Reperfusion injury natural history
|
Reperfusion injury Microchapters |
|
Treatment |
|---|
|
Reperfusion injury natural history On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Reperfusion injury natural history |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Reperfusion injury natural history |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Shivam Singla, M.D.[2] Anjan K. Chakrabarti, M.D. [3] Kashish Goel, M.D.
Overview
Natural History
The Ischemia-reperfusion injury was first seen in 1955 by Sewell while performing ligation of Dog's coronary arteries
Then later Jennings gave the term Myocardial IRI in 1960. He is the first person to name the term Ischemia Reperfusion Injury(IRI) on the basis of histological changes in canine myocardium.
Later various terms were given by the scientist depending upon the various organ system involved:
- Greenberg gave the term Intestinal IRI in 1981 by his experiment showing reperfusion induced damage in the intestinal mucosal cells of a cat after long hours of ischemia.
Ischemic preconditioning was first explained by Murry et al. In 1986 he performed a study in dog explaining the importance of ischemia reperfusion in dogs on infarct size reduction.
Ischemic post-conditioning was given by Zhao et al in 2003 and explained this with the help of an experiment showing a small episode of Ischemia or reperfusion performed immediately after the resumption of flow following a period of ischemia. They found that this helped in the reduction of infarct size in dogs by up to 40%.
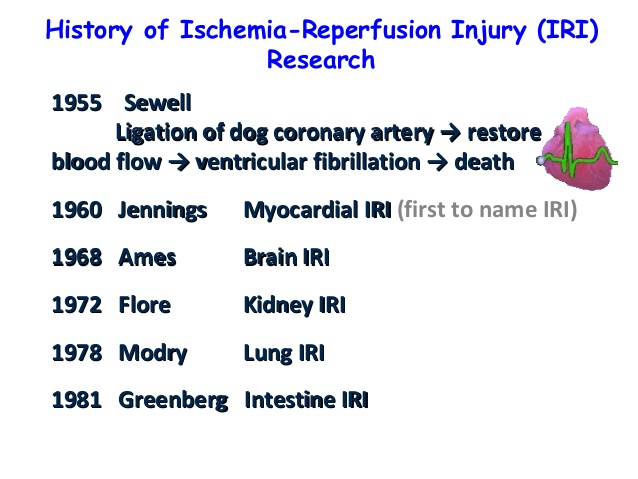 |
 |
Complications
Myocardial stunning: It is mainly defined as an abnormality in the contractile function of myocardium that sometimes persists even after the return of reperfusion and resolution of ischemia. It is mainly due to the release of reactive oxygen species and intracellular calcium overload.
- Myocardial infarction: Irreversible myocyte cell death secondary to reduced oxygen delivery for more than 20-30 minutes, will lead to infarction. Reperfusion helps prevent complete loss of the involved area, however oxidative stress due to this may prevent complete resolution.
- Acute heart failure: Loss of myocardial contractility and systolic dysfunction associated with ischemia/reperfusion injury may lead to the development of acute heart failure. Early reperfusion in the course of STEMI prevents myocardial necrosis and may lead to complete recovery of function.
- Ventricular arrhythmias: Reperfusion of the blocked coronary artery can also precipitate arrhythmias ranging from ventricular premature beats to life-threatening ventricular fibrillation.
- Intestinal ischemia reperfusion is associated with the development of necrotizing enterocolitis, hypotension, and thrombosis. It is mainly seen as a consequence of acute mesenteric ischemia that mainly results due to impaired blood flow to the intestines through the mesenteric vessels.

Prognosis
Prognosis in CNS patients
- Those patients who are identified and treated early, the prognosis is better along with the decreased incidence of intracranial hemorrhage. Outcomes usually depend on the timely recognition and prevention of precipitating factors. Hypertension management is most important before it can inflict damage in the form of edema or hemorrhage
- The prognosis following hemorrhagic transformation is poor. Mortality in such cases is 63%, and 80% of survivors have significant morbidity.
- In the case of Central nervous system the brain is a very sensitive organ to ischemia and results in death within 5 minutes of the onset of ischemia. Reperfusion is usually beneficial if it is conducted within a very short period of time after the onset of ischemia but in most cases, reperfusion leads to the development of cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage resulting in a bad prognosis.
- Ischemia reperfusion injury in kidneys is mainly associated with the development of high morbidity and mortality, worse prognosis with the involvement of corticomedullary junction.
- In CVS patients reperfusion injury is mainly associated with Arrhythmias, myocardial stunning, and myocyte death, which mainly results in the occurrence of Myocardial Infarction with a worse prognosis.