances have been observed.
Endocrine
Menstrual disturbances have been observed.
Rare reports of adrenal insufficiency in patients with compromised adrenal function have been observed.
Renal
Elevations in BUN and serum uric acid have been reported. Rarely, hemolysis, hemoglobinuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, acute tubular necrosis, renal insufficiency, and acute renal failure have been noted. These are generally considered to be hypersensitivity reactions. They usually occur during intermittent therapy or when treatment is resumed following intentional or accidental interruption of a daily dosage regimen, and are reversible when rifampin is discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
Dermatologic
Cutaneous reactions are mild and self-limiting and do not appear to be hypersensitivity reactions. Typically, they consist of flushing and itching with or without a rash. More serious cutaneous reactions which may be due to hypersensitivity occur but are uncommon.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Occasionally, pruritus, urticaria, rash, pemphigoid reaction, erythema multiforme including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, vasculitis, eosinophilia, sore mouth, sore tongue, and conjunctivitis have been observed.
Anaphylaxis has been reported rarely.
Miscellaneous
Edema of the face and extremities have been reported. Other reactions which have occurred with intermittent dosage regimens include "flu syndrome" (such as episodes of fever, chills, headache, dizziness, and bone pain), shortness of breath, wheezing, decrease in blood pressure and shock. The "flu syndrome" may also appear if rifampin is taken irregularly by the patient or if daily administration is resumed after a drug free interval.
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Rifampin (oral) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Rifampin (oral) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
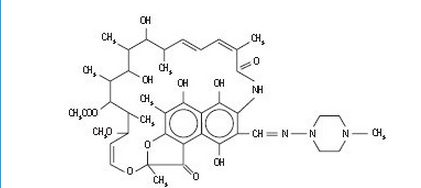
Structure
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Rifampin (oral) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Rifampin (oral) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Rifampin (oral) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Rifampin (oral) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Rifampin (oral)
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Rifampin (oral) |Label Name=Rifampin (oral)11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Rifampin (oral) |Label Name=Rifampin (oral)11.png
}}