Retinoblastoma physical examination: Difference between revisions
Simrat Sarai (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Retinoblastoma}} | {{Retinoblastoma}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{Simrat}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Simrat}} {{Sahar}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Patient|Patients]] with retinoblastoma usually appear normal. [[Physical examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] is usually remarkable for [[leukocoria]], [[strabismus]], and [[proptosis]], particularly in advanced cases. | |||
== | Other findings on [[physical examination]] of retinoblastoma include [[anisocoria]], [[orbital cellulitis]], [[hyphema]], [[heterochromia iridis]], poor [[visual acuity]], unilateral [[mydriasis]], [[rubeosis iridis]], [[vitreous]] [[hemorrhage]], and findings of intrinsic [[calcification]] on [[Fundoscopy|fundoscopic examination]]. | ||
==Physical Examination== | |||
* | ===General Appearance=== | ||
* | *[[Child|Children]] with retinoblastoma are generally well-appearing. | ||
*[[Child|Children]] may appear [[Cachexia|cachectic]] in advanced cases.<ref name="pmid6703986">{{cite journal |vauthors=MacKay CJ, Abramson DH, Ellsworth RM |title=Metastatic patterns of retinoblastoma |journal=Arch. Ophthalmol. |volume=102 |issue=3 |pages=391–6 |date=March 1984 |pmid=6703986 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
* | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*[[Vital signs]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma are usually within normal limits. | |||
* | ===Skin=== | ||
*[[Skin]] [[Physical examination|examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===HEENT=== | |||
*[[Hypertelorism]] in case of concurrent [[13q deletion syndrome]]<ref name="pmid22337189">{{cite journal| author=Mehta M, Sethi S, Pushker N, Kashyap S, Sen S, Bajaj MS et al.| title=Retinoblastoma. | journal=Singapore Med J | year= 2012 | volume= 53 | issue= 2 | pages= 128-35; quiz 136 | pmid=22337189 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22337189 }} </ref> | |||
*[[Leukocoria]] (white reflex or cat's [[eye]] reflex) | |||
*[[Strabismus]] or when both [[Eye|eyes]] do not look to the same direction | |||
*[[Periorbital edema|Periorbital swelling]] | |||
* | *[[Anisocoria]] or inequality of [[pupils]] | ||
*[[Proptosis]] | |||
to | {| | ||
* | |[[image:Retinoblastoma leukocoria.jpeg|thumb|400px|leukocoria, Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 9462]] | ||
* | <br style="clear:left" /> | ||
* | |- | ||
* | |} | ||
* | *Decreased [[visual acuity]] | ||
* | *[[Slit lamp]] [[examination]] may show: | ||
* | **[[Orbital cellulitis]] | ||
**[[Hyphema]] | |||
**[[Heterochromia iridis]] | |||
**[[Rubeosis iridis]] | |||
**Red, painful [[eye]] with [[glaucoma]] | |||
**[[Vitreous hemorrhage]] | |||
*[[Ophthalmoscopy|Funduscopic examination]] may show: | |||
**Small [[Tumor|tumors]]: Round glazed elevations of the [[retina]] with gray-white hew which develop surrounding the serous [[retinal detachments]] | |||
**Large [[Tumor|tumors]]: Intrinsic [[calcification]] and a white color with seeding into the [[Retina|subretinal]] and or the [[vitreous]] space | |||
*[[Patient|Patients]] with [[13q deletion syndrome]] may present with:<ref name="ClarkAvishay2015">{{cite journal|last1=Clark|first1=Robin D.|last2=Avishay|first2=Stefanie G.|title=Retinoblastoma: Genetic Counseling and Testing|year=2015|pages=77–88|doi=10.1007/978-3-662-43451-2_8}}</ref> | |||
**[[Hypertelorism]] | |||
**Flat [[nasal bridge]] | |||
**Small [[mouth]] and [[nose]] | |||
**High arched or [[cleft palate]] | |||
**[[Micrognathia]] | |||
**[[Microcephaly]] | |||
{| | |||
|[[image:Retinoblastoma-fundoscopy-photo.jpeg|thumb|400px|Retinoblastoma [[fundoscopy]], Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 9460]] | |||
<br style="clear:left" /> | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
===Neck=== | |||
*[[Neck]] [[Physical examination|examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Lungs=== | |||
*[[Pulmonary examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Heart=== | |||
*[[Cardiovascular]] [[examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Abdomen=== | |||
*[[Abdominal examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Back=== | |||
*[[Human back|Back]] [[examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Genitourinary=== | |||
*[[Genitourinary system|Genitourinary]] [[examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Neuromuscular=== | |||
*[[Neuromuscular]] [[examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
===Extremities=== | |||
*[[Limb (anatomy)|Extremities]] [[examination]] of [[Patient|patients]] with retinoblastoma is usually normal. | |||
*[[Simian crease]] in the [[Hand|palms]] and a broad [[thumb]] may be present in [[13q deletion syndrome]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
| |||
{{ | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:59, 29 July 2020
|
Retinoblastoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Retinoblastoma physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Retinoblastoma physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Retinoblastoma physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Simrat Sarai, M.D. [2] Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[3]
Overview
Patients with retinoblastoma usually appear normal. Physical examination of patients is usually remarkable for leukocoria, strabismus, and proptosis, particularly in advanced cases. Other findings on physical examination of retinoblastoma include anisocoria, orbital cellulitis, hyphema, heterochromia iridis, poor visual acuity, unilateral mydriasis, rubeosis iridis, vitreous hemorrhage, and findings of intrinsic calcification on fundoscopic examination.
Physical Examination
General Appearance
- Children with retinoblastoma are generally well-appearing.
- Children may appear cachectic in advanced cases.[1]
Vital Signs
- Vital signs of patients with retinoblastoma are usually within normal limits.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
HEENT
- Hypertelorism in case of concurrent 13q deletion syndrome[2]
- Leukocoria (white reflex or cat's eye reflex)
- Strabismus or when both eyes do not look to the same direction
- Periorbital swelling
- Anisocoria or inequality of pupils
- Proptosis
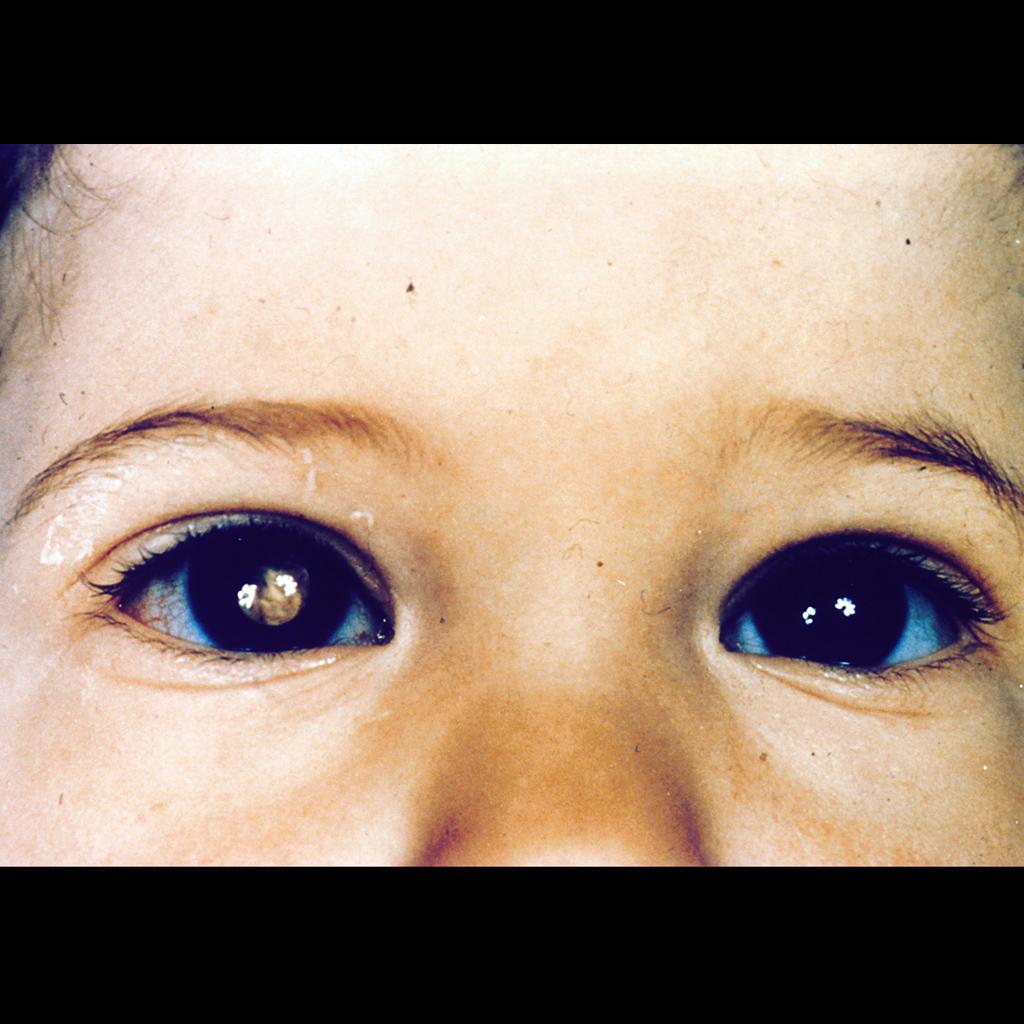
|
- Decreased visual acuity
- Slit lamp examination may show:
- Orbital cellulitis
- Hyphema
- Heterochromia iridis
- Rubeosis iridis
- Red, painful eye with glaucoma
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Funduscopic examination may show:
- Small tumors: Round glazed elevations of the retina with gray-white hew which develop surrounding the serous retinal detachments
- Large tumors: Intrinsic calcification and a white color with seeding into the subretinal and or the vitreous space
- Patients with 13q deletion syndrome may present with:[3]
- Hypertelorism
- Flat nasal bridge
- Small mouth and nose
- High arched or cleft palate
- Micrognathia
- Microcephaly
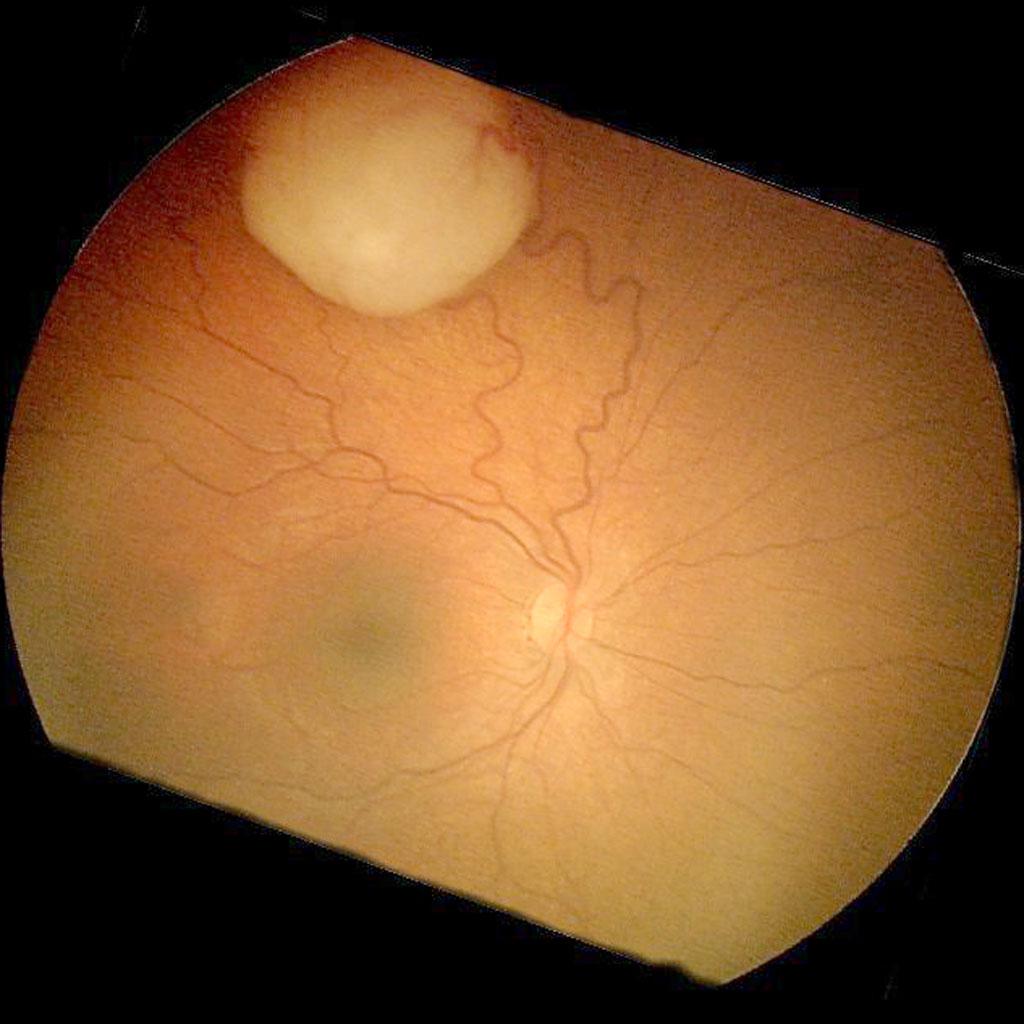
|
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Back
- Back examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
Extremities
- Extremities examination of patients with retinoblastoma is usually normal.
- Simian crease in the palms and a broad thumb may be present in 13q deletion syndrome.
References
- ↑ MacKay CJ, Abramson DH, Ellsworth RM (March 1984). "Metastatic patterns of retinoblastoma". Arch. Ophthalmol. 102 (3): 391–6. PMID 6703986.
- ↑ Mehta M, Sethi S, Pushker N, Kashyap S, Sen S, Bajaj MS; et al. (2012). "Retinoblastoma". Singapore Med J. 53 (2): 128–35, quiz 136. PMID 22337189.
- ↑ Clark, Robin D.; Avishay, Stefanie G. (2015). "Retinoblastoma: Genetic Counseling and Testing": 77–88. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-43451-2_8.